PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836631

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836631
Genome Editing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
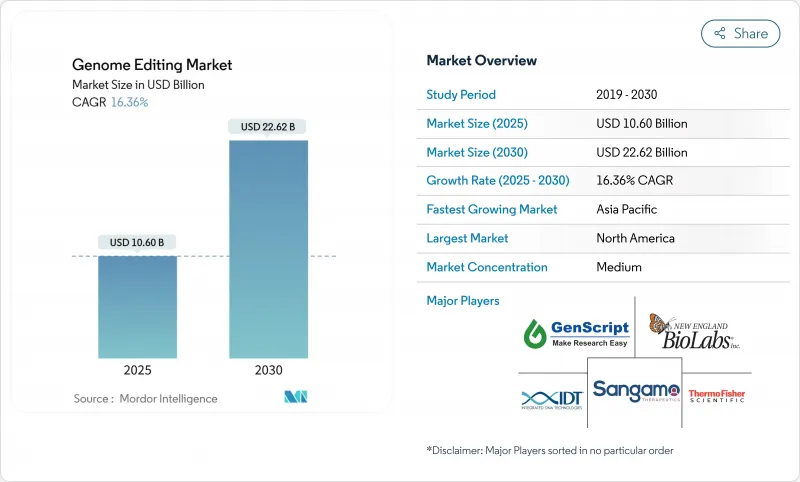
The Genome Editing Market size is estimated at USD 10.60 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 22.62 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 16.36% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Clinical validation of CRISPR-Cas9, rising demand for climate-resilient crops, and abundant venture capital all converge to accelerate commercial adoption. Growing regulatory confidence is evident in the wave of review designations granted to CRISPR therapeutics, while agricultural regulators in several countries now treat many gene-edited plants as conventionally bred. Competitive strategies focus on expanding GMP-compliant capacity, integrating AI into nuclease design, and signing platform licensing deals that lock in intellectual-property advantages. Intensifying collaboration between large pharmaceutical companies and agile start-ups broadens the therapeutic pipeline and speeds time-to-market, even as manufacturing scale-up, trade policy misalignment, and skilled-labor shortages temper the outlook.
Global Genome Editing Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Adoption of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Clinical Trials
FDA approval of the first CRISPR therapy unlocked broader clinical exploration, enabling multi-arm umbrella trials that cut development cycles by up to two years. Positive read-outs from hematology, ophthalmology, and solid-tumor studies underscore platform versatility and attract sustained capital inflows. Universities and biotech firms are scaling CRISPR-TIL protocols that achieved complete responses in gastrointestinal cancers, moving beyond monogenic indications.
Expanding Agricultural Biotechnology Demand for Climate-Resilient Crops
Genome-edited rice, drought-tolerant corn, and heat-resistant livestock exemplify solutions that mitigate climate shocks while maintaining yield. Regulatory exemptions in 16 jurisdictions where no foreign DNA persists accelerate commercialization, allowing small breeders to enter the genome editing market without onerous GMO hurdles. Public-private programs channel CRISPR tools toward nutritional fortification in staple crops, broadening market opportunities in developing regions.
Uncertain Long-Term Off-Target Safety Profile in Humans
Ultra-deep sequencing continues to reveal hundreds of potential off-target sites, prompting regulators to demand expanded biodistribution and durability studies before late-stage trials can proceed. High-fidelity Cas variants and prime-editing approaches lessen risk, but limited long-term human data keep post-marketing surveillance requirements stringent, especially in the EU.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surging VC & IPO Funding for Gene-Editing Start-Ups
- Mainstreaming In-Vivo Gene-Editing Therapeutics for Rare Diseases
- High CAPEX For GMP-Compliant Gene-Editing Manufacturing Suites
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
CRISPR delivered 41.62% genome editing market share in 2024, but TALEN exhibits a 19.89% CAGR that is reshaping the competitive mix. Evolving AI tools dramatically cut guide-RNA optimization cycles and expand the nuclease design space, spawning derivatives such as Open-CRISPR with novel sequence homology. Base- and prime-editing modalities gain traction as safety-oriented alternatives and may carve dedicated submarkets, especially in indication areas sensitive to double-strand break risks.
At the same time, zinc finger nucleases preserve niches in ultra-specific applications where intellectual-property freedom outweighs throughput. Meganucleases and oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis round out the toolkit for industrial synthetic-biology workflows. Consequently, platform providers increasingly bundle editing modalities with predictive AI software and screening libraries, anchoring broader solution sales across therapeutic, agricultural, and industrial customers.
Viral vectors generated 46.72% of 2024 revenue through predictable transduction efficiency and a well-understood regulatory path, ensuring continued demand in high-value ex-vivo therapies. Yet non-viral physical approaches will expand at 16.52% CAGR as electroporation, microfluidic squeezing, and tissue-selective lipid nanoparticles solve the immunogenicity and payload-size limits inherent to viral systems.
