PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836716

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1836716
Exoskeleton - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
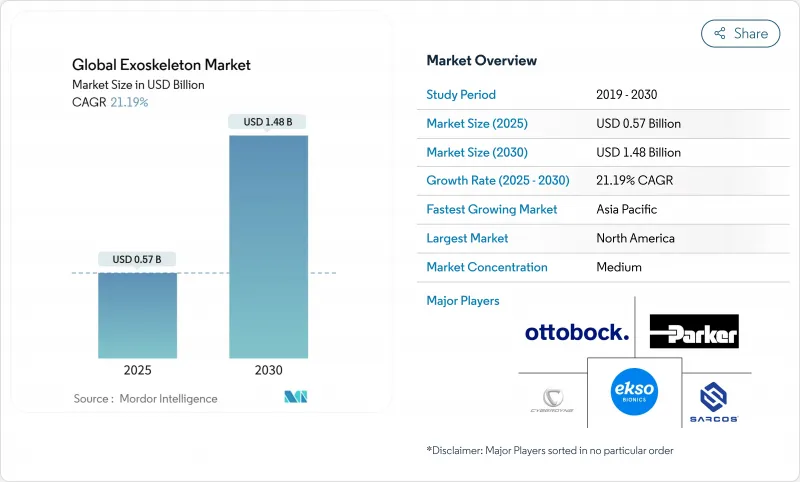
The Global Exoskeleton Market size is estimated at USD 0.57 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.48 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 21.19% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Rapid adoption is unfolding as early medical pilots convert into scaled programs, industrial ergonomics projects expand from single lines to enterprise roll-outs, and defense agencies move prototypes into limited-rate production. Artificial intelligence (AI) embedded within control software is reshaping device responsiveness, with peer-reviewed studies showing up to a 35% cut in back muscle activity during repetitive lifts, a jump that directly lowers injury claims. Parallel gains in lightweight composites, power-to-weight actuators, and battery energy density have trimmed average unit mass by roughly 30%, improving wearer comfort and session duration. The reimbursement breakthrough in the United States Medicare's January 2024 decision to classify personal exoskeletons under the brace benefit has triggered private-payer adoption and influenced similar policy moves in Germany, South Korea, and Japan. Competitive intensity is climbing as software-centric entrants secure design wins; NVIDIA's 2025 decision to place Ekso Bionics in its Connect program signaled that accelerated computing talent is now indispensable for sustained differentiation.
Global Exoskeleton Market Trends and Insights
Accelerating Prevalence of Neuro-Musculoskeletal Disorders Requiring Advanced Assistive Rehabilitation Solutions
Spinal cord injuries affect 294,000 individuals in the United States, with 17,000 new cases added annually, creating a sizeable candidate pool for robotic gait systems, while the share of people aged >= 65 is projected to reach 16% of the global population by 2030, elevating demand for mobility aids.Controlled clinical trials show that early exoskeleton intervention can lift functional recovery by up to 30% versus traditional therapy, underscoring the clinical rationale for rapid roll-out. Health-system administrators are starting to view robotic therapy as a throughput tool: units permit longer, more task-specific sessions with fewer therapists, an outcome that directly expands revenue capacity without proportionate head-count growth. Robust evidence across multiple neurological conditions stroke, multiple sclerosis, traumatic brain injury reinforces payer confidence, smoothing the path toward coverage decisions.
Growing Demand from Healthcare Sector for Robotic Rehabilitation
Hospital groups face chronic staffing gaps as rehabilitation workloads climb; surveys from 2025 show 80% of therapists reporting reduced physical strain and higher throughput when exoskeletons supplement manual assistance. Clinical benchmarking demonstrates 25-40% boosts in post-SCI walking speed after 12 weeks of structured robotic therapy at Sheltering Arms Institute, while stroke patients at BSW Rehabilitation enjoyed 32% better gait symmetry compared with conventional programs. These outcomes support a shift from pilot budgeting to multi-site procurement. Industrial engineering teams in automobile and logistics facilities are piggy-backing on medical proof points, sourcing upper-body units to curb shoulder injuries and overtime payments.
