PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846212

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846212
Sewing Machines - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
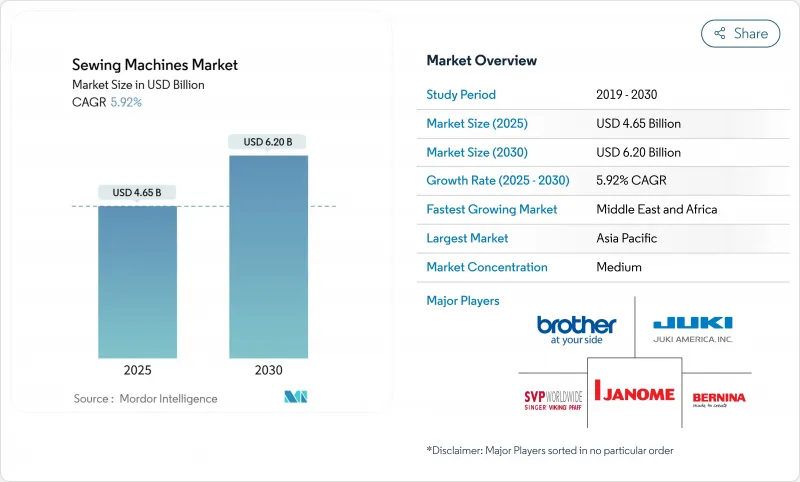
The sewing machine market attained a value of USD 4.65 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise at a 5.92% CAGR to USD 6.20 billion in 2030.
Industrial automation requirements power growth, the widening maker movement, and rapid feature upgrades that allow both factories and households to boost productivity while reducing waste. Manufacturers benefit from dual exposure: large-volume textile exports in Asia and the repair-over-replace culture in North America and Europe. Technology upgrades toward Wi-Fi connectivity, downloadable stitch libraries, and programmable logic controllers lengthen replacement cycles yet raise average selling prices, supporting revenue even when unit volumes plateau. Near-shoring of garment production back to the United States and Western Europe further expands the addressable base for flexible, small-batch industrial systems that can switch styles without lengthy retooling.
Global Sewing Machines Market Trends and Insights
Rapid Apparel-Manufacturing Expansion in Asia-Pacific
Asia continues to outpace every other region in apparel output, fueled by public incentives and export-oriented strategies. India alone targets USD 350 billion in textile exports by 2030, stimulating bulk procurement of high-throughput sewing lines . Production-linked schemes covering technical textiles lower the payback period on automated machines that handle multiple fabric weights without manual intervention. Growing wages in legacy low-cost centers push manufacturers toward units with servo motors and programmable stitch patterns that offset labor costs. Factory clustering in Vietnam and Bangladesh simplifies after-sales logistics, encouraging suppliers to embed regional service hubs. As orders shift from basic tees to higher-value athleisure and formalwear, demand tilts toward machines capable of complex seam constructions and digital platen adjustments.
DIY & Craft Culture Revival in Mature Economies
Gen Z consumers view home sewing as a route to personalized fashion and lower textile waste, and social media tutorials convert that interest into measurable hardware sales. Retailers now curate starter bundles that pair entry-level machines with downloadable patterns, easing the learning curve. Pandemic-era hobby adoption has persisted post-lockdown as a stress-relief habit, keeping retail sell-through high even as other home-improvement categories normalize. Compact form factors that fit small apartments and smartphone-like touchscreens resonate with digital natives, forcing brands to prioritize intuitive UX over mechanical complexity. The rising tide of reseller platforms for handmade items, such as Etsy, further monetizes the hobby, reinforcing equipment upgrades once users outgrow basic functions.
High Capital Outlay for Industrial Machines
Vendor financing options exist yet cover only the hardware, leaving training and maintenance outside loan packages. Banks often require collateral that small workshops lack, delaying modernization cycles and leaving production stuck with 10-year-old lockstitch units. Deferred investment saps competitiveness when brands demand tight tolerances on seam strength and digital traceability. Leasing programs introduced by JUKI in 2024 showed early adoption in Vietnam but remain a novelty elsewhere, partly because operators fear long-term commitment to proprietary software ecosystems.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancements in IoT-Enabled and CNC Sewing Machines
- Industrial Automation Push for Productivity
- Shortage of Skilled Operators
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Electric models accounted for 65.00% of revenue in 2024, underscoring their versatility for factories and households alike. Many industrial buyers regard the segment as an interim step toward full automation, adding servo drives and semi-automatic thread cutters to stretch machine life cycles. Automated units, meanwhile, are slated to expand at 6.89% CAGR through 2030 as factories chase consistent stitch quality and lower rework. The sewing machine market size for automated systems is growing, reflecting rising demand from sportswear and technical-textile plants. Manual machines linger in regions with unstable electricity grids, carving out a defensible niche among artisans who prize tactile control.