Robotic microinjection platforms quadruple embryo-editing throughput, spurring agricultural breeders to adopt non-viral protocols at scale. Ribonucleoprotein complexes deliver transient editing that fades before adaptive immunity triggers, appealing to chronic-disease programs requiring repeat dosing. Chemical carriers remain relevant for screening and research but cede ground in clinical settings to more efficient physical tools.
The Genome Editing Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Technology (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR), and More), Delivery Method (Viral Vectors, and More), Application (Cell Line Engineering, and More), by End User (Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America captured 41.25% of 2024 revenue, anchored by deep venture funding, leading clinical-trial infrastructure, and supportive FDA policies. Federal bio-economy initiatives allocate multi-billion-dollar budgets to genomics R&D and advanced manufacturing, reinforcing domestic supply chains. Nonetheless, construction-cost inflation and scarcity of GMP personnel place upward pressure on operating expenses for new facilities.
Europe combines world-class academic research with fragmented regulations that slow agricultural commercialization. The EU's GMO designation for most gene-edited crops conflicts with more permissive stances in the United Kingdom and Switzerland, prompting calls for policy harmonization. Meanwhile, biotech investment funds and Horizon Europe grants channel resources into therapeutic programs, sustaining R&D despite trade-policy uncertainty.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at 20.23% CAGR, propelled by Chinese industrial-policy incentives, Japanese regulatory streamlining for genome-edited foods, and Australia's RNA Blueprint aiming for an USD 8 billion contribution to GDP. India's risk-tiered guidelines create an expedited path for low-risk edits, catalyzing start-up formation. Technology-transfer limits and patent-pool negotiations will shape the trajectory of foreign market entrants.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Merck
- CRISPR Therapeutics AG
- Editas Medicine
- Horizon Discovery
- Intellia Therapeutics Inc.
- Beam Therapeutics Inc.
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Genscript
- Synthego Corporation
- Takara Bio
- Integrated DNA Technologies
- Lonza Group
- New England Biolabs
- OriGene Technologies
- Caribou Biosciences Inc.
- Bluebird Bio
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- Agilent Technologies
- QIAGEN
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid Adoption of CRISPR-Cas Systems in Clinical Trials
- 4.2.2 Expanding Agricultural Biotechnology Demand for Climate-Resilient Crops
- 4.2.3 Surging VC & IPO Funding for Gene-Editing Start-Ups
- 4.2.4 Mainstreaming In-Vivo Gene-Editing Therapeutics for Rare Diseases
- 4.2.5 Automation & AI-Assisted High-Throughput Screening Platforms
- 4.2.6 Government Bio-Economy Roadmaps in Emerging Countries
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Uncertain Long-Term Off-Target Safety Profile in Humans
- 4.3.2 High CAPEX For GMP-Compliant Gene-Editing Manufacturing Suites
- 4.3.3 Cross-Border Regulatory Fragmentation for Edited Seeds
- 4.3.4 Talent Shortage in Advanced Molecular Biology Skillsets
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)
- 5.1.2 Transcription Activator-Like Effector Nuclease (TALEN)
- 5.1.3 Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN)
- 5.1.4 Meganucleases
- 5.1.5 Oligonucleotide-directed Mutagenesis (ODM)
- 5.1.6 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Delivery Method
- 5.2.1 Viral Vectors
- 5.2.2 Non-viral Physical Methods
- 5.2.3 Non-viral Chemical Methods
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Cell Line Engineering
- 5.3.2 Gene & Cell Therapy
- 5.3.3 Drug Discovery & Functional Genomics
- 5.3.4 Agricultural Crop Engineering
- 5.3.5 Diagnostics & Synthetic Biology
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- 5.4.2 Academic & Government Research Institutes
- 5.4.3 Contract Research Organizations
- 5.4.4 Agriculture & Food Companies
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.2 Merck KGaA (Sigma-Aldrich)
- 6.3.3 CRISPR Therapeutics AG
- 6.3.4 Editas Medicine Inc.
- 6.3.5 Horizon Discovery Group plc
- 6.3.6 Intellia Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.7 Beam Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.8 Sangamo Therapeutics Inc.
- 6.3.9 GenScript Biotech Corporation
- 6.3.10 Synthego Corporation
- 6.3.11 Takara Bio Inc.
- 6.3.12 Integrated DNA Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.13 Lonza Group AG
- 6.3.14 New England Biolabs Inc.
- 6.3.15 OriGene Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.16 Caribou Biosciences Inc.
- 6.3.17 Bluebird Bio Inc.
- 6.3.18 Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.
- 6.3.19 Agilent Technologies Inc.
- 6.3.20 QIAGEN N.V.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




