PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848331

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848331
Artemisinin Combination Therapy - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The artemisinin combination therapy market size stands at USD 0.64 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 1.04 billion by 2030, advancing at an 8.31% CAGR.
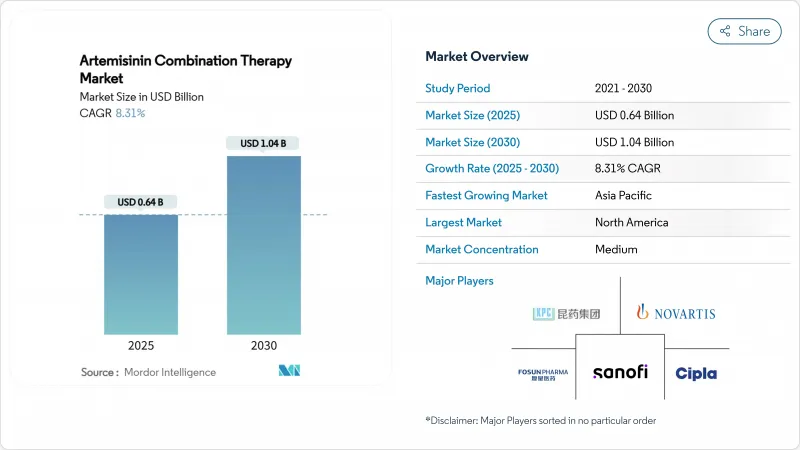
Continued reliance on artemisinin-based regimens for uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria keeps baseline demand robust, while rising resistance in East Africa accelerates therapeutic diversification. Large-scale donor procurement, notably through the Global Fund and the U.S. President's Malaria Initiative, sustains volumes even as aid volatility injects price uncertainty. Local manufacturing capacity is increasing across India, Nigeria and Ethiopia, shortening lead-times and lowering freight costs. Pediatric innovation, exemplified by Novartis's Coartem Baby, opens new sub-segments, and the pipeline of triple artemisinin combinations promises differentiation in areas with K13 mutations. Together these forces anchor an upward trajectory for the Artemisinin Combination Therapy market despite cost headwinds in raw material supply.
Global Artemisinin Combination Therapy Market Trends and Insights
High Malaria Disease Burden in Endemic Regions
WHO recorded 263 million clinical cases and 597,000 deaths in 2023, with 95% of fatalities in Africa. Climate-linked shifts lengthen transmission seasons, as observed in Burkina Faso and Mali where Novartis enrolled patients outside historic peaks. Children under 5 represent 76% of deaths, fuelling demand for pediatric ACTs. Endemic immunity limits symptomatic cases in adults, yet breakthrough infections still require rapid treatment, sustaining volume demand. Partial artemisinin resistance surpasses 30% prevalence in northern Uganda, compelling manufacturers to explore new partner drugs.
Large-Scale Government and Donor Procurement Programs
Public tenders distributed 217 million ACT courses in 2022, nearly all in sub-Saharan Africa. April 2025 warnings of aid reductions highlight funding fragility, disrupting net campaigns and chemoprevention. WHO-prequalified status delivers bidding advantage, nudging smaller regional suppliers toward joint ventures. Multiple first-line therapy policies obligate funders to split orders among at least three ACT regimens, broadening supplier rosters and diffusing single-product risks.
Emergence Of Multi-Drug Resistance in Greater Mekong and Africa
Partial artemisinin resistance involves K13 mutations now exceeding 30% in northern Uganda and 20% in Rwanda. Clinical recurrence rates of 10.3% among children signal rising treatment failure. WHO's multiple first-line therapy guidance raises procurement budgets because parallel stocks of at least three ACTs are required to blunt selection pressure, inflating inventory costs for ministries of health.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancements In Fixed-Dose Combination Drug Development
- Expansion Of WHO Prequalification and Regulatory Harmonization
- Volatile Artemisinin Raw Material Supply Chain
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Artemether-lumefantrine retained 47.82% Artemisinin Combination Therapy market share in 2024, buoyed by over 1 billion courses delivered since 1999. Yet rising K13 mutations curtail future reliance, pushing artesunate-pyronaridine to a 10.45% CAGR as countries pilot rotation regimens. Mozambique found dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine and artesunate-amodiaquine above 90% PCR-corrected cure rates, legitimizing therapeutic swap-outs. Triple combinations under evaluation may soon restructure formularies, compelling manufacturers to field multi-therapy portfolios rather than a single flagship product.
A diverse regimen pipeline reduces the single-product concentration risk that historically characterized the Artemisinin Combination Therapy market. Companies able to commercialize two or more WHO-endorsed combinations will capture procurement lots reserved for multi-line strategies, improving share resilience when efficacy shifts.
Oral tablets controlled 68.43% volume in 2024 thanks to community case management protocols that rely on lay health workers. The segment benefits from low manufacturing complexity and ambient-temperature stability. Pediatric demand accelerates dispersible formats such as Coartem Baby, illustrating the revenue unlocked when dosing meets weight-band precision.
Parenteral artesunate holds a smaller but vital niche for severe malaria, expanding at 10.67% CAGR as referral networks strengthen. WHO-certified plants run by Guilin, Macleods and Ipca safeguard quality for the 2.4 mg/kg adult protocol. Novartis's investigational intravenous cipargamin aims to replace artesunate where resistance reduces clearance rates, indicating that even low-volume hospital segments can shape R&D agendas.
