PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844514

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844514
Geofoams - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Geofoams Market size is estimated at USD 1.04 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 1.41 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.23% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
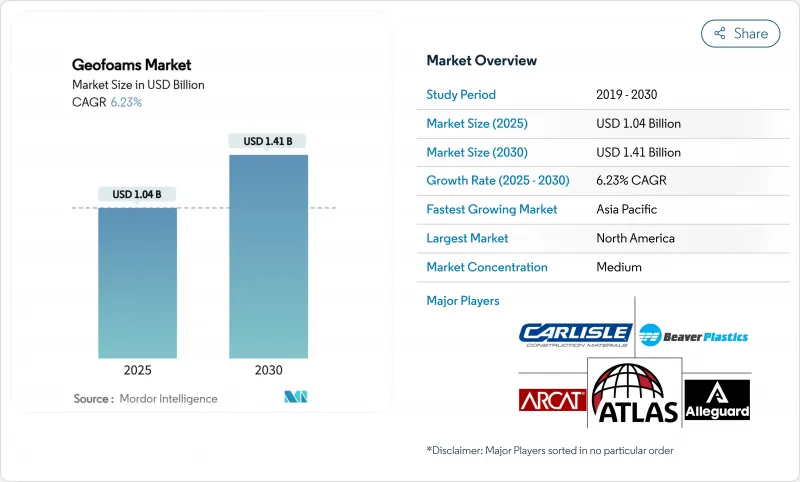
Infrastructure renewal, lightweight construction trends and growing sustainability mandates collectively underpin demand, while expanded and extruded polystyrene technologies redefine conventional earth-fill approaches. Accelerated capital expenditure on highways, bridges and urban transit systems in Asia-Pacific and North America is translating directly into larger bid volumes for geofoam blocks, especially where weak soils or seismic risk constrain traditional backfills. Design-build contractors increasingly value geofoam's factory-controlled consistency and fast installation times, reducing lane-closure periods on heavily trafficked corridors. Meanwhile, heightened regulatory interest in embodied-carbon disclosure is elevating the material's lifecycle cost advantages relative to granular fills. Competitive differentiation now hinges on vertical integration into polystyrene supply, recycled-content development and fire-retardant chemistry.
Global Geofoams Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand from Roadway & Bridge Embankments
Transportation agencies are turning to geofoam blocks to mitigate differential settlement, shorten construction schedules and avoid costly ground-improvement programs. Colorado's emergency highway repair demonstrated 30% schedule compression when geofoam replaced traditional earthwork. Norwegian highway projects show 100-year durability across 350 installations, proving the material's resilience under freeze-thaw cycles. Bridge approach ramps gain particular benefit, maintaining geometry over weak soils without deep foundations. The 1% density versus soil allows traffic to reopen days, not weeks, after placement. Long-term monitoring confirms load distribution that matches design models during seismic and thermal events.
Cost-Effective Alternative to Traditional Lightweight Fills
Geofoam's attraction extends beyond unit price. Prefabricated blocks bypass on-site mixing and curing, trimming labor hours by up to 40% in slope repair works. Transport savings are pronounced where aggregate sources lie hundreds of kilometers away. Because blocks can be manually maneuvered, smaller crews and lighter equipment reduce fuel and rental costs. Factory-controlled density and compressive strength slash quality-assurance outlays tied to field-mixed solutions. Together, these attributes reposition project budgets, freeing capital for ancillary scope such as drainage upgrades.
High Vulnerability to Petroleum Solvents & Hydrocarbons
Polystyrene's affinity for hydrocarbon solvents constrains deployment near fuel handling zones. NOAA's chemical database cites rapid volumetric loss when EPS contacts gasoline, necessitating HDPE geomembrane barriers that add 5-10% to installed cost. Roadways with high spill risk must incorporate monitoring wells and contingency liners, complicating designs. Industrial storage yards face similar exposure, pushing specifiers toward alternative fills or composite encapsulation systems. Although coating technologies are advancing, long-term field validation remains limited, keeping designers cautious in critical facilities.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surging Infrastructure CAPEX in Asia-Pacific
- Accelerated Modular Bridge Programs Using EPS Geofoam Blocks
- Stricter Fire-Resistance Standards Driving Cost Up
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Expanded polystyrene retained 65.12% of geofoams market share in 2024, while extruded polystyrene is forecast to grow at a 6.58% CAGR to 2030. EPS thrives in cost-sensitive roadway embankments where volume rules procurement strategies, sustaining the overall geofoams market. Yet XPS's lower water absorption and superior compressive strength satisfy bridge, tunnel and cold-climate foundations demanding long service life. DuPont tests reveal XPS can deliver the same thermal R-value with 30-40% thinner sections, appealing to designers seeking subgrade insulation without over-excavation.
