PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445766

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1445766
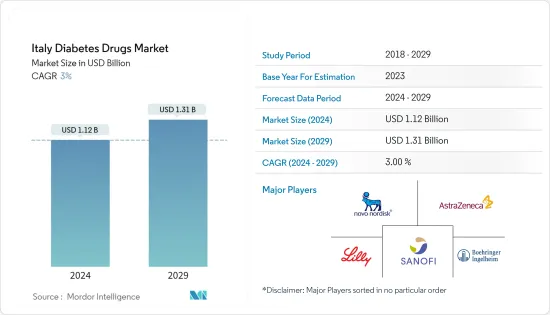
Italy Diabetes Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2024 - 2029)
The Italy Diabetes Drugs Market size is estimated at USD 1.12 billion in 2024, and is expected to reach USD 1.31 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 3% during the forecast period (2024-2029).
Within the first year since its inception, the COVID-19 pandemic has been responsible for premature deaths, particularly among older individuals. Italy was the first country in Europe affected by COVID-19. Italy is among the countries with the highest excess mortality. Most people who have died of COVID-19 were affected by the co-occurrence of two or more chronic conditions in the same individual. Several studies have confirmed that chronic diseases like diabetes are associated with adverse outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
People with diabetes have more chances to get into serious complications rather than normal people. The manufacturers of diabetes drugs have taken care during COVID-19 to deliver the medications to diabetes patients with the help of local governments. Novo Nordisk stated on their website that 'Since the start of COVID-19, our commitment to patients, our employees and the communities where we operate has remained unchanged, we continue to supply our medicines and devices to people living with diabetes and other serious chronic diseases, safeguard the health of our employees, and take actions to support doctors and nurses as they work to defeat COVID-19.'
Diabetic drugs are medicines developed to stabilize and control blood glucose levels amongst people with diabetes. Diabetic drugs have been potential candidates for treating diabetic patients affected by SARS-CoV-2 infection during the COVID-19 pandemic. About 9.9% of the Italian population has diabetes as of 2021 as per IDF. The rate of newly diagnosed Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes cases is seen to increase, mainly due to obesity, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity. The rapidly increasing incidence and prevalence of diabetic patients and healthcare expenditure are indications of the increasing usage of diabetic care products.
In May 2021, the World Health Assembly agreed on a Resolution on strengthening the prevention and control of diabetes. It recommends action in areas including increasing access to insulin; promoting convergence and harmonization of regulatory requirements for insulin and other medicines and health products for the treatment of diabetes; and assessing the feasibility and potential value of establishing a web-based tool to share information relevant to the transparency of markets for diabetes medicines and health products.
Therefore, owing to the aforementioned factors the studied market is anticipated to witness growth over the analysis period.
Italy Diabetes Drugs Market Trends
Oral anti-diabetic drugs are expected to register highest growth rate in the Italy Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period
The Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs market is expected to register the highest CAGR of about 3.5% in the Italy Diabetes Drugs Market over the forecast period.
Italy witnessed an alarming increase in the prevalence of diabetes in recent years. Patients with diabetes require many corrections throughout the day to maintain nominal blood glucose levels, such as oral anti-diabetic medication or ingestion of additional carbohydrates by monitoring their blood glucose levels. The rate of newly diagnosed Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes cases is seen to increase, mainly due to obesity, unhealthy diet, and physical inactivity. The rapidly increasing incidence and prevalence of diabetic patients and healthcare expenditure are indications of the increasing usage of diabetic drugs.
Oral Anti-Diabetic Drugs are available internationally and are recommended for use when escalation of treatment for type 2 diabetes is required along with lifestyle management. Oral agents are typically the first medications used in treating type 2 diabetes due to their wide range of efficacy, safety, and mechanisms of action. Anti-diabetic drugs help diabetes patients control their condition and lower the risk of diabetes complications. People with diabetes may need to take anti-diabetic drugs for their whole lives to control their blood glucose levels and avoid hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Oral anti-diabetic agents present the advantages of easier management and lower cost. So they became an attractive alternative to insulin with better acceptance, which enhances adherence to the treatment.
The Italy National Healthcare Service (NHS) is ensuring universal coverage for all citizens. People living with diabetes can access all the medicines, devices, and medical services they need with no out-of-pocket expenditure. Overall, Italy includes a well-developed system of diabetes care, with numerous diabetes centers throughout the country and treatment free at the point of delivery. The Italy health system is highly decentralized, with most administrative and organizational powers held by the Regions. The National Diabetes Plan defines priorities and provides guidelines to improve the quality of diabetes care with a patient-centered focus.
Owing to the above factors, the market will likely continue to grow.
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist segment holds the highest market share in the Italy Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year
Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist segment holds the highest market share of about 22% in the Italy Diabetes Drugs Market in the current year.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs) are a class of medications used for treating type 2 diabetes, and some drugs are also approved for obesity. One of the benefits of this class of drugs over older insulin secretagogues, such as sulfonylureas or meglitinides, is that they include a lower risk of causing hypoglycemia. Besides being important glucose-lowering agents, GLP-1RAs contain significant anti-inflammatory and pulmonary protective effects and a favorable impact on gut microbes' composition.
