PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844538

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844538
Brewing Enzymes - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The global brewing enzyme market size reached USD 555.37 million in 2025 and is projected to expand to USD 802.51 million by 2030, registering a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.64%.
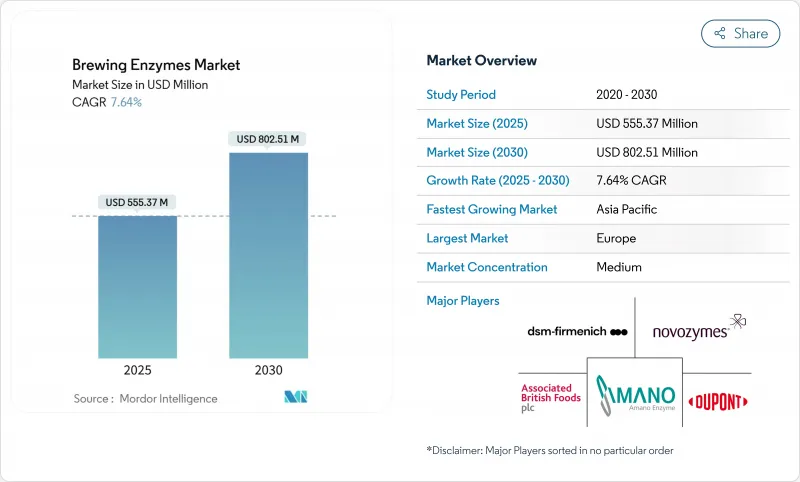
This growth trajectory reflects the industry's accelerating shift toward precision fermentation technologies and sustainable brewing practices, with enzymes becoming indispensable for optimizing yield while reducing environmental footprint. The market's expansion is particularly driven by the craft brewing revolution and the rising demand for specialty beers, including gluten-free and low-alcohol variants that require sophisticated enzymatic solutions. The market is mainly driven by the increase in demand for beer and alcoholic beverages among consumers, which has resulted in an increased number of independent breweries, microbreweries, and brewpubs on a global level. However, regulations in the brewing industry by regulatory bodies such as the FDA, USDA, and EU are the major challenge that is restraining the market growth.
Global Brewing Enzymes Market Trends and Insights
Rising Demand for Craft and Artisanal Beer Worldwide
Craft brewing requires different enzymes compared to industrial brewing, creating opportunities for specialized enzyme suppliers to charge premium prices. Small-batch production needs precise fermentation control, leading to increased use of targeted enzyme solutions that maintain consistent quality despite varying ingredients. These solutions help craft brewers overcome challenges related to raw material inconsistencies and seasonal variations in ingredient quality. The USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture has supported research on sustainable hop breeding and yeast contamination prevention, acknowledging craft brewing's economic importance. This research focuses on developing resilient hop varieties and improving quality control measures in craft brewing operations. Craft brewers use enzymes to develop distinct flavor profiles while optimizing production efficiency, as precision fermentation reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional methods. The adoption of enzymatic solutions allows brewers to achieve specific taste characteristics, improve yield, and maintain batch-to-batch consistency. This enables enzyme suppliers to increase profits through combined product sales and technical consulting services, particularly by offering customized enzyme formulations and process optimization guidance.
Increasing Adoption of Enzymes in High Gravity Brewing
High gravity brewing allows breweries to optimize facility usage by producing concentrated worts that are later diluted, which changes the enzyme requirements for starch conversion and protein modification. This brewing method involves creating a more concentrated beer during the brewing process and then diluting it to the desired alcohol content before packaging. The process reduces equipment, labor, and energy costs while increasing production capacity without requiring additional fermentation tanks or storage space. DSM-Firmenich's Maxadjunct B L enzyme targets high-gravity brewing applications, enabling brewers to use local adjuncts while reducing energy consumption. The enzyme technology helps break down complex carbohydrates more efficiently during the brewing process, improving overall yield and consistency. This enhanced efficiency results in shorter brewing cycles and reduced water consumption per unit of beer produced. This technology is valuable in emerging markets where raw material costs vary significantly, as enzymes allow brewers to replace malted barley with alternative carbohydrate sources such as corn, rice, or other locally available grains. The flexibility in raw material selection helps breweries maintain production costs while ensuring consistent product quality despite market fluctuations in ingredient prices. Additionally, the use of local adjuncts supports regional agricultural economies and reduces transportation-related costs and environmental impact.
