PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842579

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842579
Farm Equipment Rental - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Farm Equipment Rental Market size is estimated at USD 54.8 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 68.5 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.70% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
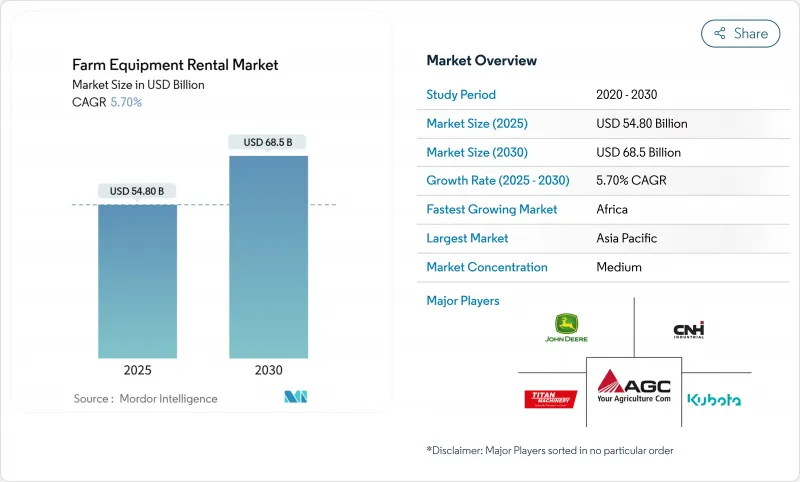
Consistent demand for tractors, rapid growth in digital rental platforms, and targeted government mechanization programs underpin this steady expansion. Asia Pacific prevailing smallholder structure, North America's short but intense harvest windows, and Europe's sustainability regulations shape distinctly regional opportunities. Digital marketplaces that marry AI-driven fleet management with on-demand booking are widening access, while ESG-linked finance is nudging providers toward electric and low-emission fleets. Competition now hinges on utilization analytics, autonomous capabilities, and last-mile service, forcing both OEM-backed dealers and technology-first entrants to refine capital-light, data-rich models for profitable growth.
Global Farm Equipment Rental Market Trends and Insights
Smart-Machinery Cost Inflation Steering Pay-Per-Use
Rising acquisition prices for GPS-enabled tractors and sensor-rich harvesters are widening the affordability gap for Asia Pacific smallholders. Rental demand surged by 35% as average machinery prices climbed 25-30%. India's Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization issued USD 872 million in subsidies between 2014-2024, catalyzing 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers that pool capital-intensive assets for village-level access. These hubs, now pairing IoT fleet monitoring with smartphone booking, let farmers tap precision agriculture without owning depreciating equipment.
Seasonal Workforce Deficit Spurring Autonomous Tractor Rentals
Labor shortages in OECD economies have trimmed the available field workforce by nearly one-fifth, pushing growers toward autonomous tractors available on flexible contracts. Rental fleets outfitted with robotics, LiDAR, and route-planning software cover repetitive tillage and spraying tasks during peak periods, lifting utilization and mitigating wage inflation. Ethical and liability debates around machine-only operations persist, yet real-time diagnostics and geofencing reduce downtime and support compliance with safety mandates.
Low Awareness of Rental Economics Among Sub-Saharan Smallholders
Mechanization rates in many African nations remain below 6% despite mobile-first matching apps. Information asymmetries and risk aversion dampen uptake even when equipment is nearby. Pilot extension programs linking custom hire to crop-insurance premiums are beginning to bridge this gap, but sustained outreach and micro-training remain essential for scale.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- App-Based Fleet Marketplaces Scaling Rapidly in Western Europe
- ESG-Linked Finance Steering Electrified Rental Fleets
- High First-/Last-Mile Logistics Cost in Fragmented APAC Markets
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tractors generated the bulk of revenue in 2024, aided by constant demand across tillage, hauling, and power-take-off applications. Their 38.10% farm equipment rental market share reflects a core role in every fleet and underpins whole-season utilization rates. Harvesters, though representing a smaller slice of the farm equipment rental market, are on track for the fastest 7.40% CAGR as their high sticker prices make short-window rental the only feasible option for many growers. Precision yield mapping and auto-steer controls embedded in newer harvester models raise per-hour value, encouraging providers to introduce outcome-based pricing. Sprayers, balers, and seeders occupy narrower rental windows tied to crop phenology, creating scheduling peaks that digital platforms smooth through predictive demand algorithms. Specialty implements are bundled into multiequipment packages, enhancing basket size and locking in customers for full production cycles.