Continued dominance of the electric segment derives from abundant spare parts and universal familiarity among operators, decreasing training periods. Singer's Wi-Fi-ready M3330 illustrates how traditional categories absorb smart features without jumping to full CNC complexity. Hydraulically actuated quilting machines populate the "other" category and find success in mattress manufacturing, expanding geographic penetration into Turkey and Poland. Price gaps between electric and entry-level automated systems have narrowed to 18%, a threshold at which CFOs start green-lighting upgrades.
Apparel retained a commanding 58.30% slice of 2024 revenue due to vast order volumes from fast-fashion giants and uniform suppliers. Sportswear gains traction as stretch fabrics require differential-feed overlockers, prompting OEMs to bundle specialized presser feet. Home textiles, including curtains and cushion covers, represent the fastest-growing niche with a 6.95% CAGR as homeowners invest in personalized decor. The sewing machine market share for home-textile applications rose 120 basis points between 2023 and 2024, signaling a durable shift toward at-home customization. Automotive upholstery, medical disposables, and industrial filters round out the non-apparel group, each demanding heavy-duty needles and reinforced work tables.
Consumer preference for sustainable interiors boosts premium thread demand, benefiting subsidiaries like American & Efird that supply eco-dyed yarns. Car seat makers specify bar-tacking capabilities at 40 stitches per second, creating opportunities for providers that can integrate high-torque servo motors. In medical PPE, ultrasonic sewing alternatives compete, yet regulatory audits still favor stitched seams for critical gowns. Rising disposable income in urban India grows the market for embroidery-only machines that let users monetize home businesses. This diversification smooths cyclical dips in garment manufacturing, cushioning OEM revenue during apparel slowdowns.
The Sewing Machines Market Report is Segmented by Machine Type (Manual, Electric, and More), by Application (Apparel, Non-Apparel Textiles, and More), by End-User (Residential and Industrial), by Distribution Channel (B2C/Retail and B2B/Directly From the Manufacturers), and by Geography (North America, South America, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific's 51.00% revenue leadership in 2024 reflects its unmatched scale in fiber-to-fashion value chains and ascending middle-class consumption. India continues to roll out Production Linked Incentives that reimburse up to 15% of capital investment, prompting mills to modernize quickly . Chinese OEMs increasingly supply servo components and human-machine interfaces to global brands, shortening lead times for feature updates. Vietnam's apparel export growth encourages suppliers to build service warehouses in Ho Chi Minh City, reducing downtime for spare-part replacements. The region also witnesses swelling consumer enthusiasm for craft hobbies, as retail chains in Jakarta and Bangkok report double-digit sales lift for entry-level home units.
The Middle East and Africa grows the fastest, projected at 7.20% CAGR, supported by infrastructure corridors like Egypt's Suez Canal Economic Zone that bundle industrial parks with duty exemptions. Ethiopia's Hawassa Industrial Park already houses 25 apparel manufacturers that collectively imported more than 5,000 programmable lockstitch machines in 2024 according to customs data. Gulf Cooperation Council states encourage textile investments under Vision-2030 plans, with Saudi Arabia earmarking USD 500 million loans for integrated mills. African consumer markets also mature; Nigeria's e-commerce platforms now list mid-range portable models that sell out during festival seasons. The challenge lies in training; OEMs partner with vocational institutes in Nairobi and Accra to certify operators on basic maintenance.
North America experiences a revival in domestic making, powered by consumers who value locally produced garments and by brands facing unpredictable trans-Pacific freight. Brands such as Nike pilot automated lines in Oregon that rely on CNC sewing heads capable of multi-material stitching. State-level grants in North Carolina and South Carolina subsidize equipment purchases for legacy mills upgrading to smart factories. Canada's apparel SMEs embrace online configurators that allow end-users to design custom patterns, indirectly boosting demand for machines that accept digital input files. Mexico secures spill-over benefits as US buyers near-source to comply with quick-response retail models.
