PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836431

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836431
High-throughput Screening - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The High-throughput Screening Market size is estimated at USD 25.71 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 41.31 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 9.94% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
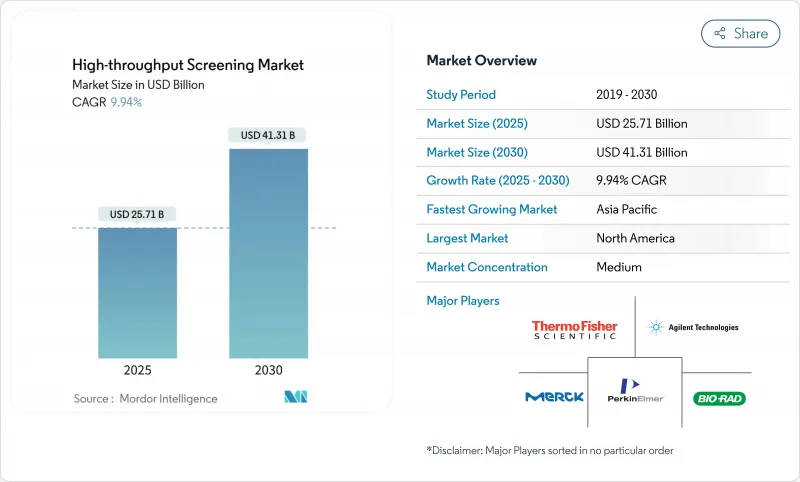
This expansion is anchored in widespread adoption of AI-enabled automation that compresses drug-discovery timelines and trims per-assay costs by 40%. Growing demand for physiologically relevant 3-D assays, rising R&D budgets focused on precision medicine, and strategic outsourcing to contract development and manufacturing organizations (CDMOs) reinforce the upward trajectory. Intensifying competition among integrated platform providers fosters rapid technology refresh cycles, while venture investment in microfluidic ultra-high-throughput screening (uHTS) platforms fuels product innovation. Regulatory encouragement of non-animal testing and sustainable laboratory practices adds momentum by redirecting capital toward advanced cell-based systems.
Global High-throughput Screening Market Trends and Insights
Advances in Robotic Liquid-Handling & Imaging Systems
Breakthroughs in adaptive robotics are elevating throughput and reproducibility across the high throughput screening market. Computer-vision modules now guide pipetting accuracy in real time, cutting experimental variability by 85% compared with manual workflows. Integrated AI detection algorithms process more than 80 slides per hour, lifting the ceiling for high-content imaging throughput. Dual-interface programming lets chemists configure complex workflows without specialist coding, broadening user access. Capital investments exceeding USD 2 million per workcell remain justified as return-on-investment profiles improve with volumes above 100,000 compounds annually. The result is a self-reinforcing cycle of platform upgrades that propels the high throughput screening market toward greater scale, speed, and data quality.
Rising Pharma/Biotech R&D Spending & Pipeline Growth
Expanded R&D budgets dedicated to precision medicine funnel capital into screening platforms that integrate computational biology with automated experimentation. AI-powered discovery has shortened candidate identification from six years to under 18 months, attracting venture flows to companies such as Recursion Pharmaceuticals, which progressed two AI-discovered oncology drugs to clinical trials in early 2025. The multiplier effect between rising budgets and algorithmic efficiency positions early-stage screening as a strategic lever for risk mitigation and timeline compression. Oncology and rare-disease pipelines especially benefit, as rapid compound triage supports combination-therapy exploration and personalized regimens.
High Capital Expenditure for Fully Automated HTS Workcells
Initial outlays near USD 5 million, including software, validation, and training, create financial friction for smaller firms. Annual maintenance and licensing inflate operating budgets by 15-20%. Although total cost of ownership favors high-volume users, capital intensity delays adoption in cash-constrained organizations and sustains demand for outsourced services. Equipment-leasing and shared-facility models partially offset the barrier, yet the pace of technology obsolescence remains an enduring hurdle to rapid market penetration.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Adoption of Physiologically Relevant Cell-Based & 3-D Assays
- AI/ML In-Silico Triage Shrinking Wet-Lab Library Size
- Shortage of Skilled Assay-Automation Specialists
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Cell-based assays held 45.14% high throughput screening market share in 2024, reflecting their capability to model complex signaling pathways and predict human efficacy more accurately than biochemical alternatives. The segment benefits from continual advances in fluorescent reporters, 3-D culture scaffolds, and label-free impedance technologies that capture subtle phenotypic shifts. The high throughput screening market size associated with lab-on-a-chip and microfluidic platforms is set to expand rapidly as 10.69% CAGR growth unlocks reagent savings and heightens assay sensitivity. Demand for ultra-high-throughput platforms remains steady among large pharmaceutical libraries, whereas label-free approaches attract safety-toxicology workflows seeking minimal assay interference.
The fusion of high-content imaging with AI-driven analytics magnifies data depth per screen, enabling phenotypic discovery that surfaces unexpected mechanisms of action. Organoid-based screening further differentiates compound responses by tissue microarchitecture, aiding oncology programs that require tumor-microenvironment fidelity. Together, these innovations fortify the cell-based segment's leading revenue position and catalyze a pipeline of next-generation systems that sustain the high throughput screening market's long-term expansion.
