PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842515

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842515
Drilling Machines - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Drilling Machines Market was valued at USD 8.37 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 10.88 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.40% CAGR.
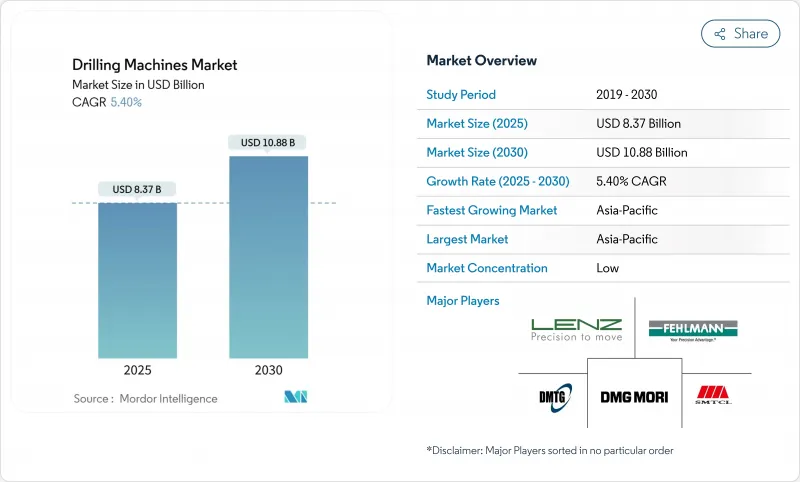
Growth is tied to high-precision, multi-spindle requirements in electric-vehicle battery lines, recovering commercial aerospace output, and expanding wind-turbine component capacity. Continued automation, wider use of lightweight materials, and demand for deep-hole, large-radial formats keep capital expenditures on track even as commodity volatility persists. Rising investments by battery producers, gearbox suppliers, and shipyards sustain equipment backlogs despite short-term procurement hesitancy in oil and gas applications. Major suppliers are broadening retrofit services and digital suites to offset skilled-operator scarcity and differentiate in technically demanding bids.
Global Drilling Machines Market Trends and Insights
Surge in EV & Renewable-Energy Manufacturing Requiring High-Precision Multi-Spindle Drilling
Battery pack assembly now demands sub-micron hole tolerances, pushing cell suppliers to specify multi-spindle systems that can maintain rigidity at elevated throughput. Leading battery groups have integrated closed-loop torque tools and 3-D positioning to control clamp-force variation, lifting annual line capacity while safeguarding electrode alignment. Similar precision thresholds are migrating into solar-tracker mounts and nacelle hubs, where lightweight aluminum sections must be drilled without compromising fatigue performance. Equipment vendors have reacted by hard-mounting vibration sensors in spindle heads and pairing them with edge-computing modules that adjust feed rates in milliseconds. Demand is strongest in the Asia-Pacific corridor, but European gigafactories and North American utility-scale solar yards also seek identical capabilities.
Accelerating Commercial Aerospace Production Boosting Demand for Large Radial Machines
Airframe primes are ramping single-aisle programs back to 60 aircraft per month, renewing tenders for long-reach radial drills that cut titanium frame members in one-setup passes. Five-axis automation and pallet pools allow fuselage sections to move through fewer stations while sustaining 25 µm positional repeatability. Digital twins now feed real-time torque and thrust data to manufacturing execution systems, flagging tool-wear anomalies before rivet misalignment can occur. The approach is critical for sustainability credentials, as material scrap reductions directly lower Scope 3 emissions. North American tier-ones remain the pacesetters, yet EU aerostructure suppliers are mirroring capacity additions to meet backlog recovery targets.
Commodity-Investment Cyclicality Dampening Capital Equipment Orders
Oil-field service firms expand machine-tool fleets when crude averages above breakeven, yet they swiftly defer procurement under price dips. Drilling contractors, therefore, swing between over-capacity and deferred maintenance, creating unpredictable quoting cycles for machine builders. Mid-stream fabrication yards mirror this rhythm, delaying purchase commitments until final investment decisions close. Currency swings add further uncertainty for Latin American miners sourcing dollar-denominated equipment. The result is elongated sales funnels requiring vendors to carry higher working capital in spares and demo fleets to capture short-window orders.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Global Expansion of Wind-Turbine Gearbox Capacity Spurring Deep-Hole Drill Investments
- Rise of On-Site Modular Construction Fueling Portable Magnetic Drill Adoption
- Global CNC-Operator and Machinist Skill Shortage
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Radial machines generated the largest revenue in 2024 on the strength of their versatility across automotive chassis, general machinery, and medium-sized casting work. At a 32.45% share, they anchor production cells that pair vertical mills and turning centers to complete prismatic components in balanced takt flows. Demand remains buoyant as vehicle OEMs still deliver volume models whose steel and iron knuckles fall within radial capacity envelopes. Yet the deep-hole/BTA subset is rising fastest, logging a 6.8% CAGR amid broader adoption in large-bore energy parts, pressure-vessel tube sheets, and aerospace wing spars. Buyers cite lower per-hole cycle times, improved coolant delivery, and automated chip evacuation as reasons for switching.
