PUBLISHER: Global Market Insights Inc. | PRODUCT CODE: 1858814

PUBLISHER: Global Market Insights Inc. | PRODUCT CODE: 1858814
Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Market Opportunity, Growth Drivers, Industry Trend Analysis, and Forecast 2025 - 2034
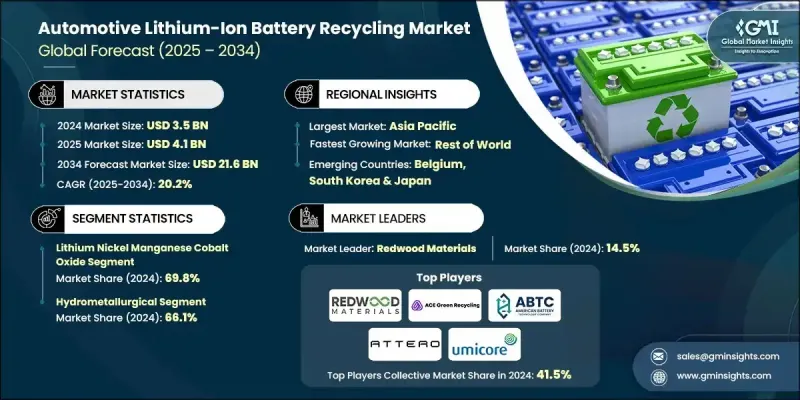
The Global Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Market was valued at USD 3.5 billion in 2024 and is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 20.2% to reach USD 21.6 billion by 2034.
A primary driver for this surge is the increasing pressure on the automotive sector to reduce its environmental footprint. Lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs), contain hazardous materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which pose risks of soil and water contamination if not disposed of properly. This has intensified the adoption of recycling technologies to recover valuable metals, reduce mining activities, and minimize environmental damage. As the demand for electric vehicles rises, so does the need for effective recycling, allowing for the conservation of natural resources and supporting a circular economy in the automotive industry.
| Market Scope | |
|---|---|
| Start Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Year | 2025-2034 |
| Start Value | $3.5 Billion |
| Forecast Value | $21.6 Billion |
| CAGR | 20.2% |
Governments and environmental organizations are also playing a pivotal role by encouraging circular economy initiatives, positioning recycling as a core strategy for sustainable development. Automakers are increasingly integrating battery recycling into their long-term environmental plans to enhance their brand image and meet stringent regulatory standards. The recycling process not only aids in safe disposal but also fosters the recovery of critical materials, reinforcing sustainable manufacturing practices. The growing role of automotive lithium-ion battery recycling is an essential step in supporting the EV transition and reducing the environmental footprint of the transportation sector.
The lithium iron phosphate (LFP) battery segment is expected to grow at a CAGR of 20.6% through 2034, driven by the high retention capacity of LFP batteries at the end of their first life. This makes them an ideal candidate for reuse in less demanding applications, which not only reduces waste but also contributes to the overall economic value of the recycling process. The potential for LFP battery reuse is strongly linked to recycling activities, promoting business growth and the development of more sustainable practices.
The physical/mechanical recycling segment is expected to grow at an 18.4% CAGR through 2034. This process is becoming increasingly popular due to its lower capital requirements when compared to more complex chemical or thermal methods. Additionally, the physical method operates under ambient conditions, minimizing harmful emissions, water usage, and secondary waste. This is appealing to recyclers focused on compliance with environmental regulations and sustainability goals, thereby boosting the market outlook.
United States Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Market held an 86.3% share. The U.S. is expected to generate over USD 3 billion in revenue by 2034, driven by the expansion of domestic EV production, which increases the availability of scrap materials and end-of-life batteries. Consumer demand for greener technologies is also pushing manufacturers to adopt circular economy models, further driving market growth.
