PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844567

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1844567
Zeolite Molecular Sieves - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
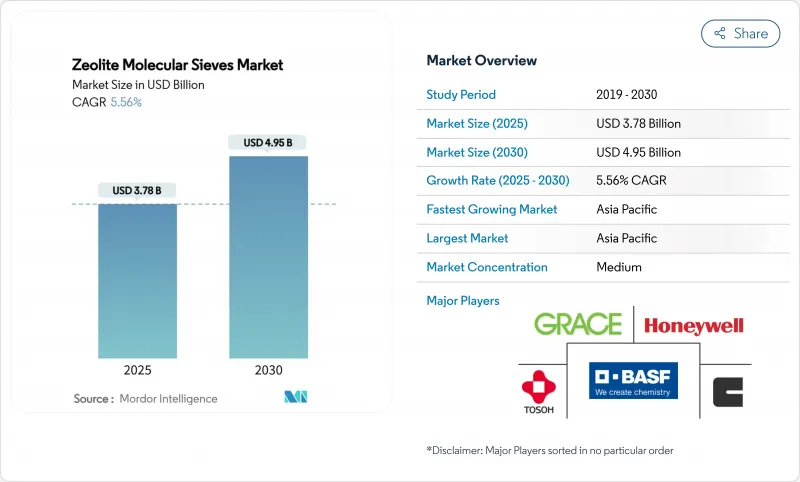
The Zeolite Molecular Sieves Market size is estimated at USD 3.78 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 4.95 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 5.56% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Demand growth is anchored in four structural forces: tightening environmental regulations that substitute phosphates in detergents, capacity additions across global petrochemical complexes, rapid urbanization in emerging economies that drives hygiene product uptake, and the accelerated pursuit of low-carbon industrial processes that favor zeolite-based adsorption and catalysis. Competitive differentiation rests on proprietary synthesis know-how that tailors pore size, silica-to-alumina ratio, and crystal morphology to specific separation or catalytic duties. Cost volatility in alumina and high-purity silica feedstocks poses a margin challenge, but circular feedstock strategies, especially the conversion of coal fly ash and other industrial residues, are mitigating raw-material risk while supporting corporate sustainability goals. Breakthrough deployments in carbon-capture and PFAS remediation are expanding the commercial frontier, positioning advanced zeolite formulations as viable alternatives to activated carbon and amine solvents in next-generation environmental systems
Global Zeolite Molecular Sieves Market Trends and Insights
Phosphate Bans in Detergents Shifting Builders to Zeolites
Global detergent regulations prohibit phosphates because of eutrophication risks, redirecting builder demand toward zeolite 4A. The European Union's 2017 ban eliminated 2.5 million tons of phosphate consumption annually, and zeolites now replace roughly 60% of that volume in both powder and liquid formulations. Similar mandates in North America, along with phased restrictions in India and Brazil, sustain predictable volume growth. Performance advantages compound the regulatory pull: zeolite 4A exhibits higher calcium-binding capacity than carbonates, securing wash performance in hard-water regions. Multinational detergent brands have embedded zeolite builders across their global portfolios, making a reversal technically and commercially unlikely. Emerging economies are poised to expand phosphate-free regulations through 2027, reinforcing the long-run demand trajectory for the zeolite molecular sieve market.
Petrochemical Dehydration and Gas-Purification Boom
Investment exceeding USD 50 billion in new ethylene and propylene complexes across China, India, and Saudi Arabia is elevating demand for 3A and 4A molecular sieves that dehydrate cracked gas and strip CO2 to parts-per-million levels. A single world-scale ethylene cracker consumes 500-800 tons of sieves in initial charging and annual top-ups. Shale-gas growth in North America accelerates the trend, because unconventional feedstocks carry higher moisture and acid-gas loads. Recent synthesis advances have produced larger zeolite crystals with enhanced mass-transfer characteristics, cutting regeneration energy by 25% and reducing lifecycle cost for petrochemical operators. Consequently, the zeolite molecular sieve market is poised to capture incremental offtake from greenfield projects and from revamps that target higher purity specifications.
Enzyme and Chemical Substitutes in Laundry Formulations
Premium detergent brands increasingly favor protease and lipase enzymes that deliver comparable soil removal at lower builder dosage, cutting zeolite content by up to 20% in liquid formats. Polycarboxylate and phosphonate builders disperse easily in concentrated liquids, where zeolite's insolubility complicates processing and packaging. As liquid detergents represent the fastest-growing category in developed markets, zeolite volumes risk erosion in the top-tier segment. Yet powder detergents and value-priced products, particularly in emerging economies, still depend on zeolite 4A for hardness control, mitigating the overall impact on the zeolite molecular sieve market.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Stringent Wastewater Discharge Norms
- Hygiene-Driven Detergent Demand in Emerging Economies
- Volatile Alumina/Silica Feedstock Pricing
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Synthetic zeolite A captured 57.89% of global volume in 2024 thanks to precise Si/Al control that engineers pore size for petrochemical dehydration and separation tasks. Cost-optimized hydrothermal, microwave-assisted, and template-free syntheses continue to elevate product purity while trimming energy consumption by 35%. In contrast, natural clinoptilolite and mordenite grades are growing at 6.12% CAGR, primarily in agriculture, odor control, and low-pressure water treatment applications where the performance-to-price ratio outranks crystal perfection. Natural deposits in Turkey and Bulgaria deliver ore that requires minimal ion-exchange to reach specification, offering a 30-40% cost edge. Regulatory drivers such as the EU's Green Deal favor non-synthetic minerals, further stimulating adoption. Looking forward, synthetic grades maintain their hold in high-pressure dehydration and catalysis, but natural zeolites increasingly claim environmental and agricultural niches, carving a complementary growth lane within the zeolite molecular sieve market.