The niche commands incremental premium margins, given its complex push-pull tooling and tight concentricity specifications. Multinational defense yards and offshore gearbox consortiums opt for gantry configurations able to reclaim heat distortion in-process. Portable magnetic and micro-drill clusters round out the category, feeding electronics and field-service channels with compact units amenable to fast redeployment. These variants, though a smaller slice of the drilling machines market, pioneer sensor fusion and battery modules that later migrate to heavier classes, creating a virtuous technology loop.
Manual rigs still occupy 45.65% of the installed base thanks to low entry costs and simple maintenance. Job-shops handle mixed-lot repair work where fixture turnover outweighs cycle efficiency, preserving the appeal of hand-feed quills and mechanical depth stops. Nevertheless, CNC/automatic systems chart the steepest 7.3% CAGR as large build-to-print houses modernize to meet traceability mandates and mitigate labor gaps. Machine builders bundle code simulation, tool-life dashboards, and shop-floor MES links as standard rather than chargeable add-ons.
Semi-automatic formats form an intermediate tier, marrying hydraulic feeds to operator supervision. They thrive in custom heavy-equipment lines where geometry changes every batch, yet cut depths stay high. Digital retrofits further blur lines; IoT spindle probes mounted on vintage columns broadcast vibration and thrust data to cloud analytics, squeezing extra utilization from sunk assets. Such retrofits enlarge the drilling machines market by inserting subscription software revenue atop hardware already depreciated.
The Drilling Machines Market is Segmented by Type (Radial Drilling Machines, and Others), by Operation (Manual, and Others), by Technology / Power Source (Mechanical, and Others), by End-User Industry (Automotive, and Others), by Work-Piece Material (Metals, and Others), and by Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific captured 46.76% of 2024 revenue and is projected to maintain a robust 7.1% CAGR through 2030. China's machine-tool park continues to swell, propelled by state incentives for domestic CNC controllers that challenge entrenched foreign incumbents. Japanese builders localize component machining across ASEAN to blunt currency risks, while Indian fabrication clusters modernize under Production-Linked Incentive schemes. Rising cell factories, offshore wind yards, and metro-car foundries keep spindle utilization high, lifting service and retrofit opportunities.
North America's installed base remains technologically advanced yet underutilized in commodity down-cycles. Reshoring incentives and clean-energy tax credits now underwrite new composite-capable cells for aerospace stringers and battery-module carriers, brightening order books for high-end builders. Canada's petrochemical plants and U.S. Gulf Coast yards upgrade to hydraulic deep-hole rigs to support LNG expansion, stabilizing the drilling machines market size for heavy-duty formats against cyclic rig counts.
Europe, though mature, pivots toward zero-emission mandates, accelerating the retirement of legacy 3-axis drills in favor of servo-electric gantries with in-line power analyzers. German integrators test predictive greasing algorithms that cut unplanned downtime by 12% on wind-tower flange lines. Southern European shipyards, galvanized by naval-fleet renewal, tender for large-diameter column machines with 6-m stroke capacity to produce bulkhead penetrations in a single pass.
The Middle East and Africa anticipate a 31% uplift in drilling rig demand, translating into yard upgrades in UAE jack-up refurbishments and Saudi fabrication villages aligned with Vision 2030 steel programs. Sub-Saharan rail infrastructure modernizations call for mobile magnetic drills able to process track joints under field conditions. South American prospects center on Brazilian pre-salt developments and Argentine shale growth, which both require tubular dressing shops equipped with high-torque hydraulic drill presses.
- DMG MORI Co. Ltd.
- Mazak Corporation
- Okuma Corporation
- Haas Automation Inc.
- Doosan Machine Tools Co. Ltd.
- Makino Milling Machine Co. Ltd.
- Dalian Machine Tool Group Co. Ltd.
