PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842587

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842587
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
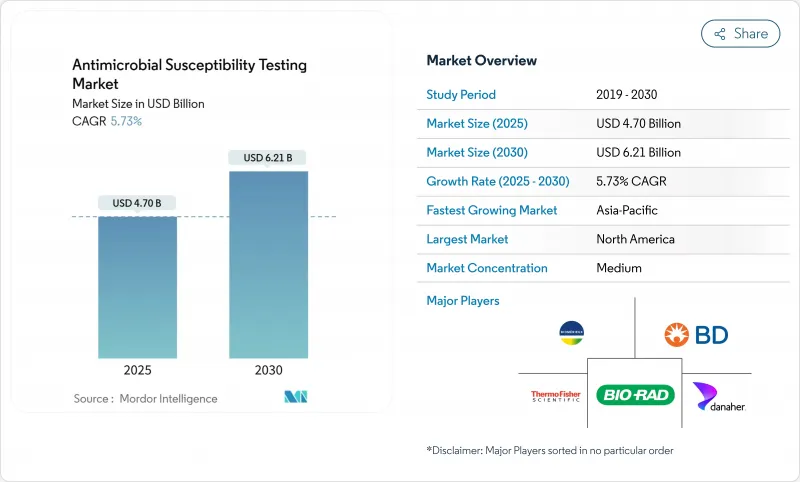
The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Market size is estimated at USD 4.70 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 6.21 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.73% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Growth stems from urgent clinical demand for rapid phenotypic results within 2 hours, rising antimicrobial resistance deaths, and the World Health Organization bacterial priority list that now covers 24 organisms. Laboratory automation, AI-driven analytics, and expanding stewardship mandates support adoption, while pharma integration of coordinated drug-diagnostic development strengthens long-term demand. Asia Pacific offers the fastest regional growth as cost-constrained systems embrace portable platforms and consensus stewardship guidelines. Strategic acquisitions and software-centric offerings suggest intensifying competition among established companies and emerging innovators.
Global Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Market Trends and Insights
Global Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance Escalating Healthcare Burden
Antimicrobial resistance drove USD 66 billion in annual economic losses and is projected to reach USD 159 billion by 2050 under present trends, prompting health systems to fund rapid testing platforms that cut inappropriate prescribing. The WHO target of a 10% annual reduction in bacterial AMR deaths has triggered stewardship programs in 170 nations, with 67% now linking prescribing to susceptibility data. Hypervirulent carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae underscores the demand for platforms that detect virulence and resistance markers in one run. These pressures are acute in regions where projected AMR mortality will rise 68% by 2050, elevating the need for cost-effective point-of-care testing. Hospitals now view rapid AST as a necessary investment that reduces length of stay and improves outcomes.
Pharma and Biotech Adoption of AST in Antibiotic Pipelines
FDA guidance mandates coordinated drug-diagnostic development, pushing antibiotic sponsors to embed AST protocols from preclinical stages. The CARB-X program added USD 10 million in 2024 for diagnostic-therapeutic combinations, reflecting industry conviction that companion AST drives commercial success. Lefamulin approval paired with defined AST methods demonstrates how early diagnostic integration improves regulatory speed. Firms expect earlier resistance monitoring to lift trial success and extend exclusivity through precision labeling. As a result, pharma demand fuels new revenues for platform suppliers.
Fragmented and Stringent Device-Approval Pathways
Companies face divergent requirements across FDA, IVDR, CLSI, and EUCAST frameworks, often adding 12-18 months to European timelines versus the United States. Local studies demanded by India or Brazil further delay launches. AI-enabled platforms require re-validation for each population, raising costs and diverting resources toward high-value markets first. The result is slower roll-out into regions with the highest resistance burden.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Precision-Medicine Push for Pathogen-Specific Therapy
- Rapid Phenotypic AST Devices (<2 H) for Point-of-care
- High Capital Cost and Poor Reimbursement for Analyzers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Manual products continued to dominate with 51.25% of antimicrobial susceptibility testing market share in 2024 owing to disk diffusion and broth microdilution usage in smaller laboratories. Automated instruments are predicted to grow at a 6.98% CAGR as consolidation favors high-throughput and standardized workflows. The segment hierarchy spans consumables, semi-automated, and fully integrated analyzers that cut hands-on time and enhance traceability. Laboratories in high-income countries prioritize full automation to mitigate labor shortages and meet documentation standards. Manufacturers bundle software analytics that flag resistance trends and enable remote support, converting one-off hardware sales into recurring service revenue.
Consumables and reagents generate predictable income as test volumes climb in reference centers. Rapid analyzers delivering sub-2-hour phenotypic results attract critical care units willing to pay premium prices for faster treatment decisions. In emerging markets, semi-automated options balance cost and efficiency, gradually shifting demand toward fully automated lines as capital financing improves. The continued dominance of manual kits in veterinary and public health settings ensures stable baseline demand across the forecast.