Regulatory Differences Across Countries
The regulatory landscape for enzymes varies significantly between regions. The European Union requires extensive safety documentation for pre-market approval under Regulation EC No 1332/2008, while the United States follows the FDA's GRAS (Generally Recognized as Safe) notification process. The USDA's National Bioengineered Food Disclosure Standard requires labeling of bioengineered foods, which may influence consumer acceptance in GMO-sensitive markets. These regulatory requirements create substantial barriers for companies seeking to enter multiple markets simultaneously. Regulatory harmonization remains challenging due to fundamental differences in safety assessment approaches - the US evaluates product characteristics, while the EU focuses on production processes. These regulatory differences require enzyme manufacturers to maintain distinct product portfolios and documentation systems. The need for separate compliance processes increases operational complexity and resource requirements for companies. As a result, manufacturers face higher compliance costs and longer market entry periods when expanding their geographical presence.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Consumer Popularity of Gluten-Free and Low-Calorie Beers
- Expanding Microbrewery and Home Brewing Culture
- Flavor Inconsistencies Caused by Overuse or Misuse of Enzymes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Amylase enzymes hold a 37.74% market share in 2024, due to their essential function in starch conversion during the mashing process. Beta glucanase represents the fastest-growing segment with an 8.05% CAGR through 2030. The growth in beta-glucanase adoption reflects brewers' emphasis on improving filtration efficiency and beer clarity, as these enzymes break down beta-glucans that increase viscosity and impede filtration. For example, Biocatalysts Ltd's DELTABREW(R) liquid beta-glucanase targets viscosity reduction and enhances beer filtration. Protease enzymes play important roles in protein modification and foam stability, while AlphaLase provides additional amylolytic activity for specific brewing needs.
The brewing enzyme market is moving toward specialized applications as the industry becomes more sophisticated. Brewers now seek targeted enzyme solutions instead of general enzyme blends. Additional enzyme types, including lipases and cellulases, serve specific functions such as flavor development and adjunct processing, enabling specialized suppliers to implement premium pricing strategies. This transition to precise enzyme applications supports sustainability objectives by reducing raw material waste and energy consumption in brewing operations.
Microbial enzymes hold 73.58% market share in 2024 and are projected to grow at 8.74% CAGR through 2030. This dominance stems from the biotechnology industry's shift toward fermentation-based production instead of traditional plant extraction methods. The precision fermentation process ensures consistent enzyme quality and allows property customization through metabolic engineering, meeting the brewing industry's requirements for reliable performance across operating conditions. Plant-based enzymes remain vulnerable to agricultural variations and seasonal availability, making microbial enzymes the preferred choice for large-scale brewing operations.
The use of genetically engineered microorganisms enables the production of enzymes with improved thermostability and pH tolerance, addressing specific brewing challenges including high-temperature mashing and acidic fermentation conditions. Microbial enzyme production reduces land use and water consumption compared to plant-based methods, supporting brewing industry sustainability goals. The production costs decrease with increased volume, making microbial enzymes economically advantageous for large brewing operations.
The Brewing Enzymes Market is Segmented Into Type (Amylase, Alphalase, Beta Glucanase, Protease, and Others), Source (Microbial and Plant), Form (Dry and Liquid), Application (Wine and Beer), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Report Offers the Market Size in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Europe maintains a 33.47% market share in 2024, built on established brewing traditions and regulatory frameworks that support enzyme adoption. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) implements clear enzyme approval processes while upholding safety standards that build consumer trust. Major brewers, including Diageo, Carlsberg, AB Inbev, and Heineken, incorporate sustainability initiatives that increase enzyme usage to minimize energy and water consumption.