A second trend is the migration of autonomy from row-crop tractors to harvest machines. Early adopters in North America now seek self-driving combines that cut labor bills during short harvest windows. This shift reshapes depreciation curves, compelling rental firms to recalibrate residual value assumptions and match lease terms to rapid technology refresh cycles. As equipment connectivity deepens, data monetization-yield maps, soil compaction insights, and machine health telemetry-emerges as a secondary revenue line alongside traditional rental income.
Mid-range 71-130 HP tractors anchored 27.40% of the 2024 farm equipment rental market size thanks to an optimal mix of fuel efficiency and capability across small-plot operations. Larger units above 250 HP, though currently niche, are forecast to outgrow all other brackets at 8.50% CAGR as farm consolidation and regulated labor hours favor bigger, smarter machinery. These high-horsepower vehicles command premium day rates and impose stringent transport and maintenance requirements that only full-service providers can meet. Sub-30 HP tractors remain vital for horticulture and tight-row crops, while 131-250 HP models bridge the gap between versatile mid-range and specialized heavy-duty tasks. The power-mix evolution pushes rental firms to diversify fleets, hedge utilization risks, and build dynamic pricing linked to fuel costs and telematics-verified load factors.
In parallel, OEMs embed Tier 4-Final engines and hybrid drivetrains across power classes, meeting tightening emission rules in Europe and California. Providers leveraging ESG-linked loans unlock lower capital costs that filter into competitive hourly rates. Telematics-enabled load tracking is also enabling a shift toward usage-based billing, aligning cost with delivered horsepower hours rather than calendar days.
The Farm Equipment Rental Market is Segmented by Equipment Type (tractors, and More), Power Output (Less Than 30 HP, and More), Drive Type (Two-Wheel Drive and More), Business Model (Offline Dealer & Co-Op Yards and More), End-User Farm Size (Small (less Than 5 Ha) and More), Rental Duration (Short-Term (less Than 3 M) and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD) and Volume (Units).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific generated 44.25% of 2024 revenue for the farm equipment rental market, underpinned by smallholder-oriented subsidy schemes. India's 74,144 Custom Hiring Centers and China's subsidy-linked land tender rules are expanding mechanization without inflating farm debt. Smartphones and vernacular apps embed transparent booking and digital payments, lifting utilization across rice, wheat, and horticulture value chains. Precision hardware costs are still high, so providers use shared ownership structures to amortize technology over broader user bases, keeping per-hectare rental charges affordable.
North America presents a mature yet evolving landscape. Peak harvest in the Corn Belt drives intense, short-term demand for >250 HP tractors and combines, widening price premiums during September-October. Right-to-repair legislation in Colorado and other states now obliges OEMs to furnish diagnostic tools, potentially lowering downtime and rental rates. Autonomous retrofits and electric drivetrains qualify for climate-linked incentives, encouraging fleet renewal among rental giants and regional independents alike.
Europe exhibits pronounced heterogeneity. Western European growers adopt app-based rental to navigate high land prices and strict emission caps. ESG-linked finance reduces borrowing costs for fleets that integrate electric tractors, biofuel harvesters, and low-till implements. The European Green Deal's sustainability targets make rental an attractive compliance pathway, shifting emphasis from asset ownership to outcome-based service. Central and Eastern Europe, still dominated by mid-sized family holdings, balance cost and technology by mixing owned core tractors with rented specialty machines.
- Deere & Company
- CNH Industrial N.V.
- AGCO Corporation
- Kubota Corporation
- Titan Machinery Inc.
- Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. (Trringo)
- Farmease
- JFarm Services
- Pacific AG Rental LLC
- The Pape Group Inc.