Production economics illustrate why EPS dominates volume: steam expansion uses less energy and input styrene, keeping unit costs 15-20% below XPS. Conversely, XPS's continuous extrusion yields uniform cell size that resists creep, supporting premium applications where design life exceeds 75 years. Recycling infrastructure favors EPS because block off-cuts can be readily granulated and steamed into new beads, whereas XPS re-extrusion demands stricter melt-filtering. Looking forward, municipalities with aggressive green-building codes may tilt share further toward XPS as moisture durability lessens maintenance budgets, but EPS will stay entrenched in large-scale bulk fills owing to its price advantage.
The Geofoams Market Report is Segmented by Type (Expanded Polystyrene (EPS), Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)), End-User Industry (Roadways, Buildings), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 35.19% of global revenue in 2024, underpinned by extensive highway rehabilitation and stringent settlement-control criteria in bridge approaches. Projects in Colorado, Minnesota and Ontario testify to lifecycle cost savings once differential settlement is curtailed. Canadian Arctic corridors leverage geofoam's insulating value to stabilize permafrost, preventing thaw settlement beneath runways and pipelines.
Asia-Pacific is projected to expand at a 6.92% CAGR to 2030, the fastest globally, on the back of USD 1.7 trillion yearly infrastructure needs. Mega-rail corridors in China and India favor geofoam to manage weak alluvial soils without deep excavation. Japanese seismic codes reward lightweight fills that reduce inertial loads, while South Korean expressways have standardized EPS blocks for ramp widening projects.
Europe demonstrates steady adoption driven by circular-economy mandates and coastal climate challenges. Germany and France integrate recycled-content geofoam into flood-defense works, aligning with EU waste-reduction targets. The United Kingdom's smart-motorway upgrades specify geofoam to minimize closure times, supporting contractor incentives tied to user delay cost savings. Nordic countries capitalize on three decades of field data validating geofoam resilience in sub-zero conditions, reinforcing public trust and regulatory approval for expanded use.
- Airfoam
- Alleguard
- ARCAT, Inc.
- Atlas Roofing Corporation
- BASF SE
- Beaver Plastics Ltd.
- Benchmark Foam Inc.
- Carlisle Construction Materials LLC
- FMI-EPS LLC
- Harbor Foam Inc.
- NOVA Chemicals Corporate
- Plasti-Fab Ltd
- Poly Molding LLC
- Styro Insulations Mat. Ind. LLC.
- ThermaFoam, LLC
- Universal Foam Products
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising demand from roadway and bridge embankments
- 4.2.2 Cost-effective alternative to traditional lightweight fills
- 4.2.3 Surging infrastructure CAPEX in Asia-Pacific
- 4.2.4 Accelerated modular bridge programs using EPS geofoam blocks
- 4.2.5 Circular-economy push for recycled-EPS geofoam reuse
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High vulnerability to petroleum solvents and hydrocarbons
- 4.3.2 Limited design know-how in emerging economies
- 4.3.3 Stricter fire-resistance standards driving cost up
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
- 5.1.2 Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Roadways
- 5.2.2 Buildings
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.3.5.3 South Africa
- 5.3.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.3.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airfoam
- 6.4.2 Alleguard
- 6.4.3 ARCAT, Inc.
- 6.4.4 Atlas Roofing Corporation
- 6.4.5 BASF SE
- 6.4.6 Beaver Plastics Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Benchmark Foam Inc.
- 6.4.8 Carlisle Construction Materials LLC
- 6.4.9 FMI-EPS LLC
- 6.4.10 Harbor Foam Inc.
- 6.4.11 NOVA Chemicals Corporate
- 6.4.12 Plasti-Fab Ltd
- 6.4.13 Poly Molding LLC
- 6.4.14 Styro Insulations Mat. Ind. LLC.
- 6.4.15 ThermaFoam, LLC
- 6.4.16 Universal Foam Products
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




