PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836624

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836624
Lung Cancer Surgery Devices - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
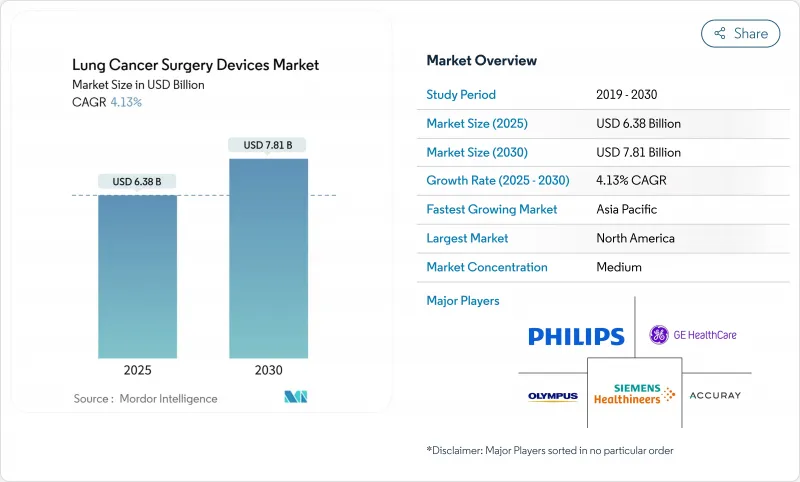
The Lung Cancer Surgery Devices Market size is estimated at USD 6.38 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 7.81 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 4.13% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Competitive intensity is now shaped less by sheer procedure volumes and more by the sophistication of robotic platforms, advanced stapling systems and AI-enabled imaging that compress operating times while sustaining oncological precision. Hospitals expand capital budgets for integrated robotic suites even as ambulatory surgical centers adopt lighter single-port systems that fit outpatient economics. Early-stage lung cancer detection through low-dose CT screening funnels an expanding cohort of surgical candidates, yet workforce shortages spur demand for automation that lets surgeons handle higher throughput without compromising lymph-node harvests. At the same time, reimbursement frameworks in North America and parts of Europe reward quality-of-life metrics, incentivizing providers to migrate from open thoracotomy to video-assisted and robotic approaches that shorten length of stay and reduce conversion rates.
Global Lung Cancer Surgery Devices Market Trends and Insights
Growing burden of lung cancer
Epidemiological projections indicate a 70% rise in surgical cases by 2035, driven by aging populations and escalating air-pollution exposure in emerging economies. Screening programs in Taiwan already detect 85% of cancers at stage 0-1, sharply increasing operable volumes while lowering per-case complexity. Device makers respond by prioritizing workflow efficiency over premium pricing curves. The epidemiological transition from late-stage palliative care to early-stage curative surgery fundamentally alters device utilization patterns and reimbursement models.
Technological advances in minimally-invasive and robotic surgery
Hospitals installed 147 da Vinci 5 systems in Q1 2025, signifying strategic commitment to articulated instruments and AI-driven analytics that improve lymph-node harvests from 5.6 to 7.5 stations per procedure. Partnerships such as Johnson & Johnson-NVIDIA focus on real-time algorithmic guidance, underscoring a shift toward software as the key differentiator. The epidemiological transition from late-stage palliative care to early-stage curative surgery fundamentally alters device utilization patterns and reimbursement models.
Effectiveness of non-surgical alternatives (SBRT, targeted therapies)
SBRT delivers >=90% local control in inoperable patients and costs USD 8,933 per course versus USD 12,197 for robotic resection, shifting treatment algorithms in frail cohorts. Novel devices must therefore present clear survival or quality-of-life edges to defend cap-ex budgets. The therapeutic landscape shift toward precision medicine and targeted therapies reduces the addressable surgical population, particularly for patients with specific molecular markers who achieve superior outcomes through systemic treatments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising air pollution and occupational exposures
- Expanding reimbursement for robotic lobectomy
- Workforce shortage of thoracic surgeons
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Minimally invasive techniques captured 55.32% lung cancer surgery devices market share in 2024 and are growing at 5.22% through 2030, outpacing thoracotomy as payers reward faster discharge and lower complication rates. The shift toward single-port VATS and uniportal robotic approaches trims average operative time to 88 minutes, nearly 28% faster than legacy multi-port procedures. Thoracotomy retains a foothold for extensive resections and complex hilum anatomy, yet its flatter adoption curve signals a limited role outside specialty centers.
Surgeons value minimally invasive workflows for reducing postoperative pneumonia and atrial arrhythmia incidence, translating to shorter 4-day median stays versus 7 days for open surgery. Single-port robotic trials exceeding 100 thoracic cases confirm feasibility for sleeve resections and segmentectomies, signalling a broadening addressable pool once training ecosystems mature.
