PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846142

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846142
Counter-IED - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The counter-IED market size is estimated at USD 2.21 billion in 2025 and is forecasted to reach USD 2.66 billion by 2030, translating into a 3.78% CAGR.
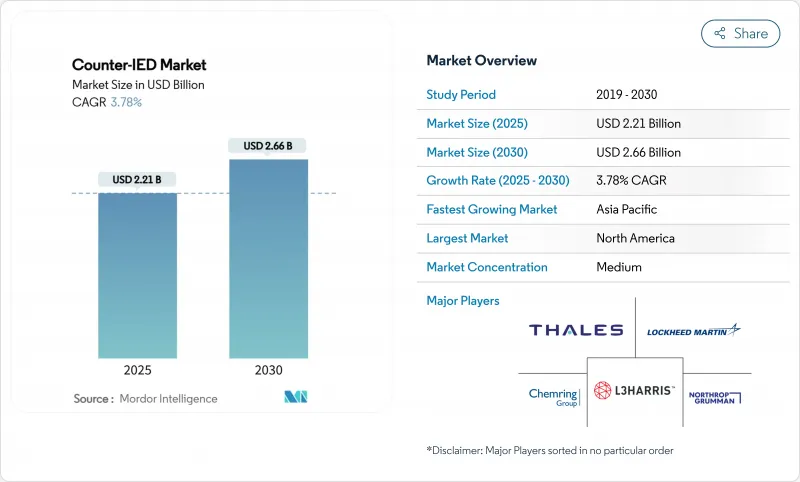
Heightened asymmetric-warfare preparedness, rising defense appropriations, and the growing convergence between counter-UAS and counter-IED technologies keep demand elevated, while spectrum-management bottlenecks and high GaN component prices temper short-term deployment rates. North America maintains spending leadership, but Indo-Pacific modernization programs are closing the gap. Detection capabilities, especially multi-sensor AI-enabled suites, account for the bulk of current procurement, yet rapid growth in neutralization technologies-directed-energy jammers and robotics-signals a strategic pivot toward active defeat solutions. Platform flexibility also matters; buyers increasingly specify vehicle-agnostic jamming kits that migrate easily from manned tactical trucks to unmanned ground vehicles. Competitive intensity is moderate: defense primes hold technology depth, but specialist firms exploiting AI, microwave weapons, and autonomous heavy equipment win share as armed forces pursue faster innovation cycles.
Global Counter-IED Market Trends and Insights
Rising defense-budget allocation to asymmetric warfare preparedness
Defense ministries now allocate larger slices of rising budgets to irregular-threat capabilities. The US FY 2026 request tops USD 1.01 trillion, explicitly funding counter-terrorism and demining technologies. European NATO members that exceeded the 2% of GDP defense benchmark in 2024 continue to channel incremental funds toward C-IED programs, influenced by operational lessons from Ukraine. East Asian expenditure reached USD 411 billion in 2023 and is still climbing, translating into fresh tenders for detection radars, handheld disruptors, and route-clearance UGVs. As budgets grow, procurement agencies emphasize open architectures and rapid technology refresh to stay ahead of proliferating homemade devices.
Accelerated fielding of manned-unmanned teaming (MUM-T) C-IED assets
MUM-T doctrine has moved from prototypes to field deployment. The US Army's Apache-Shadow-Gray Eagle experiments demonstrated autonomous convoy route-clearance, validating interoperable data links for IED defeat missions. Israel Defense Forces now operate RobDozer bulldozers and M113-based autonomous systems for high-risk neutralization, cutting human exposure on Gaza border routes. European ground forces follow suit through the Franco-British Maritime Mine Counter Measures and ELROB trials that showcased Rheinmetall's UGV convoy leader. The resulting demand favors scalable control software and standardized payload bays compatible with mixed manned and robotic teams.
High capital cost of EW-grade GaN RF front-ends
Gallium-nitride power amplifiers let CREW transmitters cover wide 5G-era threat envelopes because GaN offers higher electron mobility and thermal efficiency than older gallium-arsenide parts, allowing smaller devices to push kilowatt-class output across multioctave bands. The downside is manufacturing: GaN layers are grown on costly silicon-carbide substrates in metal-organic chemical vapor deposition reactors that still run single-digit wafer yields, so each die that survives probe testing carries a premium price. Limited trusted-foundry capacity inside the United States and Europe compounds the problem, forcing primes to compete with commercial telecom buyers for the same epitaxy slots, which keeps average selling prices well above USD 20 per watt in the L-band. Northrop Grumman engineering briefs caution that unless new 150 mm reactors and automated back-end lines come online by 2027, volume buys larger than brigade scale could slip a year or more for smaller allies that lack multiyear funding lines, prompting some defense ministries to hold legacy silicon jammers longer than planned.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid advances in AI-enabled multi-sensor fusion for IED detection
- Growing demand for vehicle-agnostic CREW kits across allied armed forces
- Spectrum-management bottlenecks limiting CREW jamming power levels
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Detection solutions generated the largest slice of the counter-IED market revenue in 2024, equal to a 59.70% counter-IED market share, as commanders prioritized finding bombs before convoys rolled. Ground-penetrating radar paired with high-resolution synthetic-aperture algorithms now distinguishes disturbed soil at a walking pace, while passive RF sniffers flag trigger circuits. The counter-IED market size for countermeasures is projected to rise 4.65% annually to 2030 as doctrine shifts toward active defeat.