Key companies operating in the Global Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Market include ACE Green Recycling, Altilium Metals, American Battery Technology Company, Attero Recycling, Cirba Solutions, Ecobat, Eramet, Fortum, Ganfeng Lithium, Glencore, Northvolt, Re.Lion.Bat, Redwood Materials, Recyclus Group, ReBAT, RecycleKaro, SK TES, Stena Recycling, SungEel Hitech, and Umicore. To strengthen their position in the Automotive Lithium-Ion Battery Recycling Market, companies are adopting various strategies such as expanding their recycling capacity, improving technology for better efficiency in material recovery, and forging partnerships with automakers to ensure a steady supply of end-of-life batteries. These companies are also investing in advanced research and development to develop cost-effective and sustainable recycling technologies, which can handle a larger volume of batteries while reducing environmental impact.
Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Methodology & Scope
- 1.1 Research design
- 1.2 Base estimates & calculations
- 1.3 Forecast model
- 1.4 Primary research & validation
- 1.4.1 Primary sources
- 1.4.2 Data mining sources
- 1.5 Market definitions
Chapter 2 Industry Insights
- 2.1 Industry synopsis, 2021 - 2034
- 2.2 Business trends
- 2.3 Chemistry trends
- 2.4 Process trends
- 2.5 Regional trends
Chapter 3 Industry Insights
- 3.1 Industry ecosystem analysis
- 3.1.1 Collection and transportation infrastructure
- 3.1.2 Pre-treatment and dismantling operations
- 3.1.3 Black mass production and characterization
- 3.1.4 Material recovery and purification
- 3.1.5 End product manufacturing and distribution
- 3.2 Cost structure analysis
- 3.3 Regulatory landscape
- 3.4 Industry impact forces
- 3.4.1 Growth drivers
- 3.4.2 Industry pitfalls & challenges
- 3.5 Growth potential analysis
- 3.6 Porter's analysis
- 3.6.1 Bargaining power of suppliers
- 3.6.2 Bargaining power of buyers
- 3.6.3 Threat of new entrants
- 3.6.4 Threat of substitutes
- 3.7 PESTEL analysis
- 3.7.1 Political factors
- 3.7.2 Economic factors
- 3.7.3 Social factors
- 3.7.4 Technological factors
- 3.7.5 Legal factors
- 3.7.6 Environmental factors
Chapter 4 Competitive landscape, 2024
- 4.1 Introduction
- 4.2 Company market share analysis, by region, 2024
- 4.2.1 North America
- 4.2.2 Europe
- 4.2.3 Asia Pacific
- 4.2.4 Rest of World
- 4.3 Strategic dashboard
- 4.4 Strategic initiatives
- 4.5 Company benchmarking
- 4.6 Innovation & technology landscape
Chapter 5 Market Size and Forecast, By Chemistry, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion & Thousand Tons)
- 5.1 Key trends
- 5.2 Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC)
- 5.3 Lithium iron phosphate (LFP)
- 5.4 Lithium cobalt oxide (LCO)
- 5.5 Others
Chapter 6 Market Size and Forecast, By Process, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion & Thousand Tons)
- 6.1 Key trends
- 6.2 Pyrometallurgical
- 6.3 Hydrometallurgical
- 6.4 Physical/Mechanical
Chapter 7 Market Size and Forecast, By Region, 2021 - 2034 (USD Billion & Thousand Tons)
- 7.1 Key trends
- 7.2 North America
- 7.2.1 U.S.
- 7.2.2 Canada
- 7.3 Europe
- 7.3.1 UK
- 7.3.2 France
- 7.3.3 Belgium
- 7.3.4 Switzerland
- 7.3.5 Germany
- 7.4 Asia Pacific
- 7.4.1 China
- 7.4.2 South Korea
- 7.4.3 Japan
- 7.5 Rest of World
Chapter 8 Company Profiles
- 8.1 ACE Green Recycling
- 8.2 Altilium Metals
- 8.3 American Battery Technology Company
- 8.4 Attero Recycling
- 8.5 Cirba Solution
- 8.6 Ecobat
- 8.7 Eramet
- 8.8 Fortum
- 8.9 Ganfeng Lithium
- 8.10 Glencore
- 8.11 Northvolt
- 8.12 Re.Lion.Bat
- 8.13 Redwood Materials
- 8.14 Recyclus Group
- 8.15 ReBAT
- 8.16 RecycleKaro
- 8.17 SK TES
- 8.18 Stena Recycling
- 8.19 SungEel Hitech
- 8.20 Umicore




