PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846144

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846144
Sheet Molding And Bulk Molding Compounds - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
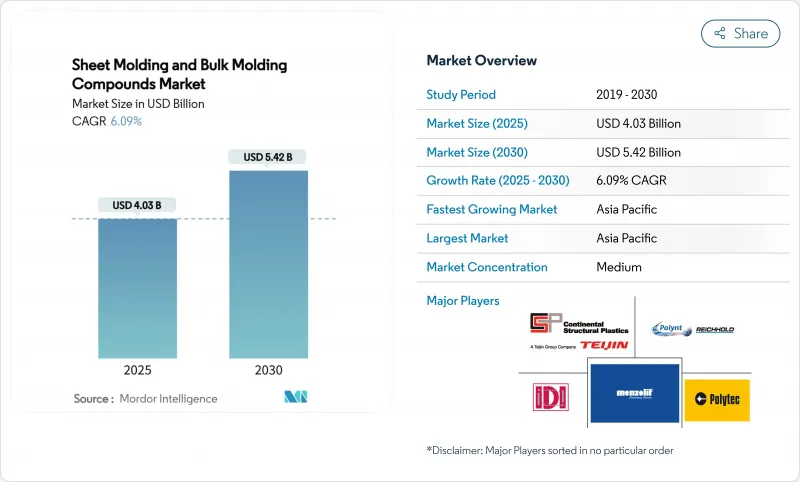
The Sheet Molding & Bulk Molding Compounds Market size is estimated at USD 4.03 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 5.42 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.09% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
Sustained demand for lightweight structural parts in electric vehicles, low scrap rates from compression molding, and improved resin chemistries keep capital flowing into new capacity. Cost reductions per part, especially in complex geometries that previously relied on multi-stage stamping, accelerate the replacement of metal stampings with compression-molded composites across automotive and electrical applications. Original equipment manufacturers now specify advanced sheet molding materials with Class-A finishes, allowing direct exterior use and eliminating secondary paint steps that once limited adoption. Asia-Pacific retains cost-leadership in high-flow, low-density sheet molding compounds, while European regulations on styrene emissions fast-track epoxy-based alternatives.
Global Sheet Molding And Bulk Molding Compounds Market Trends and Insights
Light-weighting Push from Electric Vehicles and Hybrid Vehicle OEMs
Electric models move large battery packs, so every kilogram saved extends range. Automakers therefore redesign closures, body panels, and battery housings with advanced sheet molding compounds that cut part weight by up to 40% versus comparable aluminum designs while satisfying crash-load pathways and thermal shielding demands. Tesla, General Motors, and leading Chinese brands have publicly outlined multi-part consolidation strategies that favor single-shot compression molding, reducing weld operations and line takt time. Sheet molding and bulk molding compounds market participants benefit as these programs scale from pilot to full volume production.
Rapid Capacity Additions in Electrical and Electronics Components Molding Hubs
APAC electronics clusters in China, Vietnam, and Malaysia continue installing high-tonnage compression presses equipped with automated material dosing and infrared curing control. Co-location of compounders, molders, and end-device assemblers shortens supply chains and helps manufacturers meet stringent dimensional tolerances required for connector housings and motor insulation systems. Government programs in China that target self-sufficiency in high-performance polymers reinforce this build-out, positioning the region to support global demand spikes.
Styrene and Fiberglass Price Volatility
Styrene monomer trades in tight cycles, reacting to benzene feedstock swings and shipping constraints. Each USD 100 per ton change in styrene cascades into resin pricing, squeezing margins for small sheet molding compounders that lack long-term supply contracts. Simultaneous fiberglass surcharges further hinder price stability because glass fiber content approaches 65 wt % in many structural grades.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cost-effective High-volume Compression Molding versus Metal Stamping
- High-flow, Low-density Sheet Molding Components Enabling Class-A Body Panels
- Engineering Thermoplastics Replacing SMC in Battery Boxes
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Polyester resin accounted for 55.19% sheet molding and bulk molding compounds market share in 2024 thanks to low cost, broad supplier base, and cure kinetics tailored to legacy compression lines. The segment continues to profit from automotive demand for under-hood covers and structural interior brackets. At the same time epoxy grades post a 6.92% CAGR toward 2030, driven by reduced volatile organic compound content and elevated heat resistance that appeals to electric drivetrain designers. The Evonik-led program for glass-fiber-reinforced epoxy battery housings validated weight reductions approaching 10% while maintaining crush-force thresholds critical to vehicle homologation. As epoxy systems mature, hybrid lay-ups that blend polyester skins with epoxy cores may emerge to balance economics and strength.