The Asia-Pacific brewing enzymes market projects a 9.04% CAGR through 2030, supported by economic growth and rising consumer demand for premium alcoholic beverages. China's brewing industry modernization creates opportunities for enzyme suppliers as brewers adopt international quality standards. India's growing middle class requires enzyme solutions to address raw material variations and maintain beer quality. Japan's brewing sector provides opportunities for enzyme applications in premium products. The region's diverse brewing methods, including rice-based and tropical fruit fermentation, require specialized enzyme solutions. Regional producers Angel Yeast Co. Ltd. and Jiangsu Boli Bioproducts compete with global suppliers through localized products and technical support.
North America's brewing market focuses on innovation and craft brewing development, backed by the USDA's National Institute of Food and Agriculture's research in sustainable hop breeding and yeast contamination prevention. The craft brewing segment requires specific enzyme solutions for unique flavor profiles and efficient small-batch production. Latin America, the Middle East, and Africa markets show growth potential as brewing infrastructure develops and regulations evolve. Market expansion in these regions relies on economic advancement, infrastructure improvement, and increased consumer awareness of premium beer quality, creating opportunities for enzyme suppliers focused on market development and technical support.
- Amano Enzyme Inc.
- Novozymes A/S
- Koninklijke DSM-Firmenich NV
- DuPont (IFF Biosciences)
- AB Enzymes (Groupe ABF)
- Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- Kerry Group plc
- BASF SE (BASF Enzymes)
- Lallemand Inc.
- Caldic B.V.
- Soufflet Biotechnologies (InVivo)
- Dyadic International Inc.
- Biocatalysts Ltd.
- Angel Yeast Co. Ltd.
- Leveking (Jiangsu) Bio-Engineering
- Jiangsu Boli Bioproducts
- Aumgene Biosciences
- Amano Enzyme USA
- Soufflet Malterie (enzyme blends)
- Megazyme Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Demand for Craft and Artisanal Beer Worldwide
- 4.2.2 Increasing Adoption of Enzymes in High Gravity Brewing
- 4.2.3 Cunsumer Popularity of Gluten-Free and Low-Calorie Beers
- 4.2.4 Expanding Microbrewery and Home Brewing Culture
- 4.2.5 Surge in Demand for Lager and Light Beers in Emerging Markets
- 4.2.6 Flavor Innovation Through Controlled Enzymatic Conversion
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory Differences Across Countries
- 4.3.2 Flavor Inconsistencies Caused by Overuse or Misuse of Ezymes
- 4.3.3 Potential Allergen Concern in Genetically Engineered Enzymes
- 4.3.4 Environmental Sensitivity of Enzymes Reducing Shelf Life
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE & GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Amylase
- 5.1.2 Alphalase
- 5.1.3 Beta Glucanase
- 5.1.4 Protease
- 5.1.5 Other Types
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Microbial
- 5.2.2 Plant
- 5.3 By Form
- 5.3.1 Dry
- 5.3.2 Liquid
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Beer
- 5.4.2 Wine
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 United States
- 5.5.1.1 Canada
- 5.5.1.2 Mexico
- 5.5.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 Spain
- 5.5.2.4 France
- 5.5.2.5 Italy
- 5.5.2.6 Russia
- 5.5.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 United States
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Amano Enzyme Inc.
- 6.4.2 Novozymes A/S
- 6.4.3 Koninklijke DSM-Firmenich NV
- 6.4.4 DuPont (IFF Biosciences)
- 6.4.5 AB Enzymes (Groupe ABF)
- 6.4.6 Chr. Hansen Holding A/S
- 6.4.7 Kerry Group plc
- 6.4.8 BASF SE (BASF Enzymes)
- 6.4.9 Lallemand Inc.
- 6.4.10 Caldic B.V.
- 6.4.11 Soufflet Biotechnologies (InVivo)
- 6.4.12 Dyadic International Inc.
- 6.4.13 Biocatalysts Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Angel Yeast Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Leveking (Jiangsu) Bio-Engineering
- 6.4.16 Jiangsu Boli Bioproducts
- 6.4.17 Aumgene Biosciences
- 6.4.18 Amano Enzyme USA
- 6.4.19 Soufflet Malterie (enzyme blends)
- 6.4.20 Megazyme Ltd.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