High Capital Expenditure and Maintenance Costs Limiting Widespread Commercial Adoption
List prices range between USD 50,000-150,000, with service contracts adding USD 5,000-10,000 yearly, figures that strain smaller hospitals and mid-sized factories. The return-on-investment case hinges on preventing workplace injuries and shortening inpatient stays; however, constraints in emerging markets, where public budgets dominate spend, suppress unit volumes. Vendors are subsequently pivoting to leasing and robotics-as-a-service models that charge per usage hour, but these schemes remain nascent outside North America.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancement in Robotic Technologies
- Favorable Reimbursement Frameworks Emerging in Developed Healthcare Markets
- Risks Involved with Using Exoskeletons Due to Vague Safety Guidelines
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The powered category captured 84.22% revenue in 2024, benefitting from motor-driven assistance that supports complex gait, stair ascent, and load carriage. It forms the backbone of most rehabilitation protocols and defense prototypes. However, passive devices, such as spring-based braces that offload lower-back strain, are recording a 22.82% CAGR to 2030 as logistics firms deploy hundreds of units in distribution centers. In 2025, peer-reviewed trials confirmed passive lumbar exoskeletons could cut back-extensor activity by 35% during carton handling, bringing them into occupational health budgets. Hybrid designs are emerging: powered hip joints paired with passive spinal supports lower both energy demand and component count, pointing to a mid-term convergence of the two classes.
The cost delta remains pronounced, with passive models retailing for one-third of powered alternatives. Manufacturers leverage advanced composites and elastomeric torsion elements to maintain assistance torque while trimming weight, placing passive lines within stringent procurement caps. As sensors embed directly onto brace frames, passive units are starting to feed ergonomic analytics to enterprise dashboards, closing the data gap with their powered counterparts. These uptake catalysts position the passive cohort to absorb incremental share from budget-sensitive buyers, even as powered systems sustain utility in high-acuity therapy.
Mobile exoskeletons held 68.34% of 2024 global revenue, reflecting their ability to traverse varied terrain and therefore address daily-living independence, warehouse tasks, and infantry maneuvers. Battery innovations lifted operating time to 6-8 hours, 40% longer than older models, supporting full clinic shifts and continuous production cycles. Users cite psychological benefits from eye-level interaction, a factor boosting adherence in home settings. Stationary systems, although smaller today, clock a 24.23% CAGR through 2030 because they deliver high-repeatability training in constrained motor-learning phases. Medical centers position them on gantry frames where therapists fine-tune gait kinematics via augmented-reality overlays, a configuration that accelerates neuroplasticity interventions.
Interchangeable modules allow a single chassis to switch between treadmill-mounted and overground modes, blurring the mobile-stationary divide. This flexibility appeals to mid-sized rehabilitation chains seeking to amortize capital across varied patient cohorts. Vendors are consequently shipping plug-and-play add-ons, such as handrails, harnesses, and treadmill plates, that install without specialist tooling, reducing downtime.
The Exoskeleton Market Report is Segmented by Technology (Powered / Active and Passive), Mobility (Mobile and Stationary), Body Part (Upper Limb, Lower Limb, and Full Body), Component (Hardware, Software and Services), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America captured 40.33% of 2024 exoskeleton market revenue, supported by a mature payer ecosystem and deep venture funding. Medicare's fixed reimbursement rate of USD 91,032 dramatically improved affordability for spinal cord injury patients, lifting device shipments to Veterans Health Administration centers and Level I trauma hospitals. U.S. industrial employers-including automotive assemblers and parcel logistics firms pilot upper-body exosuits to stem injury downtime, and these projects are progressively converting into framework agreements. Canada follows similar trajectories, with provincial workers' compensation boards underwriting pilot programs that assess claims reduction and productivity gains.
