PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910475

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910475
Rheumatoid Arthritis Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
Rheumatoid Arthritis Drugs Market size in 2026 is estimated at USD 38.75 billion, growing from 2025 value of USD 37.08 billion with 2031 projections showing USD 48.31 billion, growing at 4.51% CAGR over 2026-2031.
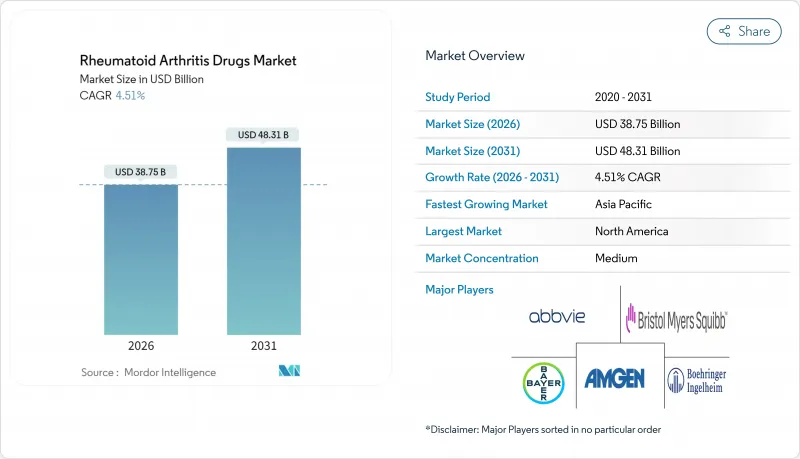
This trajectory reflects a maturing landscape in which next-generation biologics offset revenue compression from biosimilar entry while sustained disease prevalence underpins demand. Competitive intensity has grown as ten adalimumab biosimilars reached US and EU markets, yet precision-engineered biologics such as bimekizumab and upadacitinib continue to secure premium pricing and rapid uptake. Broader insurance coverage, price negotiation frameworks, and China's volume-based procurement schemes are widening patient access, while digital health tools that integrate symptom tracking with electronic records support earlier diagnosis and therapy optimization. Meanwhile, companies pursue defensive mergers and pipeline diversification-AbbVie alone spent more than USD 22 billion on acquisitions since early 2024 to mitigate biosimilar erosion and reposition for long-term growth.
Global Rheumatoid Arthritis Drugs Market Trends and Insights
Rising Global Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Aging Populations
Age-standardized prevalence continues to climb as demographic transition increases the proportion of older adults worldwide. High socio-demographic index countries such as Qatar log the steepest incidence, yet emerging markets now see parallel trends as diagnostic capacity improves. In the United States, average annual direct costs reach USD 24,068 per patient, more than quadruple non-RA cohorts. This economic burden sustains demand for efficacious long-term therapies, reinforcing volume growth for the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market. Health-system readiness in developed countries accelerates biologic adoption, while lower-income regions increasingly allocate funds to specialty care.
Regulatory Approvals of Innovative Targeted Synthetic DMARDs
FDA authorizations for agents such as bimekizumab in early 2025 broaden therapeutic choice beyond traditional TNF inhibition. Updated regulatory guidance streamlines trial design yet maintains post-market vigilance, especially for Janus-kinase inhibitors after safety warnings. Upadacitinib's EU clearance in giant cell arteritis underscores platform extension across inflammatory diseases. Clinicians increasingly combine targeted agents with prognostic biomarkers, improving remission rates and fueling premium willingness to pay. These novel approvals energize the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market by refreshing pipelines as legacy biologics lose exclusivity.
High Therapy Cost of Biologics and Targeted Agents
Annual biologic DMARD spending averages USD 36,053 versus USD 12,509 for conventional therapy, straining payer budgets and patient affordability. Private-insurance out-of-pocket obligations for US patients quadrupled, with HMO plans seeing the steepest hikes. Although biosimilars sometimes list at 85% discounts, rebate structures and coverage gaps often negate savings, limiting real-world penetration. In emerging economies, inadequate reimbursement frameworks further restrict access, tempering growth in the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market despite underlying demand.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Broader Access to Biologics Through Subsidies and Insurance Programs
- Uptake of Cost-Effective Biosimilars in Emerging Markets
- Revenue Compression Due to Biosimilar Entry
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Biopharmaceuticals controlled 67.48% of the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market in 2025 and generated the fastest 8.76% CAGR outlook through 2031, underpinned by blockbuster antibodies like risankizumab and the continual launch of next-generation platforms. The segment reflects robust uptake even as biosimilar infiltration intensifies. Notably, AbbVie's Skyrizi and Rinvoq together delivered USD 5.14 billion in Q1 2025, validating strategic pivoting away from expiring TNF franchises. Pharmaceuticals, chiefly conventional small-molecule DMARDs retain a foundational clinical role yet face moderated growth as prescribers migrate to targeted agents for refractory disease.