Demand for countermeasures centers on wideband CREW transmitters covering 20 MHz to 6 GHz and directed-energy weapons such as Iron Beam lasers that neutralize threats at the speed of light. Robotics adds another layer: armored EOD UGVs like IAI RobDozer employ 15-ton plow blades and remote-controlled disruptors, enabling route-clearance in hostile terrain without exposing sappers.
Vehicle-mounted systems accounted for 67.21% of the counter-IED market size in 2024, underpinned by convoy protection doctrines that embed jammers, cameras, and radars onto tactical trucks. The approach delivers on-board power and ballistic shielding, making it the default for brigade movement and logistics resupply.
Growth momentum, however, is shifting skyward. Aerial pods-whether slung under manned helicopters or Group 4 UAVs-are forecast to post a 5.35% CAGR, the fastest in the deployment category. Early US Navy ALMDS mine-detection pods and Army NERO EW payloads illustrate the appeal: wide area coverage, minimal exposure to roadside ambush, and quick redeployment to new theaters. Dismounted troops still rely on man-portable disruptors such as the 11 kg GMJ9500 to secure cordon searches in urban alleys.
The Counter-IED Market Report is Segmented by Capability (Detection and Countermeasures), Deployment (Vehicle-Mounted, Hand-held/Man-portable, and More), End User (Military and Homeland Security), Technology (RF Jamming, Sensor-Based Detection, and Robotic and Autonomous Systems), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America represented 49.80% of the counter-IED market revenue in 2024, sustained by a USD 1 trillion defense budget and deep operational know-how from Iraq and Afghanistan. The DoD pushes multi-domain protection prototypes into user evaluations, trimming acquisition cycles and preserving regional leadership. Canada's border-security upgrades and Mexico's focus on organized crime IEDs add incremental demand.
The Asia-Pacific counter-IED market exhibits a projected 5.21% CAGR through 2030, the fastest zone, propelled by territorial flashpoints in the South and East China seas. India invests in Israeli radars, roadside jammers, and robotic mine plows under emergency procurement rules, while Australia funds unmanned route clearance as part of its Defense Strategic Review implementation. ASEAN states adopt lower-cost man-portable disruptors to protect urban transit hubs, broadening the regional customer base.
Europe sustains buying momentum through NATO's Enhanced Forward Presence and accelerated rearmament triggered by the war in Ukraine. Multinational programs in Brussels coordinate test protocols and life-cycle support, lifting smaller member states that lack Indigenous C-IED labs. In the Middle East and Africa, procurement remains episodic, but oil-export gains allow Gulf states to purchase top-tier directed-energy systems, while UN peacekeeping missions in the Sahel fuel demand for rugged detection kits.
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Chemring Group PLC
- Thales Group
- Elbit Systems Ltd.
- Rheinmetall AG
- Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- QinetiQ Group
- Allen-Vanguard Corporation
- BAE Systems plc
- SRC, Inc.
- Armtrac Limited
- Leonardo S.p.A
- Sierra Nevada Company, LLC
- Oshkosh Defense, LLC
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising defense-budget allocation to asymmetric warfare preparedness
- 4.2.2 Accelerated fielding of manned-unmanned teaming C-IED assets
- 4.2.3 Rapid advances in AI-enabled multi-sensor fusion for IED detection
- 4.2.4 Growing demand for vehicle-agnostic CREW kits across allied forces
- 4.2.5 Convergence of C-IED and C-UAS architectures
- 4.2.6 National regulations on precursor-chemical tracking
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capital cost of EW-grade GaN RF front-ends
- 4.3.2 Spectrum-management bottlenecks limiting CREW power
- 4.3.3 Complex integration with legacy battle-management systems
- 4.3.4 Export-license delays under Wassenaar Arrangement
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS ( VALUE)
- 5.1 By Capability
- 5.1.1 Detection
- 5.1.1.1 Metal-detector-based systems
- 5.1.1.2 Ground-penetrating-radar systems
- 5.1.1.3 RF/EO/IR sensor fusion suites
- 5.1.2 Countermeasures
- 5.1.2.1 Stand-off jammers
- 5.1.2.2 Directed-energy neutralizers
- 5.1.2.3 Disruptor and EOD robotics
- 5.1.1 Detection
- 5.2 By Deployment
- 5.2.1 Vehicle-Mounted
- 5.2.1.1 Manned Tactical Vehicles
- 5.2.1.2 Unmanned Ground Vehicles
- 5.2.2 Hand-held/Man-portable
- 5.2.3 Aerial-borne Pods and Payloads
- 5.2.1 Vehicle-Mounted
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Military
- 5.3.2 Homeland Security
- 5.4 By Technology
- 5.4.1 RF Jamming
- 5.4.2 Sensor-based Detection
- 5.4.3 Robotic and Autonomous Systems
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.2 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.3 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.4 Chemring Group PLC
- 6.4.5 Thales Group
- 6.4.6 Elbit Systems Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Rheinmetall AG
- 6.4.8 Israel Aerospace Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.9 QinetiQ Group
- 6.4.10 Allen-Vanguard Corporation
- 6.4.11 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.12 SRC, Inc.
- 6.4.13 Armtrac Limited
- 6.4.14 Leonardo S.p.A
- 6.4.15 Sierra Nevada Company, LLC
- 6.4.16 Oshkosh Defense, LLC
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




