PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836693

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836693
Military Cybersecurity - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
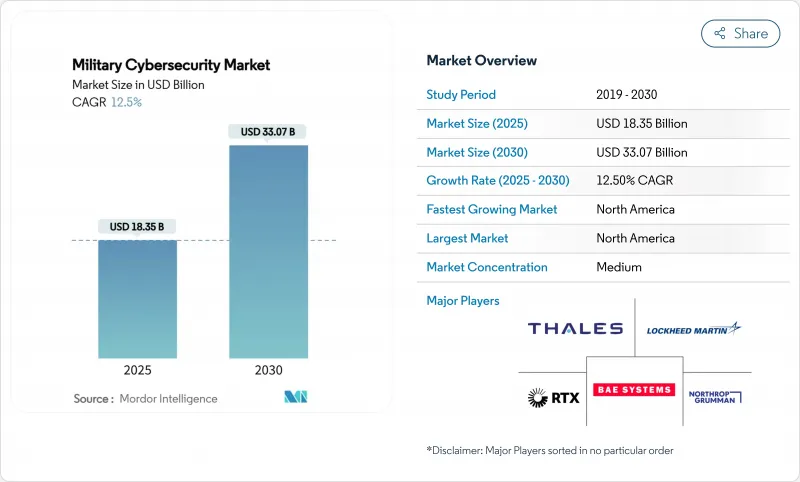
The military cybersecurity market size was valued at USD 18.35 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 33.07 billion by 2030, registering a robust 12.50% CAGR.
Growth stems from state-sponsored intrusions, zero-trust mandates, and multi-domain modernization programs that compel defense agencies to harden digital infrastructure. The Pentagon set the tone by allocating USD 14.5 billion for cyberspace activities in fiscal 2025, a year-on-year rise of USD 64 million. NATO established an Integrated Cyber Defence Centre in July 2024 to synchronize alliance responses. Asia-Pacific governments followed suit, with Japan approving a historic USD 734 billion defense budget for 2025 that embeds sizeable cyber allocations. Procurement patterns shifted toward software-defined defenses, evidenced by the US Army's Software Bill of Materials (SBOM) mandate effective February 2025. Demand surged for threat-intelligence platforms, attributing attacks to nation-state actors, while managed security services gained traction amid an acute shortage of cleared cyber talent.
Global Military Cybersecurity Market Trends and Insights
Escalating state-sponsored cyber-intrusions
Sophisticated nation-state campaigns reshaped defense priorities, shifting military procurement from perimeter defenses toward assume-breach architectures. China's December 2024 Treasury hack and the UK Ministry of Defence payroll breach highlighted persistent advanced-persistent-threat activity. In response, the 2025 US National Defense Authorization Act classified ransomware groups as hostile actors, increasing demand for platforms that identify attribution at scale. The Office of the Director of National Intelligence launched Sentinel Horizon using Recorded Future intelligence, demonstrating reliance on commercial tradecraft.
Modernization programs drive integrated cyber architectures
Joint All-Domain Command and Control (JADC2) requires defenses that secure traffic spanning land, sea, air, space, and cyber domains, pushing vendors to deliver interoperable, classification-aware solutions. NATO's Defence Innovation Accelerator funded 70 dual-use firms in 2025, each receiving EUR 100,000 (~USD 116,000) to mature technologies for secure communications. The EU Cyber Solidarity Act injected EUR 1.11 billion (~USD 1.28 billion) into cross-border Security Operations Centres, prompting demand for coalition-ready platforms. Vendors that built standards-compliant solutions captured opportunities across allied forces.
Cleared-cyber talent shortage constrains implementation velocity
Defense agencies grappled with roughly 225,000 unfilled US cyber roles, with clearances exacerbating gaps. The March 2023 Cyber Workforce Strategy pivoted to skills-based hiring, yet clearance timelines still slowed project rollouts. The Office of the National Cyber Director removed four-year degree prerequisites, but labor costs continued to climb as agencies competed for scarce expertise.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cloud and zero-trust adoption accelerates military digital transformation
- Private-5G and Open RAN deployments expand attack surfaces
- Legacy OT/ICS fragmentation creates integration challenges
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The threat intelligence and response held 28.56% of the military cybersecurity market share in 2024, reflecting commanders' need for campaign-level attribution and predictive analytics. Vendors integrated AI models to correlate indicators across multiple classification tiers, reducing latency between detection and operational action. Managed security services posted a 14.63% CAGR as organizations outsourced 24/7 monitoring to offset staff shortages. Identity and Access Management tools grew on the back of zero-trust directives that mandated continuous verification. Security information and event management platforms evolved toward cloud-native, behavior analytics engines that identify subtle anomalies rather than rely solely on rule-based alerts.
Defense agencies increasingly paired threat intelligence feeds with kinetic planning systems, allowing commanders to model cyber effects alongside physical operations. The military cybersecurity market size for threat intelligence is projected to reach USD 9.45 billion by 2030, growing at 12.3% annually. SBOM compliance tools became integral to managed-service portfolios, ensuring software supply-chain visibility for new and retrofit programs.
