PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836662

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836662
Native Starch - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The native starch market is projected to grow from USD 24.71 billion in 2025 to USD 31.70 billion by 2030, registering a 5.11% CAGR during the forecast period.
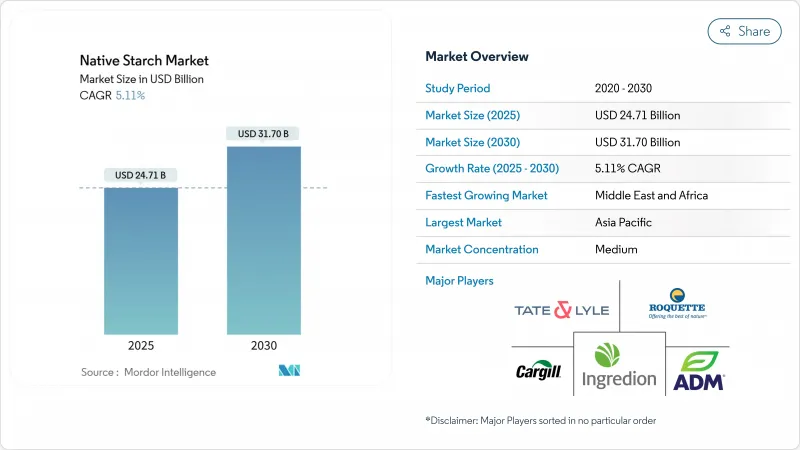
This growth is driven by expanding applications in food, pharmaceuticals, personal care, paper, adhesives, and bioplastics, alongside clean-label reformulation trends that elevate native starch as a functional, chemical-free ingredient. Producers are addressing raw-material price volatility through diversified sourcing, vertical integration, and advancements in extraction technologies that improve yields and reduce resource use. Key demand areas include bakery, confectionery, dairy, meat alternatives, and biodegradable packaging, with plant-based diets and functional foods further boosting its role as a texturizer and nutritional component. Industrial users in paper and packaging are adopting starch for sustainability goals, prompting investments in specialty grades and technologies like ultrasound-assisted extraction and heat-moisture treatments to enhance performance while maintaining a clean-label profile. Despite regulatory challenges and agricultural cost fluctuations, these factors collectively sustain the market's growth trajectory.
Global Native Starch Market Trends and Insights
Growing Usage in Bakery and Confectionery as a Texturizer
Native starch is increasingly favored in the bakery and confectionery sectors for its ability to enhance texture, retain moisture, and extend shelf life without chemical additives. This strategic reformulation helps manufacturers meet clean-label demand while reducing production costs. Maize and tapioca-derived native starches, valued for their neutral flavors, perform well in high-sugar contexts, ensuring stability and preserving sensory qualities. Acting as both a thickening agent and texturizer, native starch simplifies ingredient lists and ensures consistent product quality globally. Regulatory support further drives adoption. For example, the U.S. FDA promotes transparency in food labeling, encouraging natural ingredients, while Europe's Clean Label Project influences consumer choices toward alternatives like native starch. In the Asia-Pacific region, rising incomes and food quality awareness are boosting demand for clean-label bakery and confectionery products. These factors position native starch as essential for meeting consumer preferences and regulatory requirements, driving global market growth.
Cost-Effective Thickening Agent for Processed Foods
Native starch, increasingly favored in the processed food sector, stands out for its cost-effective thickening properties. It delivers consistent results at a lower price than hydrocolloids and other specialty ingredients. This financial edge is vital for food producers contending with inflation while maintaining stable prices. Derived from maize and potatoes, native starches undergo minimal processing, reducing production costs and conserving energy compared to modified counterparts or plant protein texturizers. Their adaptability to various pH levels and processing conditions allows for standardization in diverse products, from soups and sauces to dairy alternatives and ready meals. USDA data shows U.S. maize production reached 389.67 million metric tons in 2023/24, ensuring a steady raw material supply . This abundance enhances the cost-effectiveness of native starches, solidifying their status as a top choice for manufacturers. Advancements in starch extraction technologies have improved yield rates and functional attributes, enabling manufacturers to achieve desired viscosity and mouthfeel with less starch. These improvements reduce supply chain costs and bolster a clean label image.