Future performance hinges on pipeline depth and patent stewardship. Antibody-drug conjugates that twin anti-CD79b antibodies with cytotoxics illustrate how novel modalities can deliver anti-inflammatory action while limiting systemic immunosuppression. Meanwhile, early-stage B-cell depletion therapies acquired by Merck signal sustained capital allocation to immunology. As biosimilar discounts gain traction, innovators seek differentiation via superior convenience, broader label indications, and companion diagnostics tactics likely to preserve premium pricing and extend lifecycle value within the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market.
DMARDs commanded a 46.02% market share in 2025 while recording an 11.34% CAGR forecast, propelled by the expansion of targeted synthetic variants such as JAK, TYK2, and IRAK4 inhibitors that halt structural damage more effectively than historical standards. Methotrexate remains the first-line anchor, yet its share slipped to 34% in 2025 as prescribers escalated to JAK inhibitors for inadequate responders. Interleukin-6 inhibitors like tocilizumab outperform TNF inhibitors in real-world persistence, a key metric in chronic therapy.
The rheumatoid arthritis drugs market size for DMARDs, buoyed by regulatory fast-track pathways and biomarker-guided dosing. Combination regimens exploiting m6A methylation suppression show preclinical promise in preserving bone integrity. NSAIDs and corticosteroids increasingly serve as bridging or adjunctive agents, their volume tempered by safety surveillance programs. Collectively, DMARD innovation underscores a decisive shift toward precision medicine, further cementing the segment's centrality.
The Rheumatoid Arthritis Drugs Market Report is Segmented by Type of Molecule (Pharmaceuticals, Biopharmaceuticals), Drug Class (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, and More), Route of Administration (Oral, Parenteral, Topical), End User (Hospital Pharmacies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 40.92% share of the rheumatoid arthritis drugs market in 2025, supported by robust reimbursement and early adoption of premium therapies. In the United States, Medicare beneficiaries with rheumatoid arthritis incurred USD 23,544 annual drug-related costs before the 2025 Medicare Part D cap, highlighting cost sensitivity among fixed-income seniors. Ten Humira biosimilars launched within a single year, trimming AbbVie's US sales yet broadening patient access, while Canadian payers adopt tiered biosimilar switching policies to curb expenditure.
Asia-Pacific registers the highest 9.12% CAGR through 2031. China's biopharmaceutical output, supported by a volume-based procurement framework that simultaneously lowers prices and incentivizes domestic manufacturing. Japan presents nuanced age-stratified utilization, with biologic use tapering from 50.9% in youth to 13.7% in octogenarians, reflecting safety concerns and cost-offset strategies. India's rollout of national health insurance (Ayushman Bharat) and rapid e-pharmacy expansion similarly lift baseline demand.
Europe contributes steady single-digit growth, anchored by centralized regulatory pathways and biosimilar-friendly legislation such as Finland's pharmacy substitution bill. National health technology assessment agencies increasingly favor cost-effectiveness, accelerating the uptake of biosimilar tocilizumab and infliximab. Latin America and the Middle East and Africa offer emerging upside; expanding private insurance in Brazil and Gulf Cooperation Council countries, coupled with rising specialist capacity, improves treatment penetration, albeit from a smaller base.
- Abbvie
- Amgen
- Bayer
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Celgene
- Roche
- Merck
- Novartis
- Lupin
- Alkem Laboratories
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Pfizer
- Gilead Sciences
- UCB
- Sanofi
- Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co.
- Samsung Bioepis Co. Ltd.
- Bio-Thera Solutions Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Global Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis Among Aging Populations
- 4.2.2 Regulatory Approvals of Innovative Targeted Synthetic DMARDs
- 4.2.3 Broader Access to Biologics Through Subsidies and Insurance Programs
- 4.2.4 Uptake of Cost-Effective Biosimilars in Emerging Markets
- 4.2.5 Integration of Digital Health Platforms in Rheumatology Care
- 4.2.6 Growing Clinical Research in Personalized RA Therapies
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Therapy Cost of Biologics and Targeted Agents
- 4.3.2 Revenue Compression Due to Biosimilar Entry
- 4.3.3 Persistent Diagnostic Delays in Primary Care
- 4.3.4 Safety Concerns with Long-Term Immunosuppressive Therapy
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Type of Molecule
- 5.1.1 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.1.2 Biopharmaceuticals
- 5.2 By Drug Class
- 5.2.1 Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
- 5.2.2 Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
- 5.2.3 Corticosteroids
- 5.2.4 Analgesics
- 5.2.5 Other Drug Classes
- 5.3 By Route of Administration
- 5.3.1 Oral
- 5.3.2 Parenteral
- 5.3.3 Topical
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.4.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.4.3 Online Pharmacies
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.2 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.3 Bayer AG
- 6.3.4 Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- 6.3.5 Bristol-Myers Squibb Company
- 6.3.6 Celgene Corporation
- 6.3.7 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.3.8 Merck & Co. Inc.
- 6.3.9 Novartis AG
- 6.3.10 Lupin Limited
- 6.3.11 Alkem Laboratories
- 6.3.12 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.13 Eli Lilly and Company
- 6.3.14 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.15 Gilead Sciences Inc.
- 6.3.16 UCB S.A.
- 6.3.17 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.18 Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine Co.
- 6.3.19 Samsung Bioepis Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.20 Bio-Thera Solutions Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




