PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842417

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842417
Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Technology - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
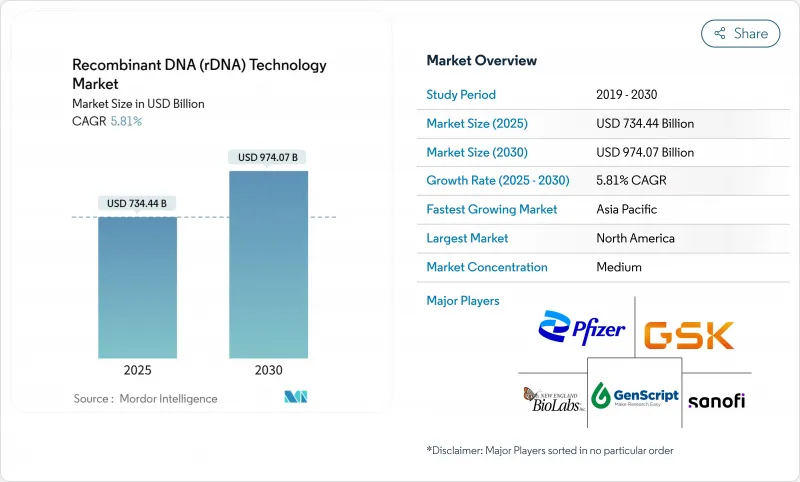
The recombinant DNA technology market reached USD 734.44 billion in 2025 and is projected to climb to USD 974.07 billion by 2030, reflecting a 5.81% CAGR.
Demand for recombinant protein therapeutics, accelerating CRISPR cost declines, and the mainstreaming of AI-enabled protein design continue to re-shape industry economics, lowering entry barriers for smaller innovators while rewarding established firms that modernize production footprints. Falling prices for single-use bioreactors and plasmid micro-factories now let developers pivot between therapeutic and agricultural projects without costly line changeovers, encouraging portfolio expansion into food, feed, and environmental services. North America still anchors financing and early-stage trials, but Asia-Pacific is installing capacity at a faster pace, narrowing historical skill gaps and fostering local supply chains that reduce geopolitical risk for global licensees. Competitive intensity is mounting as pharmaceutical leaders, agricultural majors, and purpose-built gene-therapy CDMOs all vie for the same vector raw materials and regulatory bandwidth.
Global Recombinant DNA (rDNA) Technology Market Trends and Insights
CRISPR-Cas Cost Curve Keeps Falling
Widening access to nuclease-editing kits, cheaper guide-RNA synthesis, and rising vector yields have pushed the fully loaded cost of CRISPR therapies down sharply. CASGEVY's clinical success in sickle cell disease validated the modality, even at an initial price tag near USD 3 million per patient. Aldevron then cut personalized CRISPR manufacturing time to six months, proving cycle-time gains are realistic as supply chains mature. A record 14 US review designations in 2024 signaled that regulators are gaining confidence, shrinking development risk premia. As costs trend lower, developers are pivoting from ultra-rare disease targets toward prevalent disorders, enlarging the recom¬binant DNA technology market addressable pool.
Biopharma Demand for Recombinant Protein Drugs
Novo Nordisk earmarked USD 4.1 billion for a new North Carolina site focused on injectable recombinant proteins, underscoring persistent demand in diabetes and obesity care. Eli Lilly's USD 3 billion Wisconsin investment and Amgen's 35% Q1 2025 biosimilar revenue jump to USD 700 million suggest supply, not demand, is the current bottleneck. Continuous-flow bioreactors and modular single-use lines are lowering minimum efficient scale, letting smaller biotechs commercialize targeted proteins without big-pharma backing, thereby broadening competitive participation in the recombinant DNA technology market.
Evolving Global Gene-Editing Regulations
Fragmented oversight forces developers to navigate multiple dossier formats, parallel clinical protocols, and divergent post-marketing surveillance mandates. The FDA's CoGenT Global pilot seeks alignment, yet Europe's risk-assessment model still differs from US benefit-risk weighting. China is revising its gene-therapy rules, creating uncertainty for foreign license holders even as it speeds pathways for domestic firms. Fifteen-year follow-up requirements in the US stretch the financial stamina of small developers, consolidating power among cash-rich incumbents. Collectively, regulatory divergence slows product launches and raises compliance costs, tempering near-term growth for the recombinant DNA technology market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- GM-Crop Acreage Expansion in Emerging Markets
- AI-Driven De-Novo Protein Design Platforms
- Manufacturing Complexity & CAPEX
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Medical products contributed 65.35% of overall revenue in 2024, anchored by mature therapeutic proteins that benefit from decades of process optimization and well-established reimbursement channels. The therapeutic agents subset keeps momentum through expanding GLP-1 and oncology pipelines, even as biosimilar entrants chip away at legacy monopolies. Vaccines gained new life after COVID-19 validated mRNA platforms; oncology vaccine trials now leverage the same lipid-nanoparticle chassis, cutting preclinical budgets. Outside healthcare, non-medical products are rising at a 12.25% CAGR on the back of GM crops that boost drought tolerance and specialty chemicals that replace petrochemical intermediates. Industrial enzymes now clean textiles at lower temperatures, saving energy and creating recurring royalties for enzyme licensors, an illustration of revenue resilience that cushions cyclicality in drug sales.
Specialty chemicals harness recombinant pathways to produce surfactants and fragrance precursors in fermenters, yielding lower emissions relative to petro-routes and aligning with corporate net-zero pledges. Environmental remediation organisms digest oil slicks and plastic debris, launching entirely new service niches for synthetic-biology startups. This diversification broadens the recombinant DNA technology market, reduces dependence on blockbuster drug lifecycles, and supports steady cash flows across economic cycles.
