PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842700

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1842700
Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) Market size is estimated at USD 1.43 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 2.67 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 13.20% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
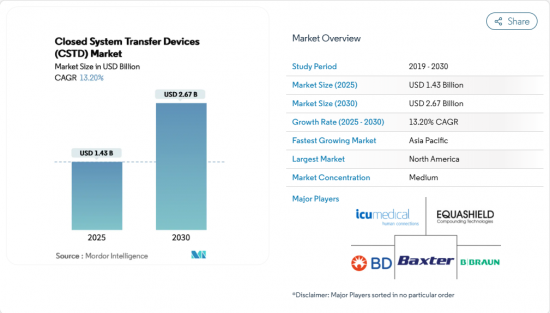
Growth is propelled by stricter occupational-safety rules that now make closed handling mandatory in many hospitals, a steady rise in global chemotherapy volumes, and the widening use of potent biologics that demand airtight containment. Providers that bundle training and environmental-monitoring services with their hardware are capturing multi-year contracts, suggesting that buyers increasingly view CSTDs as part of a broader safety ecosystem rather than stand-alone items. Established players defend share through proprietary connection mechanisms, yet new entrants target underserved regions with lower-cost kits, broadening geographic reach without diluting safety standards. Integrated robotic compounding suites incorporating CSTDs are also gaining traction, as pharmacy leaders seek technology that simultaneously improves accuracy and reduces staff exposure.
Global Closed System Transfer Devices (CSTD) Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Global Chemotherapy Volume from Rising Cancer Incidence
Cancer incidence continues to climb, with 2.04 million new cases projected in the United States alone for 2025. Larger case volumes translate into more infusion sessions, creating a cascade of demand for CSTDs at every preparation bench and bedside. Hospitals now treat higher proportions of older patients, a demographic often prescribed multi-agent regimens that elevate occupational exposure risk per dose. Facilities therefore allocate capital budgets toward devices that promise both vapor and droplet containment, a linkage that now appears in many grant proposals for new oncology wings. One noteworthy shift is that procurement committees increasingly measure proposed device impact not only by exposure data but by projected reductions in staff sick days, aligning safety investments with workforce-planning metrics.
Stricter Occupational Safety Regulations Elevating Hazardous-Drug Handling Standards
USP <800> became compendially applicable in November 2023 and has been adopted by more than 30 states, pivoting hazardous-drug guidance from recommendation to mandate. Similar enforcement traction is visible in provincial Canadian rules and in updated Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) references to hazardous-drug handling. Because regulators can now audit compliance down to product model numbers, purchasing decisions routinely involve the legal or risk-management office, widening the stakeholder pool. That additional scrutiny prompts suppliers to publish third-party containment data in readily digestible dashboards, evidencing a marketing trend that mirrors the regulation's emphasis on measurable performance. An emergent inference is that regulatory pressure indirectly boosts demand for ancillary products such as environmental monitoring swabs, as institutions seek proof of ongoing compliance rather than one-time validation.
High Lifecycle Cost of CSTD Implementation vs Standard IV Components
Full deployment of CSTDs entails acquisition, staff training, workflow redesign, and disposal, creating cost hurdles for smaller clinics. Unlike standard IV components, CSTDs must often be discarded as hazardous waste, which carries higher disposal fees by weight. Hospitals therefore perform cost-avoidance modeling that assigns dollar values to potential worker-exposure incidents, a tactic gaining traction among financial officers. Some systems negotiate volume-based rebates with suppliers, but rural facilities with lower drug throughput lack such leverage, reinforcing an urban-rural adoption divide. An emerging workaround is group purchasing organizations that aggregate demand from distributed clinics, enabling lower per-device pricing and easing entry barriers in resource-constrained settings.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Integration of CSTDs into Automated Compounding & Robotics Platforms
- Expansion of Hazardous Biologics & Immunosuppressants Requiring Closed Handling
- Lack of Universal Performance Standards Causing Procurement Uncertainty
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Needle-less systems hold 64.3% Closed System Transfer Devices market share in 2024, and that dominance roots in their dual benefit of sharps elimination and vapor containment. Hospitals value the simplified credentialing these devices provide because staff already trained on needle-free connectors transition seamlessly to hazardous-drug workflows. A fresh observation is that many institutions now pair needle-less CSTDs with antimicrobial IV ports, seeking a one-stop solution for safety and infection control.
The membrane-to-membrane segment is forecast to grow at a 14.29% CAGR between 2025 and 2030, steadily enlarging its share of the Closed System Transfer Devices market size. Dual-membrane architectures provide redundant seals, a feature especially appealing for high-potency chemotherapy and emerging antibody-drug conjugates. Pharmacy managers increasingly cite vapor-containment data when justifying the higher unit price, showing value analysis committees have adopted containment efficacy as a core metric. This segment's rise indirectly encourages cross-disciplinary collaboration because engineering departments must verify that HVAC pressure relationships support the new workflow.
Luer-Lock devices maintain 38.3% Closed System Transfer Devices market share for 2024, leveraging ISO 80369-7 standardization to plug into existing infusion ecosystems. Many institutions prefer Luer-Lock because it removes retraining costs and simplifies equipment compatibility audits. Yet the ease of twisting connections occasionally produces partial engagement errors in high-volume pharmacies, prompting safety teams to explore alternatives.
