PUBLISHER: KnowMade | PRODUCT CODE: 1886133

PUBLISHER: KnowMade | PRODUCT CODE: 1886133
LiDAR for Automotive Patent Landscape Analysis 2025
The global IP battlefield is heating up: who are the key players, and which technologies will shape the future of LiDAR for automotive?
Key Features:
- PDF with > 160 slides
- Excel file > 36,200 patent families
- Global patenting trends, including time evolution of patent publications, countries of patent filings, etc.
- Main patent assignees and IP newcomers in the different segments
- Key players' IP position and the relative strength of their patent portfolio
- IP leadership evolution of patent assignees 2021 vs 2025
- IP ecosystems including co-owned patents including group-internal and external collaboration, etc.
- Patents categorized by 18 technological segments (ToF, FMCW, phase-shift, MEMS, hybrid, OPA, flash, metasurface, LiDAR-On-Chip, 1550 nm, VCSEL, SPAD/SiPM, APD, packaging, calibration, Anti-interference, AI, fusion)
- IP profile of 30 key players (patent portfolio overview, technical coverage, geographical coverage, notable granted and pending patents, etc.)
- Excel database containing all patents analyzed in the report, including patent segmentations and hyperlinks to an updated online database
A Rapidly Expanding Global LiDAR IP Landscape
With centimeter-level accuracy and consistent performance across varied lighting conditions, LiDAR is becoming a core sensing modality for ADAS, L2-L4 autonomous driving, robotaxis and a growing range of robotics and infrastructure applications. Its rapidly expanding patent activity reflects this shift, marking LiDAR's transition from an experimental technology to a primary perception sensor in one of the most competitive IP landscapes in advanced mobility. As of October 2025, the global LiDAR patent landscape for automotive applications includes more than 36,200 patent families and over 62,900 individual patents, with strong growth across FMCW LiDAR, solid-state architectures, photonic integration, advanced beam steering and AI-driven perception. Over 24,300 patent families were filed since July 2021 alone, tripling KnowMade's previous dataset and signalling the move from early research to full-scale industrialization. Between 2020 and 2025, LiDAR-related patenting increased at an estimated CAGR of 27%, highlighting the explosive pace of innovation across the sector.
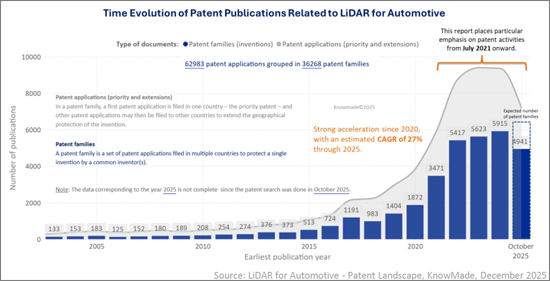
Global IP Trends and Strategic Players
A major structural shift in the LiDAR patent landscape is the rapid and sustained rise of China as the world's largest source of LiDAR-related intellectual property. By 2025, China accounts for around 40% of global LiDAR patent publications, surpassing the United States in both volume and growth rate. This trend is accompanied by a broad diversification of contributors, including LiDAR pure players, Tier-1 suppliers, automotive OEMs, autonomous-driving developers, semiconductor companies and research institutes. Their collective IP activity reflects the growing maturity of LiDAR technologies and the increasingly strategic alignment between patent portfolios and long-term technology roadmaps.
Chinese companies such as Hesai, RoboSense, Huawei Yinwang, VanJee, Zvision, Benewake and Leishen Intelligent are active across all major LiDAR technology domains and demonstrate significant momentum from 2021 to 2025. In parallel, the United States maintains a central role driven by General Motors, Alphabet-Waymo, Aurora, Ouster, Seyond and Aeva, while Europe contributes substantial activity through its automotive and photonics sectors, led by Bosch, Continental, Valeo and several OEMs focusing on components, packaging, calibration and vehicle-grade LiDAR integration. Japan and South Korea remain steady contributors through Sony, Denso, Toyota, Samsung, Infoworks and Hyundai-Kia, illustrating the global distribution of innovation efforts.
This geographic rebalancing highlights the shift from a historically U.S.- and Europe-led patent landscape toward one increasingly shaped by China's expanding photonics and semiconductor ecosystem.
Evolution of IP Leadership 2021 vs 2025
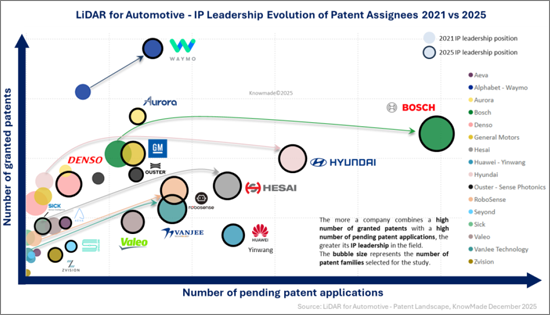
Between 2021 and 2025, LiDAR IP leadership evolved significantly as competition intensified across technologies, regions and industry segments. While the ecosystem is structured around four major categories: LiDAR pure players, Tier-1 suppliers, car makers and autonomous-driving companies, the report provides a deeper, fine-grained examination within each group, revealing how leadership positions, technology strengths and IP portfolios have shifted between 2021 and 2025 as competition intensified. In particular, LiDAR pure players show a clear acceleration in IP activity over the past few years, with many strengthening their portfolios at a pace unmatched in 2021. Detailed analysis reveals that although Tier-1 suppliers held more competitive and mature portfolios in 2021, the landscape has shifted: by 2025, multiple pure players demonstrate the scale, quality and technological depth required to position themselves as emerging IP leaders in several high-growth LiDAR domains. The report also identifies a growing cohort of IP newcomers including fast-moving pure players, autonomous-driving companies and car makers who's rapidly expanding portfolios signal their rising strategic influence. Together, these shifts illustrate how leadership is being redistributed across the LiDAR ecosystem, making this one of the most dynamic and contested IP environments in advanced sensing.