Surgical devices represented 59.63% revenue in 2024, reflecting their indispensable role in tissue dissection and stapling; however, monitoring devices log the quickest 5.98% CAGR as AI engines tether imaging to operative consoles in real time. Olympus' BF-P190 bronchoscope, equipped with a 2.2 mm channel, exemplifies hardware advances underpinning procedural agility.
Siemens' AI-Rad Companion positions monitoring gear as data generators for continuous surgical learning, nudging hospitals to bundle analytics subscriptions with capital purchases. Such hybrid revenue models solidify vendor lock-in while supporting device upgrades on software cycles rather than hardware depreciation schedules.
The Lung Cancer Surgery Devices Market Report is Segmented by Surgery Type (Thoracotomy, and Minimally Invasive Surgeries), Product (Surgical Devices and Monitoring Devices), Surgical Approach (Open, Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS), and More), End User (Hospitals, Specialty Cancer Centers and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's leadership stems from harmonized reimbursement and rapid technology clearance under the FDA 510(k) route, allowing continuous infusion of AI-guided imaging and next-generation stapling systems. Intuitive Surgical placed 367 systems in Q1 2025 in the U.S., reinforcing an installed base that already executed 2.63 million procedures in 2024.
Europe sustains stable uptake via MDR-aligned assessments that stress cost-effectiveness; Hungary's multicenter LDCT projects show pathways for member states to funnel early-stage cases into surgery, maintaining a predictable capital-purchase cadence. Simultaneously, CE-marked innovations such as Optune Lua widen therapeutic alternatives, compelling surgeons to demonstrate superiority on survival and quality-of-life endpoints.
Asia Pacific's lung cancer surgery devices market is propelled by urban pollution spikes and government-funded insurance expansion that subsidizes minimally invasive procedures in tier-1 and tier-2 cities. AI-enabled diagnosis projects in China exemplify leapfrogging strategies that integrate deep-learning triage into routine screening, potentially shortening pathways from detection to resection.
- Accuray
- GE Healthcare
- Johnson & Johnson
- Olympus
- Richard Wolf
- Siemens Healthineers
- Intuitive Surgical
- Medtronic
- Stryker
- KARL STORZ SE
- Boston Scientific
- Neomend Inc.
- Trokamed GMBH
- Scanlan International Inc.
- BSD Medical Corp.
- Teleflex
- AngioDynamics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing burden of lung cancer
- 4.2.2 Technological advances in minimally-invasive and robotic surgery
- 4.2.3 Rising air pollution and occupational exposures
- 4.2.4 Expanding reimbursement for robotic lobectomy
- 4.2.5 Integration of intra-operative AI imaging & navigation
- 4.2.6 Surge in early-stage detection via low-dose CT screening
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Effectiveness of non-surgical alternatives (SBRT, targeted therapies)
- 4.3.2 Workforce shortage of thoracic surgeons
- 4.3.3 High capital cost of robotic systems and disposables
- 4.3.4 Regulatory delays for novel energy devices
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Surgery Type
- 5.1.1 Thoracotomy
- 5.1.1.1 Lobectomy
- 5.1.1.2 Sleeve Resection
- 5.1.1.3 Segmentectomy
- 5.1.1.4 Pneumonectomy
- 5.1.2 Minimally Invasive Surgeries
- 5.1.1 Thoracotomy
- 5.2 By Product
- 5.2.1 Surgical Devices
- 5.2.2 Monitoring Devices
- 5.3 By Surgical Approach
- 5.3.1 Open
- 5.3.2 Video-Assisted Thoracoscopic Surgery (VATS)
- 5.3.3 Robotic-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (RATS)
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Specialty Cancer Centers
- 5.4.3 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Accuray Incorporated
- 6.3.2 GE HealthCare
- 6.3.3 Johnson & Johnson (Ethicon)
- 6.3.4 Olympus Corporation
- 6.3.5 Richard Wolf GmbH
- 6.3.6 Siemens Healthineers AG
- 6.3.7 Intuitive Surgical
- 6.3.8 Medtronic plc
- 6.3.9 Stryker Corporation
- 6.3.10 KARL STORZ SE
- 6.3.11 Boston Scientific Corporation
- 6.3.12 Neomend Inc.
- 6.3.13 Trokamed GMBH
- 6.3.14 Scanlan International Inc.
- 6.3.15 BSD Medical Corp.
- 6.3.16 Teleflex Incorporated
- 6.3.17 AngioDynamics Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