Push to Turn Systems are projected to register a 16.12% CAGR through 2030, making them the fastest-expanding subcategory within the Closed System Transfer Devices industry. Furthermore, audible and tactile feedback during locking in Click-to-Lock systems provides real-time confirmation, reducing incidence of mis-threaded connections during peak workload periods. A complementary trend is the rise of color-coded Click-to-Lock variants that visually align mating parts, an ergonomic twist that supports situational awareness in dimly lit chemotherapy units. Procurement data reveal that these intuitive connectors cut setup time per dose, allowing pharmacists to reallocate saved minutes toward verification tasks.
The CSTD Market Report is Segmented by System Type (Needle-Less Systems, and Membrane-To-Membrane Systems), Closing Mechanism (Color To Color Alignment Systems, Luer-Lock Systems, and More), Component (Syringe Safety Devices, Vial Access Devices, and More), Technology (Compartmentalized Devices, and More), End-User (Hospitals, Oncology Centers, and Others) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's 43.5% share of the Closed System Transfer Devices market in 2024 is anchored by robust enforcement of USP <800> and updated NIOSH hazardous-drug lists. U.S. hospital groups often tie CSTD investments to broader antimicrobial stewardship programs, linking chemical isolation with infection-control metrics. Canada follows a similar trajectory but exhibits provincial variation that encourages vendors to customize rollout timelines province by province. Mexico's private oncology clinics, stimulated by cross-border patient flows, increasingly mirror U.S. safety protocols to attract international clientele. US-based group purchasing organizations extend favorable contract pricing across the continent, harmonizing access and accelerating penetration.
Europe ranks second by revenue, with its Closed System Transfer Devices industry shaped by the European Union's Carcinogens and Mutagens Directive, which classifies hazardous drugs as occupational carcinogens. Countries such as Germany and France mandate surface contamination monitoring, so hospitals often integrate CSTD deployment into multi-year capital projects that include new clean-room construction. Eastern European clinics tap into EU structural funds to finance CSTD adoption, thereby narrowing a historical safety gap with Western counterparts. Brexit has introduced separate regulatory paths for the United Kingdom, yet most NHS trusts converge on ISO standards, sustaining cross-channel product interchangeability. A discernible pattern is that European tenders increasingly specify device reusability counts, reflecting environmental priorities under the EU Green Deal.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing geography, projected to compound at 15.23% annually through 2030 as cancer incidence rises and hospital infrastructure expands. China's new provincial cancer centers include CSTD budgets in their master plans, signaling that the technology is perceived as a baseline requirement rather than a premium add-on. Japan's mature health system prioritizes low-dead-space designs to minimize wastage of high-cost biologics, illustrating how reimbursement pressure shapes technical preference. India's metro hospitals pilot low-cost CSTD variants while rural centers experiment with rental models that bundle device supply with disposal services, revealing adaptive business strategies to match heterogeneous purchasing power. Across Asia-Pacific, device makers often partner with local distributors that handle language-specific labeling and training, shortening the adoption curve.
- Beckton Dickinson
- ICU Medical
- B. Braun
- Equashield LLC
- Baxter
- Corvida Medical
- Simplivia Healthcare
- Yukon Medical LLC
- JMS Co., Ltd.
- CODAN Medizinische Gerate
- Vygon
- Terumo Corp.
- Fresenius
- Pfizer (Hospira) Inc.
- Caragen
- Gerresheimer AG (Sensile Medical AG)
- Halyard Health
- Bespak
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating Global Chemotherapy Volume from Rising Cancer Incidence
- 4.2.2 Stricter Occupational Safety Regulations Elevating Hazardous-Drug Handling Standards
- 4.2.3 Integration of CSTDs into Automated Compounding & Robotics Platforms
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Hazardous Biologics & Immunosuppressants Requiring Closed Handling
- 4.2.5 Growing Adoption of Comprehensive Safety-Culture Programs in Healthcare Systems
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Lifecycle Cost of CSTD Implementation vs Standard IV Components
- 4.3.2 Lack of Universal Performance Standards Causing Procurement Uncertainty
- 4.3.3 Compatibility Challenges with Legacy IV & Infusion Infrastructure
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By System Type
- 5.1.1 Needle-less Systems
- 5.1.2 Membrane-to-Membrane Systems
- 5.2 By Closing Mechanism
- 5.2.1 Color-to-Color Alignment Systems
- 5.2.2 Luer-Lock Systems
- 5.2.3 Push-to-Turn Systems
- 5.2.4 Click-to-Lock Systems
- 5.3 By Component
- 5.3.1 Syringe Safety Devices
- 5.3.2 Vial Access Devices
- 5.3.3 Bag Access Devices
- 5.3.4 Other Accessories
- 5.4 By Technology
- 5.4.1 Compartmentalized Devices
- 5.4.2 Diaphragm-based Devices
- 5.4.3 Air-Filtration Devices
- 5.5 By End-User
- 5.5.1 Hospitals
- 5.5.2 Oncology Centers
- 5.5.3 Others
- 5.6 Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Becton, Dickinson & Co.
- 6.3.2 ICU Medical, Inc.
- 6.3.3 B. Braun Melsungen AG
- 6.3.4 Equashield LLC
- 6.3.5 Baxter International Inc.
- 6.3.6 Corvida Medical
- 6.3.7 Simplivia Healthcare
- 6.3.8 Yukon Medical LLC
- 6.3.9 JMS Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.10 CODAN Medizinische Gerate
- 6.3.11 Vygon SA
- 6.3.12 Terumo Corp.
- 6.3.13 Fresenius Kabi AG
- 6.3.14 Pfizer (Hospira) Inc.
- 6.3.15 Caragen Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Gerresheimer AG (Sensile Medical AG)
- 6.3.17 Halyard Health
- 6.3.18 Bespak
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