Glass fiber kept 80.22% of 2024 revenue due to favorable cost-to-performance and excellent dielectric strength for electrical parts. Continuous furnace expansions at major glass fiber producers stabilize supply, supporting high-volume automotive launches in Asia-Pacific and North America. Carbon fiber sheet molding compounds, posting a 7.06% CAGR, gain momentum in aerospace secondary structures and premium sports cars where curb-weight targets override raw-material premiums. Process simulation tools mapping fiber orientation now shorten development cycles, delivering predictable mechanical performance and cutting scrap rates. Hybridized fiber mats that alternate glass and carbon layers help designers hit mid-tier cost targets without compromising stiffness.
The Sheet Molding & Bulk Molding Compounds Market Report is Segmented by Resin Type (Epoxy and Polyester), Fiber Type (Glass Fiber and Carbon Fiber), Manufacturing Process (Compression Molding, Transfer Molding, and More), End-User Industry (Automotive and Transportation, Electrical and Electronics, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle-East and Africa).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific retains the cost advantage that underpins its 48.54% share in 2024. Intensifying domestic EV production, rising middle-class appliance consumption, and government incentives for composite part localization keep presses running near capacity. With estimated demand growth translating to a 6.45% regional CAGR, the sheet molding and bulk molding compounds market continues to shift toward Asian value chains.
North America sits second in regional revenue. Early electric-pickup launches require large structural covers, and aerospace programs consume high-modulus carbon sheet molding compounds for secondary structures. Federal policy that funds onshore battery factories encourages new composite battery-box lines, lifting local compound consumption.
Europe upholds strict environmental rules that spur adoption of low-styrene sheet molding systems and epoxy innovations. Automaker roadmaps that phase out internal combustion between 2030 and 2035 expand demand for lightweight composites. Meanwhile, robust chemical-industry infrastructure supports specialized resin additives that raise mechanical performance and prolong mold life.
- AOC
- Ashland Container Corporation
- Astar S.A.
- Continental Structural Plastics (Teijin)
- Core Molding Technologies
- CSP
- DIC Corporation
- IDI Composites International
- Kingfa Sci.&Tech. Co.,Ltd.
- LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.
- Menzolit
- National Manufacturing Group
- OPmobility SE
- POLYNT SPA
- Polynt-Reichhold
- Polytec Group
- Polytec Masterbatch LLC
- TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Light-weighting Push from Electric Vehicles and Hybrid Vehicle OEMs
- 4.2.2 Rapid Capacity Additions in Electrical and Electronics Components Molding Hubs
- 4.2.3 Cost-effective High-volume Compression Molding versus Metal Stamping
- 4.2.4 High-flow, Low-density Sheet Molding Components (SMC) enabling Class-A body Panels
- 4.2.5 Integration of In-mold Electronics (IME) for Smart Panels
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Styrene and Fiberglass Price Volatility
- 4.3.2 Engineering Thermoplastics Replacing Sheet Molding Components (SMC) in Battery Boxes
- 4.3.3 End-of-life Recycling Hurdles for Thermosets
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Resin Type
- 5.1.1 Polyester
- 5.1.2 Epoxy
- 5.2 By Fiber Type
- 5.2.1 Glass Fiber
- 5.2.2 Carbon Fiber
- 5.3 By Manufacturing Process
- 5.3.1 Compression Molding
- 5.3.2 Injection / Transfer Molding
- 5.3.3 Resin Transfer Molding (RTM)
- 5.3.4 Pultrusion
- 5.4 By End-user Industry
- 5.4.1 Automotive and Transportation
- 5.4.2 Electrical and Electronics
- 5.4.3 Building and Construction
- 5.4.4 Aerospace
- 5.4.5 Domestic Appliances
- 5.4.6 Other End-user Industries (Energy, etc.)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 Japan
- 5.5.1.3 India
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 ASEAN Countries
- 5.5.1.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 NORDIC Countries
- 5.5.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle-East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share(%)/Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 AOC
- 6.4.2 Ashland Container Corporation
- 6.4.3 Astar S.A.
- 6.4.4 Continental Structural Plastics (Teijin)
- 6.4.5 Core Molding Technologies
- 6.4.6 CSP
- 6.4.7 DIC Corporation
- 6.4.8 IDI Composites International
- 6.4.9 Kingfa Sci.&Tech. Co.,Ltd.
- 6.4.10 LyondellBasell Industries Holdings B.V.
- 6.4.11 Menzolit
- 6.4.12 National Manufacturing Group
- 6.4.13 OPmobility SE
- 6.4.14 POLYNT SPA
- 6.4.15 Polynt-Reichhold
- 6.4.16 Polytec Group
- 6.4.17 Polytec Masterbatch LLC
- 6.4.18 TORAY INDUSTRIES, INC.
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




