PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846264

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846264
Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
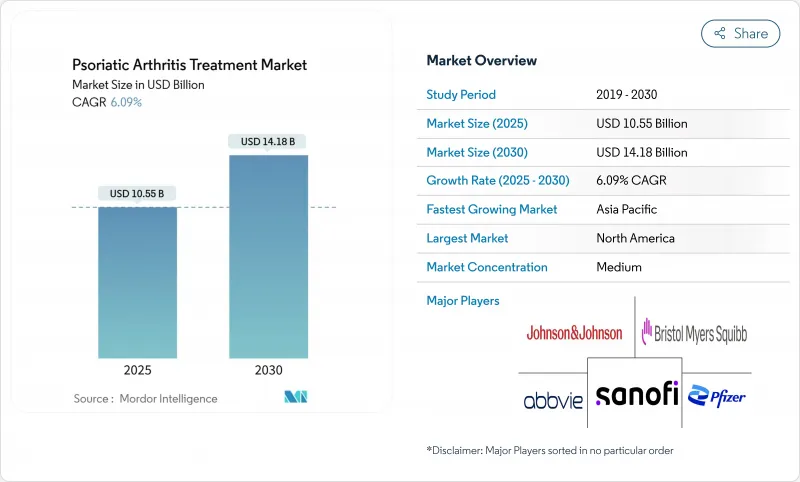
The psoriatic arthritis treatment market stood at USD 10.55 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 14.18 billion by 2030, translating into a 6.09% CAGR over the period.
Rising disease visibility, the obesity-metabolic syndrome link, and a robust biologic launch pipeline are widening both patient pools and therapeutic choice. The 2024 approval of bimekizumab, the first dual IL-17A/F inhibitor, affirms the industry's shift toward multi-cytokine blockade, while three ustekinumab biosimilars that entered the United States in early 2025 have introduced immediate price competition. Diagnostic latency continues to decline as rheumatologists adopt high-resolution imaging and biomarker panels, expanding early-stage intervention cohorts. Digital adherence platforms, especially tele-rheumatology services, improve medication persistence and are proving critical in under-served regions.
Global Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment Market Trends and Insights
Growing prevalence linked to obesity & metabolic syndrome
Obesity heightens psoriatic arthritis risk by 40-60%, and more than one-quarter of adults in high-income countries now meet metabolic-syndrome criteria, fueling sustained demand for biologic DMARDs . Adipose-derived cytokines amplify systemic inflammation, prompting earlier rheumatology referrals. Commercial payers increasingly acknowledge the comorbidity burden, widening coverage for advanced therapies that can reduce long-term disability costs.
Expansion of approved biologic & tsDMARD therapies
Bimekizumab's 2024 approval delivered the first dual IL-17A/F approach and posted superior skin clearance versus ixekizumab, broadening cytokine-specific choices. Phase 3 success for deucravacitinib in March 2025 (54.2% ACR20 versus 39.4% placebo) signals a new oral option that may expand first-line use in moderate disease . Rapid label additions reduce reliance on TNF inhibitors and enable sequence-based regimens tailored to biomarker profiles.
High total cost of care & patient OOP burden
Annual therapy costs span USD 45,000-80,000, with Medicare beneficiaries facing USD 4,423-6,950 out-of-pocket payments that drive 15-20% discontinuation rates. Step-therapy mandates delay biologic start by 3-6 months, increasing irreversible joint damage risk .
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Earlier diagnosis via imaging & biomarker panels
- Payer acceptance of value-based contracts
- Long-term immunosuppression safety concerns
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Biologic DMARDs contributed USD 4.98 billion in 2024 and represented 47.21% of psoriatic arthritis treatment market share. Ustekinumab biosimilar approvals in early 2025 have already trimmed originator sales and are expected to lower brand pricing across the class. Meanwhile, non-biologic DMARDs are set to outpace at a 7.01% CAGR to 2030 as oral small molecules such as deucravacitinib expand adoption.
Cost-sensitive prescribers are cycling more patients to methotrexate plus targeted synthetics before initiating injectable biologics, creating an opportunity for hybrid sequencing strategies. Adalimumab biosimilars captured 23% of United States anti-TNF volume by late 2024 and stimulated parallel adoption in Europe, where tender purchasing amplifies price erosion. This competitive dynamic has pushed originators to pivot toward next-generation assets, such as guselkumab and risankizumab, that offer distinct mechanisms or improved dosing convenience.