Europe blends mature industrial bases with avant-garde sustainability policies that redefine equipment specifications. Eco-design directives coming into force by 2027 will require precise energy-consumption metrics at the machine level, nudging OEMs toward high-efficiency servo motors. Germany continues to lead in technical textiles for automotive and aerospace, prompting demand for heavy-duty programmable bartackers. Italy's luxury fashion houses employ specialized hand-guided embroiderers alongside automated equipment to uphold "Made in Italy" authenticity. Eastern European factories in Romania and Bulgaria win orders redirected from Asia due to logistics volatility, necessitating rapid scale-up in machine fleets.
South America exhibits steady momentum as Brazil's garment cluster in Santa Catarina modernizes, deploying servo-motor retrofits to capture energy savings under rising electricity tariffs. Uruguay and Paraguay court Chinese investors for integrated cotton-to-apparel complexes that could localize equipment demand. Meanwhile, Chile's e-commerce penetration fosters hobbyist uptake of compact home machines designed for small apartments. Currency fluctuations remain the principal headwind, often delaying purchase decisions for imported machines until exchange rates stabilize.
- Brother Industries, Ltd.
- JUKI Corporation
- SVP Worldwide (Singer(R), Husqvarna Viking(R), Pfaff(R))
- Janome Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- Bernina International AG
- Mitsubishi Electric Corp. (Industrial Sewing Machinery)
- Jack Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- Pegasus Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- Toyota Industries Corp. (TACHINO)
- Baby Lock / Tacony Corporation
- Zoje Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- Feiyue Group Co., Ltd.
- Union Special LLC
- Rimoldi & CF
- SunStar Co., Ltd.
- Yamato Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- Typical Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- Seiko Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- Merrow Sewing Machine Company
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rapid apparel-manufacturing expansion in APAC
- 4.2.2 DIY & craft culture revival in mature economies
- 4.2.3 Advancements in IoT-enabled and CNC sewing machines
- 4.2.4 Industrial automation push for productivity
- 4.2.5 Near-shoring boosts demand for small-batch industrial units
- 4.2.6 Sustainability-driven "repair & reuse" consumer movement
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capital outlay for industrial machines
- 4.3.2 Proliferation of low-cost refurbished units
- 4.3.3 Electronics supply-chain bottlenecks (MCUs, servos)
- 4.3.4 Shortage of skilled operators for advanced models
- 4.4 Industry Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
- 4.6 Insights into the Latest Trends and Innovations in the Market
- 4.7 Insights on Recent Developments (New Product Launches, Strategic Initiatives, Investments, Partnerships, JVs, Expansion, M&As, etc.) in the Market
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Machine Type
- 5.1.1 Manual
- 5.1.2 Electric
- 5.1.3 Automated
- 5.1.4 Other Machine Types
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Apparel & Fashion
- 5.2.2 Non-apparel Textiles (Automotive, Upholstery)
- 5.2.3 Footwear & Leather Goods
- 5.2.4 Home Textiles & Crafts
- 5.2.5 Other Applications
- 5.3 By End User
- 5.3.1 Residential
- 5.3.2 Industrial
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 B2C/Retail
- 5.4.1.1 Multi-brand Stores
- 5.4.1.2 Exclusive Brand Outlets
- 5.4.1.3 Online
- 5.4.1.4 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.4.2 B2B/Directly from the Manufacturers
- 5.4.1 B2C/Retail
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 Canada
- 5.5.1.2 United States
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Peru
- 5.5.2.3 Chile
- 5.5.2.4 Argentina
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Spain
- 5.5.3.5 Italy
- 5.5.3.6 BENELUX (Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg)
- 5.5.3.7 NORDICS (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Sweden)
- 5.5.3.8 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 India
- 5.5.4.2 China
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 South Korea
- 5.5.4.6 South-East Asia (Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Philippines)
- 5.5.4.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Brother Industries, Ltd.
- 6.4.2 JUKI Corporation
- 6.4.3 SVP Worldwide (Singer(R), Husqvarna Viking(R), Pfaff(R))
- 6.4.4 Janome Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.5 Bernina International AG
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Electric Corp. (Industrial Sewing Machinery)
- 6.4.7 Jack Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Pegasus Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Toyota Industries Corp. (TACHINO)
- 6.4.10 Baby Lock / Tacony Corporation
- 6.4.11 Zoje Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Feiyue Group Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Union Special LLC
- 6.4.14 Rimoldi & CF
- 6.4.15 SunStar Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Yamato Sewing Machine Mfg. Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Typical Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Seiko Sewing Machine Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Merrow Sewing Machine Company
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 Growing demand for compact and portable sewing machines
- 7.2 Increasing prevalence of smart (integration of IoT and AI) and computerized sewing machines