Network security captured 38.45% revenue in 2024, anchored by encryption, segmentation, and cross-domain guards that protect classified links. Private 5G deployments widened the footprint for adaptive firewalls that secure software-defined radio paths. Cloud security logged a 16.45% CAGR as accredited hyperscale zones handled sensitive, unclassified workloads. Multi-tenant boundary controls, enclave-level keys, and continuous compliance checks dominated procurement requirements.
Endpoint and application security are blended into zero-trust orchestration, where device health, user behavior, and data labels drive access decisions irrespective of network location. The military cybersecurity market size for cloud security is forecast to exceed USD 6.2 billion by 2030. Meanwhile, hardware-based encryption modules supported post-quantum roadmaps, ensuring traffic protection beyond 2035.
The Military Cybersecurity Market Report is Segmented by Solution (Threat Intelligence and Response, and More), Security Layer (Endpoint Security, Network Security, and More), Deployment (On-Premise and Cloud), Operation Domain (Land Forces, and More), Component (Hardware and Software and Services), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 45.70% market share in 2024, underpinned by the United States' USD 30 billion cyber allocation and mature acquisition ecosystem. Regional programs such as DISA's Thunderdome, the Army's SBOM mandate, and private 5G rollouts shaped global requirements. Canada leveraged NATO's Defence Innovation Accelerator to co-fund dual-use startups, while Mexico advanced military cloud accreditation to secure border operations. The military cybersecurity market size for North America is projected to reach USD 15.2 billion by 2030.
Asia-Pacific posted the highest 13.40% CAGR as Japan adopted an active cyber defense posture, authorizing pre-emptive operations against adversaries. QUAD initiatives standardized software security audits across Australia, India, Japan, and the United States, easing vendor entry. ASEAN militaries formed dedicated cyber commands; Singapore's Digital Intelligence Service operationalized integrated threat-hunting across maritime and land assets. China's Volt Typhoon campaign against Guam's infrastructure accelerated investment in island-based early-warning systems.
Europe benefited from the EUR 1.11 billion (~USD 1.28 billion) Cyber Solidarity Act and the NATO Integrated Cyber Defence Centre. Finland hosted technology hubs working on 6G secure communications, attracting Northern European startups. However, fragmented procurement and divergent cryptographic standards slowed cross-border scaling. The Middle East and Africa expanded cyber budgets to protect critical infrastructure amid regional conflicts, though growth remained uneven due to fiscal constraints.
- BAE Systems plc
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (General Dynamics Corporation)
- RTX Corporation
- Thales Group
- Airbus Defence and Space (Airbus SE)
- International Business Machines Corporation
- Booz Allen Hamilton, Inc.
- Leidos Holdings, Inc.
- CACI International Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- Cisco Systems, Inc.
- Fortinet, Inc.
- DXC Technology Company
- Tyto Athene, LLC
- Clavister Holding AB
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating state-sponsored cyber-intrusions
- 4.2.2 Modernization programs (JADC2, DIANA, etc.)
- 4.2.3 Cloud and Zero-Trust adoption across DoD
- 4.2.4 Private-5G/Open RAN roll-outs drive RF-layer security
- 4.2.5 SBOM mandates for weapon-system software
- 4.2.6 Post-quantum cryptography urgency
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Cleared-cyber talent shortage
- 4.3.2 Budget constraints/cost overruns
- 4.3.3 Legacy OT/ICS fragmentation
- 4.3.4 Data-sovereignty and export-control barriers
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Solution
- 5.1.1 Threat Intelligence and Response
- 5.1.2 Identity and Access Management
- 5.1.3 Data Loss Prevention
- 5.1.4 Security Information and Event Management
- 5.1.5 Unified Threat Management
- 5.1.6 Risk and Compliance Management
- 5.1.7 Managed Security Services
- 5.1.8 Others
- 5.2 By Security Layer
- 5.2.1 Endpoint Security
- 5.2.2 Network Security
- 5.2.3 Cloud Security
- 5.2.4 Application Security
- 5.3 By Deployment
- 5.3.1 On-Premise
- 5.3.2 Cloud
- 5.4 By Operation Domain
- 5.4.1 Land Forces
- 5.4.2 Air Forces
- 5.4.3 Naval Forces
- 5.5 By Component
- 5.5.1 Hardware Appliances
- 5.5.2 Software and Services
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 Germany
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Russia
- 5.6.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Mexico
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 UAE
- 5.6.5.1.3 Israel
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.2 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.3 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.4 General Dynamics Mission Systems, Inc. (General Dynamics Corporation)
- 6.4.5 RTX Corporation
- 6.4.6 Thales Group
- 6.4.7 Airbus Defence and Space (Airbus SE)
- 6.4.8 International Business Machines Corporation
- 6.4.9 Booz Allen Hamilton, Inc.
- 6.4.10 Leidos Holdings, Inc.
- 6.4.11 CACI International Inc.
- 6.4.12 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.13 Palo Alto Networks, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Cisco Systems, Inc.
- 6.4.15 Fortinet, Inc.
- 6.4.16 DXC Technology Company
- 6.4.17 Tyto Athene, LLC
- 6.4.18 Clavister Holding AB
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