Expression systems accounted for a 64.53% slice of recombinant DNA technology market share in 2024, reflecting their indispensability across human therapeutics, animal vaccines, and industrial enzymes. Mammalian cell hosts command premium pricing because they perform human-like glycosylation, a must for complex antibodies. Bacterial and yeast lines remain the workhorses for insulin and enzyme production, favored for rapid doubling times and lower media costs. Cloning vectors, growing at 9.85% CAGR, are propelled by surging gene-therapy trials that require high-grade plasmids and viral backbones.
Single-use plasmid micro-factories now fit within standard laboratory footprints, letting hospitals craft personalized vectors for compassionate-use cases. Adeno-associated and lentiviral vectors fetch prices up to USD 200,000 per batch, creating lucrative micro-segments for specialized CDMOs. The spread of distributed manufacturing is especially pronounced in low-volume rare-disease pipelines, where localized production avoids cold-chain delays and alleviates customs bottlenecks.
The Recombinant DNA Technology Market Report is Segmented by Product (Medical [Therapeutic Agents, and More] and Non-Medical), Component (Expression System and Cloning Vector), Application (Food and Agriculture, Health and Disease, and More), End User (Biotech & Pharma Companies, Academic & Govt Institutes, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 37.82% of revenue in 2024, supported by robust venture funding, favorable reimbursement, and FDA frameworks that shorten review cycles for breakthrough therapies. US biomanufacturers benefit from tax incentives and university-laboratory networks that funnel skilled graduates into industry. Canada's investments in gene-therapy incubators add regional diversity, particularly in viral-vector R&D. The recombinant DNA technology market now sees strong state-level competition for capacity, with North Carolina, Massachusetts, and California offering matching grants for facility build-outs.
Asia-Pacific logged the fastest CAGR at 11.81% to 2030, underpinned by China's strategic shift toward Southeast Asian partnerships that secure downstream markets and resilient supply chains. Japan's government has revived biotech stimulus programs, targeting synthetic biology for sustainable chemicals, while South Korea's Chaebol groups co-invest in CDMOs to capture biologics export revenue. India's reform of its Biotechnology Regulatory Authority promises faster clearance for gene-edited crops, strengthening its position as a seed-production hub. Together, these moves are narrowing the historical production gap with Western markets and boosting local availability of recombinant inputs.
Europe balances innovation with consumer skepticism, particularly for GMO foods. The forthcoming EU Pharmaceutical Strategy aims to streamline centralized approvals for advanced therapies, yet crop approvals still face member-state opt-outs. Contract manufacturers in Ireland, Germany, and Switzerland capitalize on this split by offering scale bioreactors for global clients, letting therapy sponsors sidestep local regulatory snags in favor of export-only production. The Middle East and Africa are at a nascent stage but show policy momentum: Saudi Arabia has budgeted sovereign-fund capital for genomics centers, and Ghana's GM cowpea clearance signals a pragmatic stance on food security. South America's soy and corn belts provide fertile ground for GM traits, though macroeconomic volatility can dampen foreign direct investment. These diverse trajectories ensure the recombinant DNA technology market remains geographically plural, reducing concentration risk and enabling cross-border collaboration.
- Amgen
- Eli Lilly and Company
- F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (Genentech)
- Genscript
- Horizon Discovery
- Merck
- New England Biolabs
- Novartis
- Novo Nordisk
- Pfizer
- Sanofi
- Syngene International
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Biogen
- Bayer CropScience (Monsanto)
- Illumina
- Lonza Group
- Agilent Technologies
- Aldevron
- Johnson & Johnson
- GlaxoSmithKline
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 CRISPR-Cas Cost Curve Keeps Falling
- 4.2.2 Biopharma Demand For Recombinant Protein Drugs
- 4.2.3 GM-Crop Acreage Expansion In Ems
- 4.2.4 AI-Driven De-Novo Protein Design Platforms
- 4.2.5 Distributed, Single-Use Plasmid DNA Micro-Factories
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Evolving Global Gene-Editing Regulations
- 4.3.2 Manufacturing Complexity & CAPEX
- 4.3.3 Pharmaceutical-Grade Vector Raw-Material Shortages
- 4.3.4 Consumer Push-Back On Gene-Edited Foods
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.4.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Medical
- 5.1.1.1 Therapeutic Agents
- 5.1.1.2 Human Proteins
- 5.1.1.3 Vaccines
- 5.1.2 Non-medical
- 5.1.2.1 Biotech Crops
- 5.1.2.2 Specialty Chemicals
- 5.1.2.3 Other Non-medical Products
- 5.1.1 Medical
- 5.2 By Component
- 5.2.1 Expression Systems
- 5.2.2 Cloning Vectors
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Food & Agriculture
- 5.3.2 Health & Disease
- 5.3.3 Environment
- 5.3.4 Other Applications
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Biotech & Pharma Companies
- 5.4.2 Academic & Govt Institutes
- 5.4.3 Other End Users
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.2 Eli Lilly & Co.
- 6.3.3 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. (Genentech)
- 6.3.4 GenScript
- 6.3.5 Horizon Discovery
- 6.3.6 Merck KGaA
- 6.3.7 New England Biolabs
- 6.3.8 Novartis AG
- 6.3.9 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 6.3.10 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.11 Sanofi
- 6.3.12 Syngene International
- 6.3.13 Thermo Fisher Scientific
- 6.3.14 Biogen
- 6.3.15 Bayer CropScience (Monsanto)
- 6.3.16 Illumina
- 6.3.17 Lonza Group
- 6.3.18 Agilent Technologies
- 6.3.19 Aldevron
- 6.3.20 Johnson & Johnson
- 6.3.21 GSK plc
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