The antibacterial category led revenues with 42.43% share yet the antiparasitic segment posts the highest 7.12% CAGR through 2030 as neglected tropical disease programs intensify surveillance. Antifungal testing benefits from multidrug-resistant Candida auris outbreaks in immunocompromised patients. The antiviral niche expands gradually alongside chronic hepatitis and HIV resistance monitoring requirements. Surveillance bodies endorse broader panels that include mycobacterial organisms, although extended incubation periods limit throughput.
Substantial investments in malaria, leishmaniasis, and schistosomiasis control campaigns drive new demand for parasite-specific assays. Laboratories integrate multiplex workflows that consolidate bacterial and fungal tests, boosting consumable utilization. Research funding encourages development of novel panels that detect co-infections and resistance determinants simultaneously, strengthening the antiparasitic business case.
The Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing Market Report is Segmented by Product (Manual AST, Automated AST Instruments, Consumables and Reagents, and Software and Services), Testing Type (Antibacterial, Antifungal, Antiparasitic, and More), Application (Clinical Diagnostics, Drug Discovery and Development, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America controlled 42.95% of 2024 revenue due to sophisticated lab infrastructure and incentive frameworks that speed adoption of new platforms. Europe displays consistent growth supported by harmonized surveillance networks and funding for laboratory upgrades.
The Asia Pacific region, however, is projected to record a 7.33% CAGR through 2030 driven by healthcare expansion and government investment in diagnostic capacity. National AMR action plans in China and India allocate funds for lab automation, while Japan and South Korea embrace AI-enhanced systems that streamline workflows. Southeast Asian nations deploy cost-efficient portable kits to extend stewardship into community settings, creating entry points for new vendors.
South America follows through Brazil's surveillance partnership with the CDC, encouraging platform roll-outs in tertiary hospitals. Economic volatility tempers short-term purchases yet multilateral funding addresses critical gaps. The Middle East and Africa remain under-penetrated but present long-range opportunities as donor programs fund infrastructure and training. Collaboration with international agencies accelerates technology transfer and helps overcome skilled labor shortages.
- bioMerieux
- Beckton Dickinson
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- Danaher
- Merck
- Bio-Rad Laboratories
- HiMedia Laboratories
- Alifax Srl
- Accelerate Diagnostics, Inc.
- Bruker
- QIAGEN
- Liofilchem S.r.l.
- Luminex
- Creative Diagnostics
- Resistell
- T2 Biosystems, Inc.
- Mast Group Ltd.
- Seegene
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Global Spread of Antimicrobial Resistance Escalating Healthcare Burden
- 4.2.2 Pharma And Biotech Adoption of AST in Antibiotic Pipelines
- 4.2.3 Precision-Medicine Push for Pathogen-Specific Therapy
- 4.2.4 Rapid Phenotypic AST Devices (<2 H) for Point-of-care
- 4.2.5 Integration of AI/Cloud Analytics to Scale Laboratory Throughput
- 4.2.6 Low-Cost Portable Kits Unlocking LMIC Stewardship Programs
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fragmented and Stringent Device-Approval Pathways
- 4.3.2 High Capital Cost and Poor Reimbursement for Analyzers
- 4.3.3 Shortage of Trained Microbiologists in Emerging Markets
- 4.3.4 Genotype-Phenotype Discordance n Rapid Molecular AST
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Manual AST
- 5.1.1.1 MIC Strips
- 5.1.1.2 Susceptibility Plates
- 5.1.1.3 Disk Diffusion Kits
- 5.1.1.4 Others
- 5.1.2 Automated AST Instruments
- 5.1.2.1 Semi-automated Systems
- 5.1.2.2 Fully Automated Systems
- 5.1.3 Consumables and Reagents
- 5.1.4 Software and Services
- 5.1.1 Manual AST
- 5.2 By Testing Type
- 5.2.1 Antibacterial
- 5.2.2 Antifungal
- 5.2.3 Antiparasitic
- 5.2.4 Antiviral AST
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Application
- 5.3.1 Clinical Diagnostics
- 5.3.2 Drug Discovery and Development
- 5.3.3 Epidemiology and Surveillance
- 5.3.4 Veterinary Applications
- 5.3.5 Environmental Monitoring
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospital Laboratories
- 5.4.2 Reference Laboratories
- 5.4.3 Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology Companies
- 5.4.4 Academic and Research Institutes
- 5.4.5 Contract Research Organizations (CROs)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 Japan
- 5.5.4.3 India
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 South Korea
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 GCC
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 bioMerieux SA
- 6.3.2 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.3.3 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.4 Danaher Corporation
- 6.3.5 Merck KGaA
- 6.3.6 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- 6.3.7 HiMedia Laboratories
- 6.3.8 Alifax Srl
- 6.3.9 Accelerate Diagnostics, Inc.
- 6.3.10 Bruker Corporation
- 6.3.11 QIAGEN N.V.
- 6.3.12 Liofilchem S.r.l.
- 6.3.13 Luminex Corporation
- 6.3.14 Creative Diagnostics
- 6.3.15 Resistell AG
- 6.3.16 T2 Biosystems, Inc.
- 6.3.17 Mast Group Ltd.
- 6.3.18 Seegene Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet Need Assessment