The Artemisinin Combination Therapy Market Report is Segmented by Combination Therapy Type (Artemether-Lumefantrine, Artesunate-amodiaquine, and More), Formulation (Oral Tablets, and More), Distribution Channel (Public Sector & NGO Tenders, and More), End-User (Hospitals, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America currently holds 42.43% of Artemisinin Combination Therapy market share, reflecting its outsized role in donor-financed global distribution. Purchases made by the U.S. President's Malaria Initiative and Global Fund hubs in Atlanta secure multi-year framework contracts that stabilize regional demand. Advanced cold-chain logistics and stringent pharmacovigilance systems support rapid batch release, keeping stock-out risk low for both domestic travel clinics and overseas partners. The presence of R&D leaders such as Novartis and Sanofi attracts clinical trials that further anchor supplier relationships with procurement agencies. Nevertheless, recent indications of federal budget tightening have injected uncertainty that could reallocate some future orders toward emerging manufacturing centers in Asia.
Asia-Pacific is projected to expand its Artemisinin Combination Therapy market size at a 9.43% CAGR through 2030, the fastest pace worldwide. India's large-scale plants operated by Cipla and Ipca combine low conversion costs with growing domestic consumption, enabling the region to compete aggressively in tenders. Governments in Myanmar, Papua New Guinea and Cambodia are aligning national treatment guidelines with WHO's multiple first-line therapy approach, widening the addressable product portfolio. As more Asian facilities secure WHO prequalification, ministries are shortening lead times and reducing currency exposure by sourcing within the region..
Middle East & Africa continues to shoulder the heaviest disease burden yet captures a smaller share of global spending because treatment access relies heavily on external grant. Nigeria, Tanzania and Uganda are adopting digital pack-verification codes to combat falsified ACTs, a move expected to lift public confidence and stimulate legitimate retail demand. Local manufacturers in Nigeria and Ethiopia are scaling capacity with technical support from Medicines for Malaria Venture, aiming to double the number of WHO-qualified African suppliers by 2030. Europe contributes primarily through donor financing and vaccine R&D rather than direct consumption, but its stringent quality standards shape global specifications that all suppliers must meet.
- Novartis
- Cipla
- Sanofi
- Guilin Pharmaceutical (Fosun)
- Ipca Laboratories
- Ajanta Pharma
- Desano Pharma
- KPC Pharmaceuticals
- Hovid Berhad
- Shelys Africa Pharma
- Strides Pharma Science
- Mylan (Viatris)
- Macleods Pharma
- Cipla QCIL (Uganda)
- Shin Poong Pharma
- Bliss GVS Pharma
- Omega Pharma
- Artepharm Co.
- Ipca-Ajanta JV (Myanmar)
- Renata Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope Of The Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 High Malaria Disease Burden in Endemic Regions
- 4.2.2 Large-Scale Government and Donor Procurement Programs
- 4.2.3 Advancements in Fixed-Dose Combination Drug Development
- 4.2.4 Expansion of WHO Prequalification and Regulatory Harmonization
- 4.2.5 Scale-Up of Local Manufacturing Capacity in Africa And Asia
- 4.2.6 Integration of ACT With Community Case Management and Digital Supply Chains
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Emergence of Multi-Drug Resistance in Greater Mekong And Africa
- 4.3.2 Volatile Artemisinin Raw Material Supply Chain
- 4.3.3 Increasing Competition from Novel Single-Dose Antimalarials And Vaccines
- 4.3.4 Proliferation of Substandard and Counterfeit ACTs in Informal Markets
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity Of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Combination Therapy Type
- 5.1.1 Artemether-Lumefantrine
- 5.1.2 Artesunate-Amodiaquine
- 5.1.3 Artesunate-Pyronaridine
- 5.1.4 Artesunate-Sulfadoxine-Pyrimethamine
- 5.1.5 Other Combination Therapy Types
- 5.2 By Formulation
- 5.2.1 Oral Tablets
- 5.2.2 Oral Suspension (Pediatric)
- 5.2.3 Parenteral (IV/IM Artesunate)
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Public Sector & NGO Tenders
- 5.3.2 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.3.3 Retail & Online Pharmacies
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Community Health Centres
- 5.4.3 Travel Clinics
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Novartis AG
- 6.3.2 Cipla Ltd.
- 6.3.3 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.4 Guilin Pharmaceutical (Fosun)
- 6.3.5 Ipca Laboratories
- 6.3.6 Ajanta Pharma
- 6.3.7 Desano Pharma
- 6.3.8 KPC Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.9 Hovid Berhad
- 6.3.10 Shelys Africa Pharma
- 6.3.11 Strides Pharma Science
- 6.3.12 Mylan (Viatris)
- 6.3.13 Macleods Pharma
- 6.3.14 Cipla QCIL (Uganda)
- 6.3.15 Shin Poong Pharma
- 6.3.16 Bliss GVS Pharma
- 6.3.17 Omega Pharma
- 6.3.18 Artepharm Co.
- 6.3.19 Ipca-Ajanta JV (Myanmar)
- 6.3.20 Renata Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




