PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846284

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1846284
Myasthenia Gravis Therapeutics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
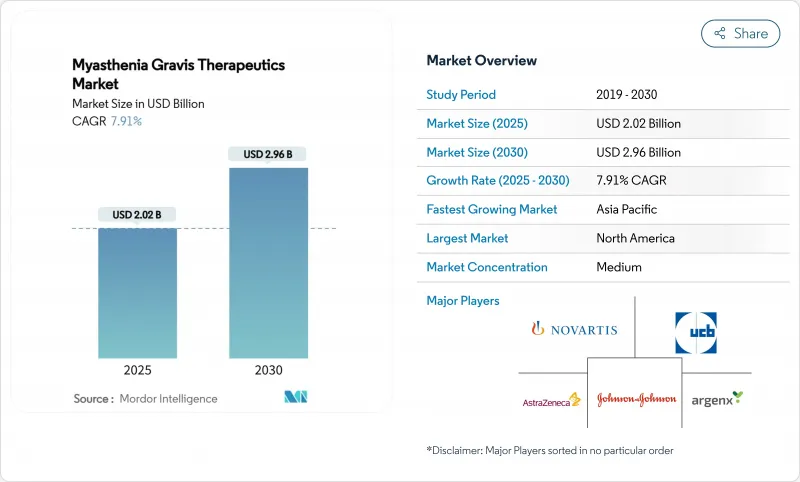
The myasthenia gravis therapeutics market stood at USD 2.02 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 2.96 billion by 2030 at a 7.91% CAGR.
Rising biologic adoption, especially FcRn antagonists and complement inhibitors, is redefining care pathways and prompting payers to reassess reimbursement frameworks. Pipeline maturation, orphan-drug incentives and venture-backed collaborations have shortened development cycles, while subcutaneous (SC) formulations are accelerating treatment decentralization. Strong prevalence growth, earlier diagnosis through AI-enabled tools and premium pricing latitude further strengthen revenue prospects. Competitive intensity is expected to increase as Johnson & Johnson, argenx and UCB scale new launches and as biosimilar programs prepare post-2030 entries.
Global Myasthenia Gravis Therapeutics Market Trends and Insights
Rising incidence & earlier diagnosis
Incidence rose to 68.5 new U.S. cases per million in 2024, reflecting growing awareness and improved insurance coverage for neuromuscular testing. AI-assisted ocular-motor analytics now confirm fatigue signatures in under 60 seconds, cutting average diagnostic lag from 2.3 years to less than 12 months in tertiary clinics. Early confirmation lets clinicians start immune-modifying therapy sooner, and centers that achieve sub-one-year diagnosis report 40% higher minimal-manifestation rates at two-year follow-up. Broader tele-neurology access, coupled with payer incentives for prompt work-ups, continues to enlarge the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market patient pool.
Accelerated approvals of FcRn/complement biologics
Between 2023 and 2025, four breakthrough drugs-rozanolixizumab, zilucoplan, nipocalimab and SC efgartigimod-completed regulatory review in just 6-8 months under priority pathways. Condensed timelines shorten cash-burn periods, encouraging venture investors and fostering big-pharma deal activity. Parallel approvals in the EU, Japan and Australia allow near-simultaneous launches, accelerating global revenue capture during exclusivity windows. These dynamics add scale and depth to the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market and validate precision immunology as a core growth theme.
High biologic therapy cost
Annual FcRn inhibitor expenditure approximates USD 833,000, while cost-utility studies suggest prices must fall by up to 88% to meet willingness-to-pay thresholds in the United States and Europe. Budget caps trigger prior-authorization delays of four to six weeks, and emerging-market patients often default to steroids or plasmapheresis because of high co-payments. Wide affordability gaps therefore temper demand growth for the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market despite clinical superiority of novel agents.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rare-disease incentives & premium pricing
- SC biologics improving adherence
- Low disease awareness in emerging economies
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Gene and cell therapies are the fastest-growing treatment category at a 9.73% CAGR, though medication regimens still captured 69.37% of 2024 revenue. Early CAR-T case studies show Quantitative MG scores dropping from 21 to 5, sustaining muscle strength gains without ongoing immunosuppression. Telitacicept's 98.1% MG-ADL response in late-stage trials and CAART technology that selectively depletes pathogenic B cells reinforce growing confidence in curative approaches. Venture capital and disease-foundation grants provide critical funding, while regulators familiar with AAV vectors streamline IND reviews. As one-time interventions mature, the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market may shift toward front-loaded revenue, with chronic medication budgets gradually pivoting to post-treatment monitoring.
The existing medication segment remains sizeable because steroids, cholinesterase inhibitors and IVIg continue to manage mild or rapidly progressive episodes. Nonetheless, FcRn antagonists and complement inhibitors now enable steroid tapering in nearly half of patients, eroding dependence on broad immunosuppressants. Combination protocols blending biologics with targeted gene-editing may create hybrid models of care that preserve maintenance margins while unlocking durable remission for high-risk groups. Such innovation sustains revenue diversity in the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market and cushions drug makers against binary regulatory outcomes.
Subcutaneous administration is growing 10.12% annually and is poised to chip away at intravenous dominance, which accounted for 63.56% of revenue in 2024. EMA endorsement of self-injected rozanolixizumab and FDA clearance for Vyvgart Hytrulo prefilled syringes confirm the safety and efficacy of patient-controlled delivery. SC dosing can be completed in five minutes at home, compared with several-hour infusion visits, lifting adherence to 89% and driving switch-over among patients eager to reduce clinic time. Such convenience broadens the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market size by engaging rural residents and mobility-limited patients who previously skipped biologic therapy.