Clear Segmentation of Innovation Across LiDAR Technologies

The report reveals strong innovation activity across all major LiDAR technology layers. Patents are concentrated in five key areas:
- Core Ranging & Imaging Principles: Pulsed ToF, FMCW and phase-shift ranging, along with MEMS, hybrid scanning, OPA and flash beam-steering architectures; advanced beam steering technologies as metasurface and nanophotonic approaches, as well as photonic-integrated LiDAR.
- Optical & Photonic Components: 1550 nm laser sources, VCSEL arrays, SPAD/SiPM detectors and APDs.
- System & Algorithmic Intelligence: Solid-state packaging, calibration, interference mitigation, AI and multi-sensor fusion.
In-Depth IP Profiles Across Key Industry Segments
This report delivers a structured and data-driven IP profile analysis of 30 influential LiDAR patent assignees, selected based on their IP leadership and recent activity from 2021 to 2025. The analysis covers the full spectrum of ecosystem actors, including LiDAR pure players (Hesai, RoboSense, Ouster/Sense Photonics, VanJee, Seyond, Zvision, Aeva, Leishen Intelligent, Sick, Benewake, SOSLAB, Oradar, Luminar, SiLC Technologies, Innoviz, MicroVision, Ibeo Automotive, Mobiltech, Infoworks, Blickfeld, OLEI, LiangDao, Aeye), Tier-1 suppliers (Bosch, Huawei-Yinwang, Valeo), autonomous-driving companies (Aurora, Alphabet-Waymo) and car makers (Hyundai, General Motors). For each company, the report provides a consistent assessment of IP leadership evolution, portfolio dynamics, geographic footprint, technical segmentation and recent patent activities.
Useful Excel patent database
This report includes an extensive Excel database with the 36,200+ patent families (inventions) analyzed in this study and a focus set of 24,300+ families added in the last four years, including patent information (publication numbers, assignees, dates, title, abstract, etc.), hyperlinks to an updated online database (original documents, legal status, etc.), and structured classification by technological segments (ToF, FMCW, phase-shift, MEMS, hybrid, OPA, flash, metasurface, LiDAR-On-Chip, 1550 nm, VCSEL, SPAD/SiPM, APD, packaging, calibration, Anti- interference, AI, fusion). This patent database supports advanced multi-criteria searches and provides direct access to updated records, enabling users to benchmark portfolios, monitor competitors, identify potential partners or acquisition targets and evaluate freedom-to-operate constraints.
Companies mentioned in the report (non-exhaustive):
|
|
and more.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
INTRODUCTION
- Context of the report
- Scope and objectives of the report
- Reading guide
- Excel database
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
PATENT LANDSCAPE OVERVIEW
- Time evolution of patent publications
- Main patent assignees
- Timeline of IP players
- IP leadership of patent assignees evolution 2021 vs 2025
- Geographical coverage of main players' patents
- High-impact patent assignees
- Main co-owned IP
PATENT SEGMENTATION
- Core Ranging & Imaging Principles:Ranging: Pulsed ToF, FMCW, Phase Shift
- Beam Steering: MEMS, Hybrid Scanning, OPA, Flash
- Advanced beam steering: LiDAR-On-Chip, Metasurface
- Optical & Photonic Components: 1550 nm, VCSEL, SPAD / SiPM, APD
- System & Algorithmic Intelligence: AI, Anti-Interference, Packaging & Integration, Fusion with Camera and Radar, Calibration
- For each segment:
- Segment definition
- Patent portfolio overview
- Main patent assignees
- Notable patents
IP PROFILE OF A SELECTION OF PATENT ASSIGNEES
- LiDAR pure player:
- IP leadership of patent assignees evolution 2021 vs 2025
- IP leadership of patent assignees 2025
- Patent portfolio overview, analysis and description of recent patent activities for LiDAR pure players (7) : Hesai, RoboSense, Ouster -Sense Photonics, VanJee Technology, Seyond, Zvision, Aeva
- Patent portfolio overview for LiDAR pure players (16) : Leishen Intelligent, Sick, Benewake, SOSLAB, Oradar, Luminar, SiLC Technologies, Innoviz, MicroVision, Ibeo Automotive, Mobiltech, Infoworks, Blickfeld, OLEI, LiangDao, Aeye
- Tier one suppliers:
- IP leadership of patent assignees evolution 2021 vs 2025
- Patent portfolio overview, analysis and description of recent patent activities for Tier one suppliers (3) : Bosch, Huawei -Yinwang, Valeo
- Autonomous driving/vehicle players:
- IP leadership of patent assignees evolution 2021 vs 2025
- Patent portfolio overview, analysis and description of recent patent activities for Autonomous driving/vehicle players (2) : Aurora, Alphabet -Waymo
- Car makers:
- IP leadership of patent assignees evolution 2021 vs 2025
- Patent portfolio overview, analysis and description of recent patent activities for Car makers (2) : Hyundai, General Motors
PATENT LITIGATION
ANNEX
- Methodology for patent search, selection and analysis
- Terminology
KNOWMADE PRESENTATION