Primary and secondary screening applications contributed 53.56% of the high throughput screening market size in 2024, underscoring their foundational role in hit identification. Automated assay miniaturization and AI triage have accelerated sample throughput, aligning with discovery teams' need for rapid lead selection. In contrast, toxicology and ADME workflows are poised for 13.82% CAGR through 2030 as global regulators press for non-animal safety data. The shift reflects an economic calculus wherein early safety interrogation minimizes late-stage attrition costs, a prime consideration for venture-backed programs operating on compressed timelines.
In vitro toxicology platforms now incorporate human-derived cell lines, organ-on-chip devices, and predictive AI models, offering 360-degree safety profiling that informs candidate prioritization. CRISPR-enabled target validation accelerates disease-gene linkage studies, while multiplexed biomarker readouts sharpen translational relevance. Collectively, these dynamics diversify revenue streams by balancing legacy high-volume screens with safety-centric assays that draw premium pricing, reinforcing stability across the high throughput screening market.
The High Throughput Screening Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Technology (Ultra-High-Throughput Screening, Cell-Based Assays, and More), Application (Target Identification, and More), Product and Service (Instruments, and More), End User (Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology Firms, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 39.81% revenue in 2024, sustained by mature pharmaceutical ecosystems, high adoption of AI-enabled automation, and robust venture capital participation. Expansive compound libraries and favorable reimbursement landscapes accelerate platform upgrades, anchoring region-wide demand. The high throughput screening market size in the United States benefits from strategic National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants that incentivize translational research partnerships between academia and industry.
Europe maintains steady growth through stringent quality standards and supportive regulatory frameworks that encourage 3-D cell culture adoption. Clusters in Germany, the Netherlands, and the Scandinavian countries champion sustainable laboratory initiatives, spurring investments in reusable microfluidic cartridges that dovetail with continental environmental goals. The regional market also attracts Horizon-Europe funding earmarked for next-generation toxicology.
Asia-Pacific is forecast to advance at a 14.16% CAGR, outpacing Western counterparts as China's biotech sector experiences renewed capital inflows and supportive policy measures. A 60% biotech stock rally in 2025 outperformed AI sector indices, channeling investor confidence toward drug-discovery infrastructure. Licensing deals between Western majors and Asian biotech firms establish screening hubs that leverage competitive operating costs while adhering to international compliance standards. Rapid adoption of organ-on-chip and microfluidic technologies positions Asia to leapfrog legacy modalities, expanding the high throughput screening market's geographic diversification.
Emerging markets in South America and the Middle East & Africa exhibit untapped potential. Brazil and the United Arab Emirates spearhead national innovation agendas that fund shared HTS facilities within biotechnology parks. Infrastructure limitations and regulatory variability presently temper adoption rates, yet global CDMO expansion into these regions sets the stage for technology transfer and local capacity building, offering a future lift to worldwide high throughput screening market penetration.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- PerkinElmer (Revvity)
- Danaher (Molecular Devices)
- Agilent Technologies
- Merck
- Beckman Coulter (Life Sciences)
- Tecan Group
- GE Healthcare (Cytiva)
- Axxam
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Hamilton Company
- Promega
- Corning Life Sciences
- HighRes Biosolutions
- Charles River Labs
- Eurofins
- Evotec
- Abcam
- DiscoverX (Crownbio)
- Labcyte (Echo) - Beckman
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Advances in Robotic Liquid-Handling & Imaging Systems
- 4.2.2 Rising Pharma/Biotech R&D Spending & Pipeline Growth
- 4.2.3 Adoption of Physiologically Relevant Cell-Based & 3-D Assays
- 4.2.4 AI/ML In-Silico Triage Shrinking Wet-Lab Library Size
- 4.2.5 Venture-Backed Microfluidic uHTS Platforms
- 4.2.6 Rising CDMOs Bundling HTS In Integrated Discovery Contracts
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Capital Expenditure for Fully Automated HTS Workcells
- 4.3.2 Shortage of Skilled Assay-Automation Specialists
- 4.3.3 Data-Quality & Reproducibility Issues Across Labs
- 4.3.4 Sustainability Push Against Single-Use 1536-Well Plastics
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Ultra-high-throughput Screening (uHTS)
- 5.1.2 Cell-based Assays
- 5.1.3 Lab-on-a-chip / Microfluidics
- 5.1.4 Label-free Technologies
- 5.1.5 High-content Screening
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Target Identification / Validation
- 5.2.2 Primary & Secondary Screening
- 5.2.3 Toxicology & ADME
- 5.3 By Product & Service
- 5.3.1 Instruments
- 5.3.2 Reagents, Kits & Consumables
- 5.3.3 Software & Informatics
- 5.3.4 Services
- 5.4 By End-user
- 5.4.1 Pharma & Biotech Firms
- 5.4.2 Contract Research / CDMOs
- 5.4.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.2 PerkinElmer (Revvity)
- 6.3.3 Danaher (Molecular Devices)
- 6.3.4 Agilent Technologies
- 6.3.5 Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich)
- 6.3.6 Beckman Coulter (Life Sciences)
- 6.3.7 Tecan Group
- 6.3.8 GE Healthcare (Cytiva)
- 6.3.9 Axxam SpA
- 6.3.10 Bio-Rad Laboratories
- 6.3.11 Hamilton Company
- 6.3.12 Promega Corporation
- 6.3.13 Corning Life Sciences
- 6.3.14 HighRes Biosolutions
- 6.3.15 Charles River Labs
- 6.3.16 Eurofins Discovery
- 6.3.17 Evotec SE
- 6.3.18 Abcam plc
- 6.3.19 DiscoverX (Crownbio)
- 6.3.20 Labcyte (Echo) - Beckman
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