Injectables retained 72.44% revenue share thanks to high-dose bioavailability requirements for monoclonal antibodies. Subcutaneous self-dosing every eight to twelve weeks improves adherence compared with weekly regimens, supporting sustained parenteral demand. Nevertheless, oral products delivered the fastest growth at 7.04% CAGR and could elevate their psoriatic arthritis treatment market size to USD 3.12 billion by 2030.
JAK and TYK2 inhibitors, including tofacitinib and deucravacitinib, are central to this shift, allowing rheumatologists to initiate therapy without injection-training infrastructure. Head-to-head trials show similar efficacy to subcutaneous comparators, with survey data indicating 78% of patients would prefer oral dosing if safety and efficacy are equivalent.
The Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment Market is Segmented by Drug Class (NSAIDs, Biologic DMARDs, and More), Route of Administration (Oral, Parenteral, and Others), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, and Online Pharmacies), Age Group (Adults, Pediatric, and Geriatric) and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained leadership with USD 4.42 billion sales in 2024 and 41.89% psoriatic arthritis treatment market share. Early FDA approvals, high biologic penetration, and mature specialty pharmacy networks offset access friction from prior-authorization delays. Medicare patients still face USD 4,423-6,950 average annual out-of-pocket spending, driving discontinuation and prompting policy debates over Part D redesign. Step-therapy protocols, while intended to control spending, may postpone optimal therapy, leading to functional decline and heightened downstream costs.
Asia-Pacific posted the fastest 7.21% CAGR and could overtake Europe by 2030. Japan already treats 55.3% of psoriatic arthritis cases with biologics following guideline revisions that prioritize early intensive therapy. China and India are scaling domestic biosimilar production, trimming unit costs and making advanced care more attainable for urban middle-class populations. South Korea's single-payer model funds risankizumab and guselkumab after managed-entry agreements that cap budget impact.
Europe's steady growth rests on health-technology assessments that weigh clinical benefit against price, accelerating biosimilar penetration for cost containment. Outcomes-based contracts in Germany and France tie reimbursement to real-world PASI and ACR responses, influencing global price-setting strategies. Latin American markets lag owing to specialist shortages and funding constraints, yet public-private partnerships in Brazil and Argentina are expanding rheumatology clinics and subsidizing targeted agents.
- Abbvie
- Pfizer
- Johnson & Johnson
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- UCB
- Eli Lilly and Company
- Amgen
- Novartis
- Sanofi
- Eisai
- Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.
- Sumitomo Pharma Co.
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Alvotech
- Coherus BioSciences
- Galapagos NV
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Horizon Therapeutics
- Biogen
- Samsung Bioepis
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Prevalence Linked to Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome
- 4.2.2 Expansion of Approved Biologic & tsDMARD Therapies
- 4.2.3 Earlier Diagnosis Via Imaging & Biomarker Panels
- 4.2.4 Payer Acceptance of Value-Based Contracts for Biologics
- 4.2.5 Digital Adherence & Monitoring Solutions Adoption
- 4.2.6 Uptake Of Biosimilar Biologics Lowering Entry Barriers
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Total Cost of Care & Patient OOP Burden
- 4.3.2 Long-Term Immunosuppression Safety Concerns
- 4.3.3 Limited Rheumatologist Capacity in Emerging Markets
- 4.3.4 Reimbursement Delays for Novel Targeted Agents
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porters Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Drug Class
- 5.1.1 NSAIDs
- 5.1.2 Non-Biologic DMARDs
- 5.1.3 Biologic DMARDs
- 5.1.4 Immunosuppressants
- 5.1.5 Other Drug Classes
- 5.2 By Route of Administration
- 5.2.1 Oral
- 5.2.2 Parenteral
- 5.2.3 Others
- 5.3 By Distribution Channel
- 5.3.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.3.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.3.3 Online Pharmacies
- 5.4 By Age Group
- 5.4.1 Adults
- 5.4.2 Geriatric
- 5.4.3 Pediatric
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.2 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.3 Johnson & Johnson (Janssen)
- 6.3.4 Bristol-Myers Squibb
- 6.3.5 UCB S.A.
- 6.3.6 Eli Lilly and Company
- 6.3.7 Amgen Inc.
- 6.3.8 Novartis AG
- 6.3.9 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.10 Eisai Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.11 Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co.
- 6.3.12 Sumitomo Pharma Co.
- 6.3.13 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- 6.3.14 Alvotech
- 6.3.15 Coherus BioSciences
- 6.3.16 Galapagos NV
- 6.3.17 Sun Pharma
- 6.3.18 Horizon Therapeutics
- 6.3.19 Biogen Inc.
- 6.3.20 Samsung Bioepis
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