Fluctuating Agricultural Raw Material Prices Impact Industry Profit Margins
Producers in the native starch industry face margin pressures due to agricultural commodity price volatility. Maize starch manufacturers are particularly affected, competing with the biofuel sector for raw materials. Climate change-induced weather disruptions, such as droughts in key regions, have worsened harvest uncertainties, causing supply shortages and price spikes that cannot be quickly passed to industrial clients with long-term contracts. To address this, producers are diversifying starch sources and integrating vertically into agricultural production. Many are forming direct farmer partnerships with guaranteed pricing to secure supply chains and investing in processing technologies to handle varying crop qualities while maintaining product standards. Although these strategies require significant capital, they are essential for staying competitive in the market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rise in Demand for Plant-Based and Functional Food Ingredients
- Adoption of Native Starch in Industrial Applications Beyond Food
- Complex Regulatory Requirements
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, maize leads the native starch market with a 79.04% share, driven by its cost-effectiveness, availability, and versatile properties. Wet milling processes for maize starch extraction provide economic advantages over alternatives. Wheat starch, though secondary, offers unique protein interactions for bakery applications, but faces growth challenges due to gluten allergen concerns. Potato starch, valued for its thickening power and neutral flavor, is favored in clean-label applications despite higher costs. Tapioca starch, the fastest-growing segment, is projected to grow at a 5.46% CAGR (2025-2030) due to its freeze-thaw stability and clear gel formation, ideal for frozen foods and transparent sauces.
The competitive dynamics among starch sources are shifting as manufacturers increasingly develop specialized grades optimized for specific applications rather than treating native starches as commodity ingredients. This specialization strategy is particularly evident in the tapioca segment, where producers are leveraging its natural functional properties to target premium clean label applications without chemical modification. Simultaneously, research into unconventional starch sources like pea, palm, and other botanical origins is expanding the industry's raw material base, creating opportunities for product differentiation and supply chain resilience that will reshape competitive dynamics over the forecast period.
The Native Starches Market Report is Segmented by Source (Maize, Wheat, Potato, Tapioca and Other Sources), Form (Powder and Liquid), Application (Food and Beverage, Pharmaceutical, Personal Care and Cosmetics, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2024, Asia-Pacific leads the native starch market with a 32.26% share, fueled by its vast food processing sector and broadening industrial uses. China and India, prioritizing food security and industrial autonomy, act as the region's main growth drivers. Benefiting from rich agricultural resources and reduced production costs, producers in Asia-Pacific can sustain healthy margins even when raw material prices fluctuate. Thailand, bolstered by supportive weather and government initiatives, has positioned itself as a key player in tapioca starch, enhancing cassava production. Meanwhile, India's native starch landscape is evolving, with maize output projected to hit 42 million tons by 2025-26 . This surge is set to bolster domestic processing, curtail imports, and elevate India to the status of an emerging exporter.
Europe holds a prominent stance in the market, leading in potato and wheat starch production. The continent has honed specialized extraction techniques, ensuring top-tier product quality. Europe's regulatory stance, especially on GMO matters, has influenced its production dynamics, leading to distinct supply chains that fetch premium prices globally. North America, with its efficient maize starch production, sees the U.S. as a key global player and exporter. Emphasizing technological advancements, companies like Ingredion highlight that starches made up nearly 49% of their USD 7.4 billion net sales in 2024 .