- Messick's
- Flaman Group of Companies
- Premier Equipment Rental
- Friesen Sales & Rentals
- Aktio Corporation
- United Rentals (Agricultural Line)
- H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- Kwipped Inc.
- Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Cost-inflation of Smart Machinery Accelerating Pay-per-Use Adoption in Asia Pacific
- 4.2.2 Seasonal Workforce Deficit in OECD Nations Driving Autonomous Tractor Rentals
- 4.2.3 Peak-Harvest Demand Spikes in US Corn-Belt Reinforcing Short-Term Leases
- 4.2.4 Indian CHC-Linked Subsidies Catalyzing Village-Level Rental Hubs
- 4.2.5 App-Based Fleet Marketplaces Scaling Rapidly in Western Europe
- 4.2.6 ESG-Linked Finance Steering Electrified Rental Fleets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Low Awareness of Rental Economics among Sub-Saharan Smallholders
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of Less than 250 HP Units during North-American Harvest Window
- 4.3.3 High First-/Last-Mile Logistics Cost in Fragmented APAC Markets
- 4.3.4 Equipment Misuse Elevating Maintenance Downtime & Liability
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD) and Volume (Units))
- 5.1 By Equipment Type
- 5.1.1 Tractors
- 5.1.2 Harvesters
- 5.1.3 Balers
- 5.1.4 Sprayers
- 5.1.5 Seeders & Planters
- 5.1.6 Tillage & Soil-Cultivation Equipment
- 5.1.7 Other Implements
- 5.2 By Power Output (HP)
- 5.2.1 Less than 30 HP
- 5.2.2 31-70 HP
- 5.2.3 71-130 HP
- 5.2.4 131-250 HP
- 5.2.5 More than 250 HP
- 5.3 By Drive Type
- 5.3.1 Two-Wheel Drive
- 5.3.2 Four-Wheel Drive
- 5.4 By Business Model
- 5.4.1 Offline Dealer & Co-op Yards
- 5.4.2 Online / App-Based Platforms
- 5.5 By End-User Farm Size
- 5.5.1 Small (Less than 5 ha)
- 5.5.2 Medium (5-20 ha)
- 5.5.3 Large (More than 20 ha)
- 5.6 By Rental Duration
- 5.6.1 Short-Term (Less than 3 m)
- 5.6.2 Seasonal (3-9 m)
- 5.6.3 Annual / Long-Term (More than 9 m)
- 5.7 By Geography
- 5.7.1 North America
- 5.7.1.1 United States
- 5.7.1.2 Canada
- 5.7.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.7.2 South America
- 5.7.2.1 Brazil
- 5.7.2.2 Argentina
- 5.7.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.7.3 Europe
- 5.7.3.1 Germany
- 5.7.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.7.3.3 France
- 5.7.3.4 Italy
- 5.7.3.5 Spain
- 5.7.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.7.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.7.4.1 China
- 5.7.4.2 India
- 5.7.4.3 Japan
- 5.7.4.4 South Korea
- 5.7.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.7.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.7.5.2 UAE
- 5.7.5.3 Turkey
- 5.7.5.4 South Africa
- 5.7.5.5 Egypt
- 5.7.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.7.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles
- 6.4.1 Deere & Company
- 6.4.2 CNH Industrial N.V.
- 6.4.3 AGCO Corporation
- 6.4.4 Kubota Corporation
- 6.4.5 Titan Machinery Inc.
- 6.4.6 Mahindra & Mahindra Ltd. (Trringo)
- 6.4.7 Farmease
- 6.4.8 JFarm Services
- 6.4.9 Pacific AG Rental LLC
- 6.4.10 The Pape Group Inc.
- 6.4.11 Messick's
- 6.4.12 Flaman Group of Companies
- 6.4.13 Premier Equipment Rental
- 6.4.14 Friesen Sales & Rentals
- 6.4.15 Aktio Corporation
- 6.4.16 United Rentals (Agricultural Line)
- 6.4.17 H&E Equipment Services Inc.
- 6.4.18 Kwipped Inc.
- 6.4.19 Ashtead Group plc (Sunbelt)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




