PUBLISHER: Global Market Insights Inc. | PRODUCT CODE: 1801939

PUBLISHER: Global Market Insights Inc. | PRODUCT CODE: 1801939
Azotobacter-based Biofertilizer Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034
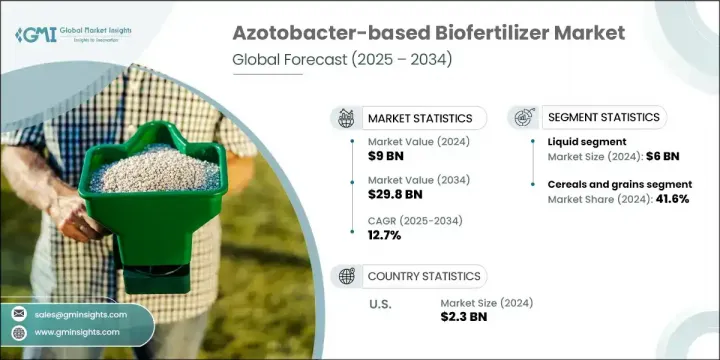
The Global Azotobacter-based Biofertilizer Market was valued at USD 9 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 12.7% to reach USD 29.8 billion by 2034. This rapid growth is being driven by the rising global population, increasing focus on sustainable farming, and a shift toward organic agricultural practices. As concerns around the harmful effects of synthetic fertilizers grow, farmers are steadily moving toward more eco-friendly alternatives. Consumers' demand for chemical-free produce is further encouraging the switch to biofertilizers. Governments are also stepping in to promote sustainable practices through incentive-based programs, creating momentum in the biofertilizer industry. Azotobacter-based products are particularly gaining traction as they naturally fix atmospheric nitrogen, enrich soil quality, and support plant development-all while minimizing the environmental burden and offering a cost-effective solution compared to conventional options.
Azotobacter-based biofertilizers face challenges around consistency in performance due to environmental variability. Factors such as soil pH, temperature, and moisture content influence outcomes and may discourage farmers when results fluctuate across different regions. Limited shelf life is another hurdle, as any loss in product efficacy can lead to poor user experience and restrained adoption in some areas, potentially slowing down widespread use.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $9 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $29.8 Billion |
| CAGR | 12.7% |
The liquid formulations segment generated USD 6 billion in 2024, holding a leading position due to their application efficiency, uniform coverage, and ease of handling. These attributes make them a preferred option, particularly for large-scale farming operations. Their compatibility with agricultural application systems further supports their widespread use across multiple farming environments.
The cereals and grains accounted for 41.6% share in 2024, maintaining the largest share by crop type. This dominance is supported by rising global demand for food security, government-backed organic farming initiatives, and the proven ability of azotobacter-based biofertilizers to improve grain and cereal crop yields. With growing awareness around soil health, many farmers are adopting these biofertilizers to meet sustainability goals while maintaining productivity.
U.S. Azotobacter-based Biofertilizer Market was valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2024, driven by modern agricultural techniques, a strong push toward organic farming, and a well-established farming sector. Supportive regulatory frameworks and heightened awareness around soil conservation continue to boost adoption rates across the country. In Canada, the market is growing rapidly with increasing adherence to environmentally responsible practices and an emphasis on sustainable agriculture. Collaboration between research organizations and key players is helping bring out new, efficient product variants and expanding the usage scope of azotobacter-based solutions.