Middle East and Africa, starting from a modest base, is poised for the most rapid growth, with a projected 5.78% CAGR from 2025 to 2030. This growth is largely driven by strategic investments in food security, especially in Gulf Cooperation Council nations aiming to lessen their import reliance. However, the region grapples with challenges like water scarcity and agricultural constraints. These hurdles are steering investments towards efficient processing technologies and alternative starch sources that align with local agricultural conditions. In South America, Brazil and Argentina dominate the scene, leveraging their abundant maize production to offer competitive advantages for native starch producers catering to both local and international markets.
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- Ingredion Incorporated
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Tate & Lyle PLC
- Roquette Freres S.A.
- AGRANA Beteiligungs AG
- Tereos S.A.
- Royal Avebe
- Gulshan Polyols Ltd.
- AKV Langholt
- Bluecraft Agro Private Limited
- SPAC Starch Products Limited
- Anhui BBCA Biochemical
- Thai Wah Public Co.
- Manildra Group
- Tongaat Hulett
- Santhosh Starch Products Limited
- KMC Ingredients
- Argrum Foods India Private Limited
- Alvand Starch Industries
- Emland Group
- Varalaksmi Starch Industries (P) Ltd
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Usage in Bakery and Confectionary as a Texturizer
- 4.2.2 Cost-Effective Thicking Agent for Processed Foods
- 4.2.3 Rise in Demand for Plant-Based and Functional Food Ingredients
- 4.2.4 Adoption of Native Starch in Industrial Applications Beyond Food
- 4.2.5 Strategic Collaboration Between Food Giants and Local Starch Producers
- 4.2.6 Inclusion of Native Starch in Food Driven by Clean Label Trend
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fluctuating Agricultural Raw Material Prices Impact Industry Profit Margins
- 4.3.2 Complex Regulatory Requirements
- 4.3.3 Potential Allergen Concerns for Wheat-Based Starch
- 4.3.4 Moisture Sensitivity of Native Starch Reduces Shelf Life
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Source
- 5.1.1 Maize
- 5.1.2 Wheat
- 5.1.3 Potato
- 5.1.4 Tapioca
- 5.1.5 Other Sources
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Powder
- 5.2.2 Liquid
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Food and Beverage
- 5.3.2 Pharmaceutial
- 5.3.3 Personal Care and Cosmetics
- 5.3.4 Animal Feed
- 5.3.5 Paper and Corrugating
- 5.3.6 Other Applications
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.2 Germany
- 5.4.2.3 Spain
- 5.4.2.4 France
- 5.4.2.5 Italy
- 5.4.2.6 Netherlands
- 5.4.2.7 Sweden
- 5.4.2.8 Poland
- 5.4.2.9 Belgium
- 5.4.2.10 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 South Korea
- 5.4.3.6 Indonesia
- 5.4.3.7 Thailand
- 5.4.3.8 Singapore
- 5.4.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Chile
- 5.4.4.4 Colombia
- 5.4.4.5 Peru
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 South Africa
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Egypt
- 5.4.5.6 Morocco
- 5.4.5.7 Turkey
- 5.4.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Archer Daniels Midland Company
- 6.4.2 Ingredion Incorporated
- 6.4.3 Cargill, Incorporated
- 6.4.4 Tate & Lyle PLC
- 6.4.5 Roquette Freres S.A.
- 6.4.6 AGRANA Beteiligungs AG
- 6.4.7 Tereos S.A.
- 6.4.8 Royal Avebe
- 6.4.9 Gulshan Polyols Ltd.
- 6.4.10 AKV Langholt
- 6.4.11 Bluecraft Agro Private Limited
- 6.4.12 SPAC Starch Products Limited
- 6.4.13 Anhui BBCA Biochemical
- 6.4.14 Thai Wah Public Co.
- 6.4.15 Manildra Group
- 6.4.16 Tongaat Hulett
- 6.4.17 Santhosh Starch Products Limited
- 6.4.18 KMC Ingredients
- 6.4.19 Argrum Foods India Private Limited
- 6.4.20 Alvand Starch Industries
- 6.4.21 Emland Group
- 6.4.22 Varalaksmi Starch Industries (P) Ltd
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