Technology partnerships, like argenx's USD 30 million expansion with Halozyme, target higher drug concentrations and smaller injection volumes, enhancing comfort and logistics. The shift frees infusion chairs for other specialties, a benefit valued by hospital administrators, and lowers payer facility costs. Oral formulations remain confined to legacy cholinesterase inhibitors and steroids, yet future extended-release or nanoparticle biologics could move additional therapies into home care. Broader SC penetration will therefore continue reshaping revenue allocation within the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market.
The Myasthenia Gravis Therapeutics Market Report is Segmented by Treatment (Medication, Rapid Immunotherapies [Intravenous Immunoglobulin and More], Gene & Cell Therapies and More), Route of Administration (Oral, Intravenous and More), Drug Class (Cholinesterase Inhibitors, Monoclonal Antibodies and More), End-User (Hospitals, Home-Care Settings and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 44.43% of 2024 revenue, underpinned by broad insurance coverage and rapid biologic uptake following FDA breakthrough designations. Incidence now sits at 68.5 per million, equating to roughly 82,700 U.S. adults needing ongoing therapy. AI-enabled ocular-motor testing and tele-neurology reduce specialist bottlenecks, promoting early starts that heighten cumulative drug exposure. Competitive intensity rose in 2025 when Johnson & Johnson launched nipocalimab, adding price tension that may widen patient access by tempering annual cost escalators.
Europe follows with a cohesive regulatory environment that approved rozanolixizumab in January 2024 and SC self-administration in February 2025. Health-technology assessments secure 20-30% list-price discounts, yet still recognise orphan-drug value where real-world data show faster steroid tapering and fewer crises. Preference studies confirm 83% of European patients favor SC dosing, letting payers reallocate infusion budgets to drug acquisition. Conditional approvals require post-market surveillance, ensuring safety transparency while allowing income flow during data collection. Rising biosimilar programs for complement inhibitors could generate additional savings, potentially funding broader FcRn adoption across national formularies.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing region at a 9.78% CAGR, buoyed by PMDA and NMPA reviews that now lag U.S. clearances by less than six months. Japan approved efgartigimod as VYVDURA for generalized myasthenia gravis and immune thrombocytopenia, while China authorised both IV and SC forms for gMG and CIDP. Despite these gains, out-of-pocket costs still average 40% of annual household income in China, which caps utilisation for high-priced biologics. Tele-medicine and AI-based infrared spectroscopy with 100% diagnostic accuracy are beginning to close specialist gaps. Continued healthcare-infrastructure investment and local manufacturing initiatives, including planned FcRn biosimilars, should lift the regional contribution to the myasthenia gravis therapeutics market over the next decade.
- AstraZeneca
- argenx SE
- UCB
- Johnson & Johnson
- Novartis
- Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma
- CSL Behring
- Horizon Therapeutics
- Immunovant Inc.
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Roche
- Takeda Pharmaceuticals
- Astellas Pharma
- Pfizer
- CuraVac N.V.
- Chugai Pharmaceutical
- Abbvie
- Grifols
- Bausch Health
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Incidence & Earlier Diagnosis Of MG
- 4.2.2 Accelerating Approvals Of Complement- & FcRn-Targeted Biologics
- 4.2.3 Rare-Disease Incentives & Premium Pricing Leverage
- 4.2.4 Robust Clinical-Trial Pipeline Driven By Venture/Big-Pharma Deals
- 4.2.5 Self-Administered SC Biologics Improving Adherence
- 4.2.6 AI-Based Electromyography Analytics Enabling Earlier Intervention
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Cost Of Long-Term Biologic Therapy
- 4.3.2 Low Disease Awareness In Emerging Economies
- 4.3.3 Cold-Chain & Assay QA Complexity For mAbs
- 4.3.4 Price-Erosion Risk Post-Soliris LOE & Biosimilar Entry
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technology Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value-USD)
- 5.1 By Treatment
- 5.1.1 Medication
- 5.1.2 Rapid Immunotherapies
- 5.1.2.1 Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIg)
- 5.1.2.2 Plasmapheresis
- 5.1.3 Gene & Cell Therapies
- 5.1.4 Other Emerging Therapies
- 5.2 By Route of Administration
- 5.2.1 Oral
- 5.2.2 Intravenous
- 5.2.3 Sub-cutaneous
- 5.3 By Drug Class
- 5.3.1 Cholinesterase Inhibitors
- 5.3.2 Corticosteroids & Other Immunosuppressants
- 5.3.3 Monoclonal Antibodies
- 5.3.4 Complement Inhibitors
- 5.3.5 FcRn Antagonists
- 5.3.6 Others
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Specialty Neurology Clinics
- 5.4.3 Home-care Settings
- 5.4.4 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AstraZeneca
- 6.3.2 argenx SE
- 6.3.3 UCB Pharma
- 6.3.4 Johnson & Johnson (Janssen)
- 6.3.5 Novartis AG
- 6.3.6 Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma
- 6.3.7 CSL Behring
- 6.3.8 Horizon Therapeutics
- 6.3.9 Immunovant Inc.
- 6.3.10 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.11 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd
- 6.3.12 Takeda Pharmaceutical
- 6.3.13 Astellas Pharma
- 6.3.14 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.15 CuraVac N.V.
- 6.3.16 Chugai Pharmaceutical
- 6.3.17 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.18 Grifols S.A.
- 6.3.19 Bausch Health
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & unmet-need assessment