The Zeolite Molecular Sieve Report is Segmented by Raw Material (Natural Zeolite and Synthetic Zeolite), End-User Industry (Detergents, Petrochemical and Refining, Industrial Gas Production, Waste and Water Treatment, Air Purification and HVAC, and Agriculture and Animal Feed, Other End-User Industries), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific generated 37.56% of global sales in 2024 and is set to grow at a 6.21% CAGR. China spearheads investment in ethylene crackers and coal-to-chemicals complexes, each requiring hundreds of tons of molecular sieves for dehydration duty. Asia Pacific's convergence of production scale, tightening environmental norms, and large consumer bases drives the region's leadership. China's Zhejiang and Guangdong ethylene projects require molecular-sieve dehydration units that remove moisture to below 1 ppm, while local wastewater standards enforce ammonia limits that spur zeolite tertiary systems.
North America exhibits mature but technology-rich demand. Shale-gas processing plants in Texas deploy 3A molecular sieves to strip moisture before cryogenic NGL recovery, seeking higher efficiency and longer bed life. EPA PFAS discharge proposals accelerate trials of high-silica zeolites that capture perfluoro-alkyl compounds at parts-per-trillion levels, an emerging revenue stream for specialty producers.
Europe prioritizes sustainability and circularity. Plants in Germany and the Netherlands validate fly-ash-derived zeolites at commercial scale, delivering 40% embodied-carbon reduction relative to virgin mineral routes. Middle-East and Africa capitalize on petrochemical diversification and water scarcity. Saudi Arabia's Vision 2030 resin capacities rely on large-format molecular-sieve towers for feedstock preparation. South Africa's mining sector adopts clinoptilolite for acid-mine drainage remediation, benefitting from domestic natural deposits that eliminate import costs. Collectively, these regional developments underscore the expanding geographic canvas for the zeolite molecular sieve market.
- Arkema
- Axens
- BASF
- CLARIANT
- CWK Chemiewerk Bad Kostritz GmbH
- HengYe Inc.
- Honeywell International Inc.
- JIUZHOU CHEMICALS
- KMI Zeolite Inc.
- KNT Group
- KURARAY CO., LTD.
- Luoyang Jalon Micro-Nano New Material
- Sorbchem India Pvt Ltd.
- Tosoh Corporation
- W. R. Grace & Co.
- Zeochem
- Zeolyst International
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Phosphate Bans in Detergents Shifting Builders to Zeolites
- 4.2.2 Petrochemical Dehydration and Gas-Purification Boom
- 4.2.3 Stringent Wastewater Discharge Norms
- 4.2.4 Hygiene-Driven Detergent Demand in Emerging Economies
- 4.2.5 Bio-Refinery Shift Demanding Shape-Selective Catalysts
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Enzyme And Chemical Substitutes in Laundry Formulations
- 4.3.2 Volatile Alumina/Silica Feedstock Pricing
- 4.3.3 High Energy Footprint Questioned by ESG Investors
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Raw Material
- 5.1.1 Natural Zeolite
- 5.1.2 Synthetic Zeolite
- 5.2 By End-user Industry
- 5.2.1 Detergents
- 5.2.2 Petrochemical and Refining
- 5.2.3 Industrial Gas Production
- 5.2.4 Waste and Water Treatment
- 5.2.5 Air Purification and HVAC
- 5.2.6 Agriculture and Animal Feed
- 5.2.7 Other End-user Industries
- 5.3 By Geography
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.1.1 China
- 5.3.1.2 India
- 5.3.1.3 Japan
- 5.3.1.4 South Korea
- 5.3.1.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.3.2 North America
- 5.3.2.1 United States
- 5.3.2.2 Canada
- 5.3.2.3 Mexico
- 5.3.3 Europe
- 5.3.3.1 Germany
- 5.3.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.3.3.3 France
- 5.3.3.4 Italy
- 5.3.3.5 Russia
- 5.3.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.3.4 South America
- 5.3.4.1 Brazil
- 5.3.4.2 Argentina
- 5.3.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.3.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.3.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.3.5.2 South Africa
- 5.3.5.3 Rest of Middle-East Africa
- 5.3.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Arkema
- 6.4.2 Axens
- 6.4.3 BASF
- 6.4.4 CLARIANT
- 6.4.5 CWK Chemiewerk Bad Kostritz GmbH
- 6.4.6 HengYe Inc.
- 6.4.7 Honeywell International Inc.
- 6.4.8 JIUZHOU CHEMICALS
- 6.4.9 KMI Zeolite Inc.
- 6.4.10 KNT Group
- 6.4.11 KURARAY CO., LTD.
- 6.4.12 Luoyang Jalon Micro-Nano New Material
- 6.4.13 Sorbchem India Pvt Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Tosoh Corporation
- 6.4.15 W. R. Grace & Co.
- 6.4.16 Zeochem
- 6.4.17 Zeolyst International
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessmen
- 7.2 Increasing Demand for Using Green Technologies