Europe ranks second in revenue, anchored by Germany, France, and the Nordics. Germany's BARMER coverage decision encompassed 8.5 million beneficiaries, bringing reimbursed access to nearly half of statutory-insured citizens. Research collaborations thrive under Horizon Europe grants, linking robotics labs in Aachen, Zurich, and Genoa with clinical partners. Industrial uptake is buoyed by strict ergonomic directives; automotive OEMs in Bavaria deploy shoulder-support exoskeletons on production lines to comply with musculoskeletal exposure thresholds. The evolving ExosCE certification path eases product rollout by combining medical and machinery directives into one dossier, shortening approval timelines.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing cluster at 23.78% CAGR through 2030. South Korean manufacturer WIRobotics launched the WIM gait-assist robot in the United States in 2025, highlighting the region's export ambitions mobihealthnews.com. China's Made-in-China 2025 agenda attaches grant incentives to rehabilitation robotics factories, while Japan's ageing demographics funnel public R&D to assistive mobility. Despite pockets of reimbursement uncertainty, industrial customers in electronics and shipbuilding sectors procure lumbar-support suits en masse to curb compensation claims. Public-private partnerships in Singapore and Australia focus on urban ageing initiatives that integrate exoskeletons with smart-home ecosystems.
- CYBERDYNE Inc.
- Ekso Bionics
- Ottobock
- Parker Hannifin
- Sarcos Technology & Robotics Corp.
- ReWalk Robotics
- BIONIK Laboratories Corp.
- Bioservo Technologies
- Gogoa Mobility Robots
- Rehab-Robotics Co. Ltd.
- Bioness Inc. (Bioventus)
- B-Temia
- Myomo Inc.
- Lockheed Martin Corp.
- Seismic Powered Clothing
- RB3D SAS
- Wearable Robotics SRL
- Fourier Intelligence
- Panasonic Corp. (Atoun)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Accelerating Prevalence of Neuro-Musculoskeletal Disorders Requiring Advanced Assistive Rehabilitation Solutions
- 4.2.2 Growing Demand from Healthcare Sector for Robotic Rehabilitation
- 4.2.3 Advancement in Robotic Technologies
- 4.2.4 Favorable Reimbursement Frameworks Emerging in Developed Healthcare Markets
- 4.2.5 AI Integration in Control Systems
- 4.2.6 Lightweight Materials and Battery Efficiency Gains
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Capital Expenditure and Maintenance Costs Limiting Widespread Commercial Adoption
- 4.3.2 Risks Involved with Using Exoskeletons Due to Vague Safety Guidelines
- 4.3.3 Limited Clinical Evidence on Long-Term Efficacy Affecting Payer & Clinician Acceptance
- 4.3.4 Limited Insurance Coverage in Emerging Markets
- 4.4 Technological Outlook
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Technology
- 5.1.1 Powered / Active
- 5.1.2 Passive
- 5.2 By Mobility
- 5.2.1 Mobile
- 5.2.2 Stationary
- 5.3 By Body Part
- 5.3.1 Upper Limb
- 5.3.1.1 Hand Exoskeleton
- 5.3.1.2 Arm Exoskeleton
- 5.3.2 Lower Limb
- 5.3.2.1 Hip
- 5.3.2.2 Knee
- 5.3.2.3 Ankle & Foot
- 5.3.3 Full Body
- 5.3.1 Upper Limb
- 5.4 By Component
- 5.4.1 Hardware
- 5.4.2 Software
- 5.4.3 Services
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 CYBERDYNE Inc.
- 6.3.2 Ekso Bionics Holdings Inc.
- 6.3.3 Ottobock SE & Co. KGaA
- 6.3.4 Parker Hannifin Corp.
- 6.3.5 Sarcos Technology & Robotics Corp.
- 6.3.6 ReWalk Robotics Ltd.
- 6.3.7 BIONIK Laboratories Corp.
- 6.3.8 Bioservo Technologies AB
- 6.3.9 Gogoa Mobility Robots
- 6.3.10 Rehab-Robotics Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.11 Bioness Inc. (Bioventus)
- 6.3.12 B-Temia Inc.
- 6.3.13 Myomo Inc.
- 6.3.14 Lockheed Martin Corp.
- 6.3.15 Seismic Powered Clothing
- 6.3.16 RB3D SAS
- 6.3.17 Wearable Robotics SRL
- 6.3.18 Fourier Intelligence
- 6.3.19 Panasonic Corp. (Atoun)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