Key participants in the Azotobacter-based Biofertilizer Market include Growtech Agri Science, Biotech International, K. N. BIO SCIENCES, Unisun Agro, IFFCO, Rizobacter, FARMADIL INDIA LLP, Green Vision Life Sciences, Gujarat State Fertilizers & Chemicals, and Jaipur Bio Fertilizers. Companies in the global azotobacter-based biofertilizer market are expanding their market presence by focusing on product innovation, targeted collaborations, and diversification of formulations. Leading players are investing in R&D to develop stable, long-lasting biofertilizers suitable for diverse soil and climate conditions. Strategic partnerships with research institutions and universities enhance product performance and regional adaptability. Several firms are emphasizing tailored solutions for different crops and expanding their distribution networks to reach under-served agricultural regions.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Market scope and definition
- 1.2 Research design
- 1.2.1 Research approach
- 1.2.2 Data collection methods
- 1.3 Data mining sources
- 1.3.1 Global
- 1.3.2 Regional/Country
- 1.4 Base estimates and calculations
- 1.4.1 Base year calculation
- 1.4.2 Key trends for market estimation
- 1.5 Primary research and validation
- 1.5.1 Primary sources
- 1.6 Forecast model
- 1.7 Research assumptions and limitations
Chapter 2 Executive Summary
- 2.1 Industry 3600 synopsis
- 2.2 Key market trends
- 2.2.1 Product type trends
- 2.2.2 Crop type trends
- 2.2.3 Application method trends
- 2.2.4 End user trends
- 2.2.5 Regional trends
- 2.3 TAM Analysis, 2025-2034
- 2.4 CXO perspectives: Strategic imperatives
- 2.4.1 Executive decision points
- 2.4.2 Critical success factors
- 2.5 Future Outlook and Strategic Recommendations
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Supplier landscape
- 3.1.2 Profit margin
- 3.1.3 Value addition at each stage
- 3.1.4 Factor affecting the value chain
- 3.1.5 Disruptions
- 3.2 Industry impact forces
- 3.2.1 Growth drivers
- 3.2.2 Industry pitfalls and challenges
- 3.2.3 Market opportunities
- 3.3 Growth potential analysis
- 3.4 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4.1 North America
- 3.4.2 Europe
- 3.4.3 Asia Pacific
- 3.4.4 Latin America
- 3.4.5 Middle East & Africa
- 3.5 Porter’s analysis
- 3.6 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7 Technology and Innovation landscape
- 3.7.1 Current technological trends
- 3.7.2 Emerging technologies
- 3.8 Price trends
- 3.8.1 By region
- 3.8.2 By product type
- 3.9 Future market trends
- 3.10 Patent Landscape
- 3.11 Trade statistics (HS code) (Note: the trade statistics will be provided for key countries only)
- 3.11.1 Major importing countries
- 3.11.2 Major exporting countries
- 3.12 Sustainability and environmental aspects
- 3.12.1 Sustainable practices
- 3.12.2 Waste reduction strategies
- 3.12.3 Energy efficiency in production
- 3.12.4 Eco-friendly initiatives
- 3.13 Carbon footprint consideration
Chapter 4 Competitive Landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.2.1.1 North America
- 4.2.1.2 Europe
- 4.2.1.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.1.4 LATAM
- 4.2.1.5 MEA
- 4.2.1 By region
- 4.3 Company matrix analysis
- 4.4 Competitive analysis of major market players
- 4.5 Competitive positioning matrix
- 4.6 Key developments
- 4.6.1 Mergers & acquisitions
- 4.6.2 Partnerships & collaborations
- 4.6.3 New product launches
- 4.6.4 Expansion plans
Chapter 5 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Product Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Liquid
- 5.3 Carrier-based (powder or granules)
Chapter 6 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Crop Type, 2021-2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Cereals and grains
- 6.3 Oilseeds and pulses
- 6.4 Fruits and vegetables
- 6.5 Others (including cash crops, fiber crops, etc.)
Chapter 7 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Application Method, 2021-2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 Soil treatment
- 7.3 Seed treatment
- 7.4 Foliar application
Chapter 8 Market Estimates and Forecast, By End Use, 2021-2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 8.1 Key trends
- 8.2 Farmers/cultivators
- 8.3 Research institutions
- 8.4 Agricultural cooperatives
Chapter 9 Market Estimates and Forecast, By Region, 2021-2034 (USD Billion) (Kilo Tons)
- 9.1 Key trends
- 9.2 North America
- 9.2.1 U.S.
- 9.2.2 Canada
- 9.3 Europe
- 9.3.1 Germany
- 9.3.2 UK
- 9.3.3 France
- 9.3.4 Spain
- 9.3.5 Italy
- 9.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 9.4 Asia Pacific
- 9.4.1 China
- 9.4.2 India
- 9.4.3 Japan
- 9.4.4 Australia
- 9.4.5 South Korea
- 9.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 9.5 Latin America
- 9.5.1 Brazil
- 9.5.2 Mexico
- 9.5.3 Argentina
- 9.5.4 Rest of Latin America
- 9.6 Middle East and Africa
- 9.6.1 Saudi Arabia
- 9.6.2 South Africa
- 9.6.3 UAE
- 9.6.4 Rest of Middle East and Africa
Chapter 10 Company Profiles
- 10.1 Biotech International
- 10.2 FARMADIL INDIA LLP
- 10.3 Green Vision Life Sciences
- 10.4 Growtech Agri Science
- 10.5 Gujarat State Fertilizers & Chemicals
- 10.6 IFFCO
- 10.7 Jaipur Bio Fertilizers
- 10.8 K. N. BIO SCIENCES
- 10.9 Rizobacter
- 10.10 Unisun Agro




