PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836491

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836491
Asia-Pacific Nuclear Medicine - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market is valued at USD 3.36 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 6.14 billion by 2030, advancing at a 12.77% CAGR.
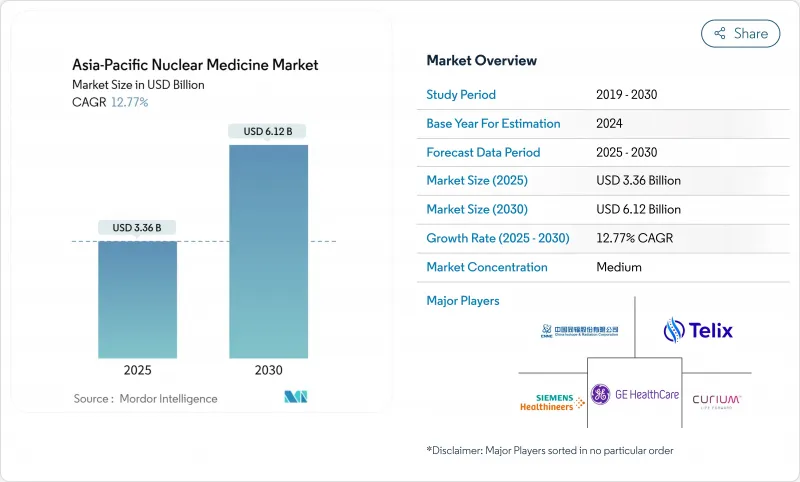
Growth reflects the region's decisive shift toward precision oncology and theranostics, backed by expanding hybrid imaging fleets, widening radiopharmaceutical pipelines, and steady public-sector investment in isotope production. China's 1,000-plus nuclear medicine departments, India's expanding network of 300 centers of excellence, and Australia's early adoption of PSMA-targeted agents anchor this expansion. Clinical workloads are rising most sharply in oncology and cardiology, while supply-chain partnerships are easing access to short-lived isotopes. Continued regulatory harmonization is expected to lower approval timelines, enabling a broader roll-out of radioligand therapy programs across emerging economies.
Asia-Pacific Nuclear Medicine Market Trends and Insights
Rising Burden of Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases
Asia accounts for 49.2% of global cancer cases and 56.1% of cancer deaths, with lung malignancies topping incidence tables in large populations such as China and Indonesia. The region also records pronounced cardiovascular disease prevalence, as East Asia reports 1,014.06 heart-failure patients per 100,000 population versus 389.97 per 100,000 in South Asia. These epidemiological patterns create sustained demand for both SPECT and PET procedures in oncology and cardiology. Ageing demographics in Japan and South Korea are intensifying oncologic caseloads that require early detection through nuclear imaging. High smoking rates-54.4% among Indonesian men and 41.5% among Chinese men-suggest a continued pipeline of pulmonary cancers that will rely on molecular imaging for staging and therapy monitoring. Consequently, the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market is positioned as a critical component of regional disease-management strategies.
Rising Adoption of Hybrid Imaging Technologies
Total-body PET/CT scanners installed at institutions such as Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center have completed 30,000 examinations in three years, cutting radiation exposure and acquisition times.Upright CT platforms launched at Keio University Hospital improve diagnostic confidence for musculoskeletal and respiratory assessments in elderly patients. SPECT systems are transitioning to semiconductor detectors that deliver higher spatial resolution and shorter scan windows. Artificial-intelligence algorithms embedded in these hybrid modalities enable automated lesion detection and quantitative analytics, which reduce reporting time and support remote reading in underserved locations. As procurement programs in China, Japan, and Australia emphasize whole-body scanners, the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market gains a technology refresh cycle that boosts procedure volumes and diagnostic accuracy.
High CAPEX for Cyclotrons and Imaging Equipment
Emerging economies face budget constraints when acquiring PET/CT scanners that can cost USD 2-5 million, plus annual service contracts approaching USD 200,000. The Philippines, for example, operates only three cyclotrons, all in Manila, which inflates travel expenses for provincial patients. In India, stringent quality-assurance standards for PET systems escalate procurement timelines and compliance costs. Capital needs extend to radiation-shielded hot cells, Good Manufacturing Practice suites, and certified staff, pushing payback periods beyond five years in many public hospitals. Limited reimbursement policies often shift financial burden to patients, potentially delaying adoption of next-generation theranostics. As a result, the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market must rely on public-private partnerships and concessional financing to overcome infrastructure barriers.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Initiatives and Healthcare Infrastructure Development
- Expansion of Molecular Imaging Applications and Personalized Medicines
- Complex Multi-Agency Isotope Transport Regulations
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Diagnostics accounted for 71.22% of the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market in 2024, driven by well-established SPECT and PET applications in myocardial perfusion, tumor staging, and brain imaging. Multi-head gamma cameras now achieve higher count sensitivity, which shortens scan times and improves patient throughput. Cardiac stress protocols benefit from new solid-state detectors that lower radiation dose without compromising image quality. Hospitals across China and Japan have standardized PET/CT for oncology work-ups, creating consistent demand for technetium-99m and fluorine-18 doses. Procedure volumes are supported by public insurance schemes that reimburse both tracer and scanner time, stabilizing revenue for service providers.