Italian law regulates the clinical care of people with diabetes and creates a framework involving medical organizations, prevention programs, personnel training, and legal protection. The National Health Program is structured in essential levels of assistance that can be defined differently in the various regions. The National Health Program is structured in LEAs (essential levels of assistance). LEAs define all the medical assistance modalities offered by the INHS to citizens, with or without partial contributions, based on a patient's income.
Diabetes is a significant health problem and one of the tremendous challenges for healthcare systems all over Italy. The disease's growing incidence, prevalence, and progressive nature encouraged the development of new drugs to provide additional treatment options for diabetic patients. The roll-out of many new products, increasing international research collaborations in technology advancement, and increasing awareness about diabetes among the people are some of the market opportunities for the players in the Italy diabetes drugs market.
Italy Diabetes Drugs Industry Overview
The Italy Diabetes Drugs Market is moderately fragmented, with major manufacturers, namely Eli Lilly, Sanofi, Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, and other generic players, holding a presence in the region. A major share of the market is held by manufacturers concomitant with strategy-based M&A operations and constantly entering the market to generate new revenue streams and boost existing ones.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET DYNAMICS
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SEGMENTATION
- 5.1 Insulins
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.1.1.1 Lantus (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.2 Levemir (Insulin Detemir)
- 5.1.1.3 Toujeo (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.1.4 Tresiba (Insulin Degludec)
- 5.1.1.5 Basaglar (Insulin Glargine)
- 5.1.2 Bolus or Fast Acting Insulins
- 5.1.2.1 NovoRapid/Novolog (Insulin Aspart)
- 5.1.2.2 Humalog (Insulin Lispro)
- 5.1.2.3 Apidra (Insulin Glulisine)
- 5.1.3 Traditional Human Insulins
- 5.1.3.1 Novolin/Actrapid/Insulatard
- 5.1.3.2 Humulin
- 5.1.3.3 Insuman
- 5.1.4 Biosimilar Insulins
- 5.1.4.1 Insulin Glargine Biosimilars
- 5.1.4.2 Human Insulin Biosimilars
- 5.1.1 Basal or Long Acting Insulins
- 5.2 Oral Anti-diabetic drugs
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.2.1.1 Metformin
- 5.2.2 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.2.1 Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
- 5.2.3 Dopamine D2 receptor agonist
- 5.2.3.1 Bromocriptin
- 5.2.4 SGLT-2 inhibitors
- 5.2.4.1 Invokana (Canagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.2 Jardiance (Empagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.3 Farxiga/Forxiga (Dapagliflozin)
- 5.2.4.4 Suglat (Ipragliflozin)
- 5.2.5 DPP-4 inhibitors
- 5.2.5.1 Onglyza (Saxagliptin)
- 5.2.5.2 Tradjenta (Linagliptin)
- 5.2.5.3 Vipidia/Nesina(Alogliptin)
- 5.2.5.4 Galvus (Vildagliptin)
- 5.2.6 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.6.1 Sulfonylureas
- 5.2.7 Meglitinides
- 5.2.7.1 Meglitinides
- 5.2.1 Biguanides
- 5.3 Non-Insulin Injectable drugs
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.3.1.1 Victoza (Liraglutide)
- 5.3.1.2 Byetta (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.3 Bydureon (Exenatide)
- 5.3.1.4 Trulicity (Dulaglutide)
- 5.3.1.5 Lyxumia (Lixisenatide)
- 5.3.2 Amylin Analogue
- 5.3.2.1 Symlin (Pramlintide)
- 5.3.1 GLP-1 receptor agonists
- 5.4 Combination drugs
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
- 5.4.1.1 NovoMix (Biphasic Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.2 Ryzodeg (Insulin Degludec and Insulin Aspart)
- 5.4.1.3 Xultophy (Insulin Degludec and Liraglutide)
- 5.4.2 Oral Combinations
- 5.4.2.1 Janumet (Sitagliptin and Metformin)
- 5.4.1 Insulin combinations
6 MARKET INDICATORS
- 6.1 Type-1 Diabetic Population
- 6.2 Type-2 Diabetic Population
7 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 7.1 COMPANY PROFILES
- 7.1.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.1.2 Takeda
- 7.1.3 Pfizer
- 7.1.4 Eli Lilly
- 7.1.5 Janssen Pharmaceuticals
- 7.1.6 Astellas
- 7.1.7 Boehringer Ingelheim
- 7.1.8 Merck and Co.
- 7.1.9 AstraZeneca
- 7.1.10 Bristol Myers Squibb
- 7.1.11 Novartis
- 7.1.12 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2 COMPANY SHARE ANALYSIS
- 7.2.1 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 7.2.2 Sanofi Aventis
- 7.2.3 Eli Lilly
- 7.2.4 Merck and Co.
- 7.2.5 Others
8 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE TRENDS