- SMTCL (Shenyang Machine Tool)
- Tongtai Machine & Tool Co. Ltd.
- Hurco Companies Inc.
- ERNST LENZ Maschinenbau GmbH
- Fehlmann AG
- Gate Machinery International Ltd.
- Kaufman Manufacturing Company
- DATRON AG
- Scantool Group
- Taiwan Winnerstech Machinery Co. Ltd.
- Roku-Roku Co. Ltd.
- Hsin Geeli Hardware Enterprise Co. Ltd.
- Minitool Inc.
- LTF SpA*
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surge in EV & Renewable-Energy Manufacturing Requiring High-Precision Multi-Spindle Drilling
- 4.2.2 Accelerating Commercial Aerospace Production Boosting Demand for Large Radial Machines
- 4.2.3 Global Expansion of Wind-Turbine Gearbox Capacity Spurring Deep-Hole Drill Investments
- 4.2.4 Rise of On-Site Modular Construction Fueling Portable Magnetic Drill Adoption
- 4.2.5 Localization Mandates in Defense Shipbuilding Programs Worldwide
- 4.2.6 Upstream Oilfield Revamps Increasing Demand for Heavy-Duty Tooling
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Commodity-Investment Cyclicality Dampening Capital Equipment Orders
- 4.3.2 Global CNC-Operator and Machinist Skill Shortage
- 4.3.3 Substitution by Additive Manufacturing for Complex Geometries
- 4.3.4 High Up-Front Cost of 5-Axis Drilling Centers for Small & Medium Enterprises
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Trends
- 4.7 Manufacturing-Sector Outlook
- 4.8 Industry Attractiveness - Porter's Five Forces
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, In USD Billion)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Radial Drilling Machines
- 5.1.2 Upright/Column/ Pillar Drilling Machines
- 5.1.3 Sensitive/Bench Drilling Machines
- 5.1.4 Gang Drilling Machines
- 5.1.5 Deep-Hole/BTA & Gun Drilling Machines
- 5.1.6 Portable Drilling Machines
- 5.1.7 Turret Drilling Machines
- 5.1.8 Others (Magnetic, Micro/Mini Drilling, Special-Purpose Drilling Machines)
- 5.2 By Operation
- 5.2.1 Manual
- 5.2.2 Semi-Automatic
- 5.2.3 CNC/Automatic
- 5.3 By Technology / Power Source
- 5.3.1 Mechanical/Electric
- 5.3.2 Hydraulic
- 5.3.3 Pneumatic
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive
- 5.4.2 Aerospace & Defense
- 5.4.3 Fabrication & Industrial Machinery
- 5.4.4 Construction
- 5.4.5 Oil & Gas and Energy
- 5.4.6 Electronics & Electricals
- 5.4.7 Shipbuilding & Marine
- 5.4.8 Other End-users (Heavy Equipment, Medical Devices, etc.)
- 5.5 By Work-piece Material
- 5.5.1 Metals
- 5.5.2 Composites, Polymers & Plastics
- 5.5.3 Wood
- 5.5.4 Others (Ceramics, Glass, Concrete, etc.)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Peru
- 5.6.2.4 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, and Luxembourg)
- 5.6.3.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden)
- 5.6.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 Australia
- 5.6.4.5 South Korea
- 5.6.4.6 ASEAN (Indonesia, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia, Vietnam)
- 5.6.4.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Qatar
- 5.6.5.4 Kuwait
- 5.6.5.5 Turkey
- 5.6.5.6 Egypt
- 5.6.5.7 South Africa
- 5.6.5.8 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.9 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 DMG MORI Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Mazak Corporation
- 6.4.3 Okuma Corporation
- 6.4.4 Haas Automation Inc.
- 6.4.5 Doosan Machine Tools Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Makino Milling Machine Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Dalian Machine Tool Group Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.8 SMTCL (Shenyang Machine Tool)
- 6.4.9 Tongtai Machine & Tool Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.10 Hurco Companies Inc.
- 6.4.11 ERNST LENZ Maschinenbau GmbH
- 6.4.12 Fehlmann AG
- 6.4.13 Gate Machinery International Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Kaufman Manufacturing Company
- 6.4.15 DATRON AG
- 6.4.16 Scantool Group
- 6.4.17 Taiwan Winnerstech Machinery Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Roku-Roku Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Hsin Geeli Hardware Enterprise Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Minitool Inc.
- 6.4.21 LTF SpA*
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