Therapeutics, though smaller today, is rising at a 17.24% CAGR. Lutetium-177 dotatate gained approvals for neuroendocrine tumors and is rapidly expanding into prostate cancer therapy through Pluvicto roll-outs. Alpha emitters such as actinium-225 promise higher linear-energy transfer, enhancing cell kill in micro-metastatic disease. South Korea's plan to initiate domestic actinium-225 production by mid-2025 will shorten supply lines and lower dose costs. Clinical guidelines are evolving to include radioligand therapy earlier in treatment algorithms, especially for prostate and thyroid malignancies. Continuous data generation from regional registries strengthens payor confidence and accelerates reimbursement, expanding the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine industry footprint in therapeutics.
Technetium-99m retained 40.68% share of the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market size in 2024. Its 6-hour half-life and favorable photon energy underpin its ubiquity in bone, renal, and myocardial imaging. Nevertheless, reliance on ageing reactors for molybdenum-99 production exposes the region to periodic shortages, prompting countries such as Australia and Japan to evaluate accelerator-based supply solutions. Digital logistics platforms in China now track generator shipments in real time, mitigating stock-out risk for remote clinics.
Lutetium-177, posting a 12.12% CAGR, anchors the therapeutic pipeline through versatile beta-emission profiles that are suitable for both imaging and therapy. SHINE-Primo Biotech agreements extend non-carrier-added lutetium-177 access to Taiwan, Japan, and Singapore, which collectively support more than 25 clinical trials. The isotope's 6.7-day half-life facilitates regional shipping without excessive decay loss, addressing a key distribution challenge for shorter-lived agents. Fluorine-18 continues to expand in oncology imaging, while gallium-68-based tracers gain traction in infection and inflammation mapping. Early research on terbium-161 and thorium-228 signals an impending diversification of therapeutic isotopes, broadening revenue streams for the Asia-Pacific nuclear medicine market.
The Asia-Pacific Nuclear Medicine Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Diagnostics[SPECT and PET], Therapeutics[alpha Emitters and More]), Radioisotope (Technetium-99m, Fluorine-18 and More), Application (Cardiology, Oncology, and More), End User (Hospital, Diagnostic Imaging Centers and More) and Geography (China, Japan, India, Australia, South Korea and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD)
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- GE Healthcare
- Siemens Healthineers
- Koninklijke Philips
- Canon
- Curium Pharma
- Telix Pharmaceuticals
- Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
- Nordion
- NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.
- China Isotope & Radiation Corp. (CIRC)
- Advanced Accelerator Applications (Novartis)
- Jubilant Radiopharma
- AdvanCell (Australia)
- Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical
- Institute of Nuclear Energy Research (Taiwan)
- Jiangsu Huayi Technology
- Zhejiang Jiutai New Drug
- Cyclopharma Laboratories
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Burden Of Cancer & Cardiovascular Diseases
- 4.2.2 Rising Adoption of Hybrid Imaging Technologies
- 4.2.3 Government Initiatives and Healthcare Infrastructure Development
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Molecular Imaging Applications and Personalized Medicines
- 4.2.5 Rising Awareness and Demand for Theranostics
- 4.2.6 Initiatives taken by Market Players and Launch of Products
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX For Cyclotrons & Imaging Equipment
- 4.3.2 Complex Multi-Agency Isotope Transport Regulations
- 4.3.3 Short Half-Life Isotope Supply Chain Risk
- 4.3.4 Shortage Of Certified Nuclear-Medicine Pharmacists Outside Tier-1 Cities
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technology Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value-USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Diagnostics
- 5.1.1.1 SPECT
- 5.1.1.2 PET
- 5.1.2 Therapeutics
- 5.1.2.1 Alpha Emitters
- 5.1.2.2 Beta Emitters
- 5.1.2.3 Brachytherapy Isotopes
- 5.1.1 Diagnostics
- 5.2 By Radioisotope
- 5.2.1 Technetium-99m
- 5.2.2 Iodine-131
- 5.2.3 Fluorine-18
- 5.2.4 Lutetium-177
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Oncology
- 5.3.2 Cardiology
- 5.3.3 Neurology
- 5.3.4 Endocrinology
- 5.3.5 Other Applications
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Diagnostic Imaging Centers
- 5.4.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.4.4 Specialty Clinics
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 China
- 5.5.2 Japan
- 5.5.3 India
- 5.5.4 Australia
- 5.5.5 South Korea
- 5.5.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 GE Healthcare
- 6.3.2 Siemens Healthineers AG
- 6.3.3 Philips Healthcare
- 6.3.4 Canon Medical Systems Corp.
- 6.3.5 Curium Pharma
- 6.3.6 Telix Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.7 Bracco Imaging S.p.A.
- 6.3.8 Nordion Inc.
- 6.3.9 NTP Radioisotopes SOC Ltd.
- 6.3.10 China Isotope & Radiation Corp. (CIRC)
- 6.3.11 Advanced Accelerator Applications (Novartis)
- 6.3.12 Jubilant Radiopharma
- 6.3.13 AdvanCell (Australia)
- 6.3.14 Shenzhen Mindray Bio-Medical
- 6.3.15 Institute of Nuclear Energy Research (Taiwan)
- 6.3.16 Jiangsu Huayi Technology
- 6.3.17 Zhejiang Jiutai New Drug
- 6.3.18 Cyclopharma Laboratories
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




