PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848063

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848063
Food Acidulants - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The food acidulants market size was valued at USD 3.57 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 4.46 billion by 2030, advancing at a 4.54% CAGR over the period.
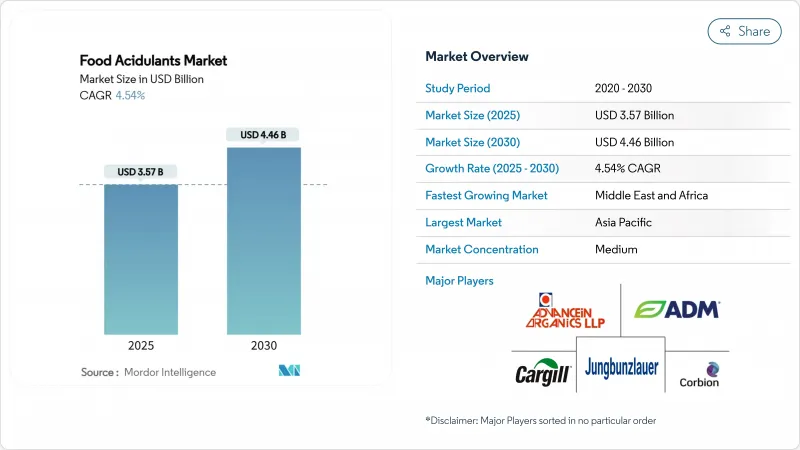
This growth is primarily driven by the implementation of stricter global food-safety regulations, increasing consumer preference for clean-label formulations, and the expanding adoption of processed foods in emerging economies. Regulatory developments in key regions, including China, the European Union, and Canada, present both challenges and opportunities for the adoption of naturally derived acidulants. Concurrently, innovations in bio-based production technologies are playing a pivotal role in reducing the carbon footprint associated with the production of citric, lactic, and succinic acids. Supply-chain vulnerabilities, particularly fluctuations in corn prices, are prompting manufacturers to diversify raw material sources, with a growing focus on cassava, sugarcane, and biowaste substrates. The competitive landscape is characterized by significant consolidation, exemplified by Tate and Lyle's acquisition of CP Kelco. Additionally, strategic investments in fermentation-based production assets are enhancing the industry's application-development capabilities, particularly in high-demand segments such as beverages, bakery products, and plant-based meat alternatives.
Global Food Acidulants Market Trends and Insights
Growing interest in natural and clean-label ingredients
With a growing emphasis on ingredient transparency, bio-based citric, malic, and lactic acids are increasingly securing premium-priced contracts. The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has introduced revised guidance on novel foods, which will come into effect in February 2025. This updated framework is streamlining the approval process for fermentation-derived acids, thereby accelerating their path to commercialization. Jungbunzlauer, a key player in the market, has strategically prioritized naturally fermented citric acid, enabling the company to establish supply agreements with European beverage manufacturers that require GRAS-certified ingredients. The demand for clean-label products is particularly strong in categories such as sparkling water, functional shots, and premium juices, where apple-derived malic acid plays a pivotal role in enhancing flavor profiles. Although scaling up fermentation capacity remains a capital-intensive endeavor, companies with robust biobased portfolios are successfully capturing higher margins, which help mitigate the impact of rising raw material costs.
High demand for processed and convenience foods
Urbanization and evolving lifestyles in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East regions are driving a significant increase in the demand for shelf-stable food products, including noodles, sauces, and ready-to-eat rice bowls. This sustained demand has resulted in consistently high baseline consumption of citric and acetic acids. In China, the implementation of GB 2760-2024 has introduced stricter regulations on synthetic preservatives while simultaneously expanding the permissible applications for organic acids. This regulatory shift has led to a notable rise in orders from domestic food processors. Furthermore, the lactic-acid bacteria can effectively mitigate off-flavors in plant-based dairy products, thereby unlocking new opportunities for value creation in this segment. Additionally, regional taste preferences, such as the tamarind-associated tartness popular in South Asia, are driving the development of customized acidulant blends tailored to local palates. To address the challenges posed by raw material price volatility, multinational corporations are implementing hedging strategies and diversifying their sourcing approaches by utilizing multiple feedstocks.
Corn price volatility post Black-Sea disruptions squeezing citric margins
Citric-acid fermenters primarily rely on corn steep liquor as a key input; however, disruptions in supply chains caused by war-related events have significantly increased corn prices. In the United States, domestic production capacity fulfills only one-third of the total demand, thereby intensifying the country's dependence on imports to bridge the gap. Smaller processors, particularly those without hedging mechanisms in place, are disproportionately affected by these cost escalations, leaving them vulnerable to operational shutdowns or potential acquisitions by larger entities. Although alternative substrates, such as cassava, present a possible solution, their adoption necessitates re-validation processes and substantial capital expenditure, further straining short-term profitability. The persistent price pressures in the market are driving larger firms to pursue vertical-integration strategies, enabling them to secure upstream feedstock acreage and mitigate supply chain risks effectively.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Shelf-stable plant-based meat demand boosting lactic and fumaric usage
- Cola-brand investments in low-sugar CSDs increasing phosphoric/malic uptake
- Stringent regulatory frameworks on food additives posing challenges
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, citric acid led the food acidulants market with a 64.8% share, supported by well-established supply chains and GRAS approvals across various jurisdictions. Succinic acid, though a niche segment, is experiencing a 10.2% CAGR (2025-2030), driven by fermentative processes that lower greenhouse gas emissions and facilitate its application in compostable packaging resins. Lactic acid, traditionally used for yogurt preservation, is expanding its applications to include vegan cheese and growth media for cultured meats. Phosphoric acid, despite facing regulatory challenges in cola formulations, remains functionally relevant.
Declining fermentation costs are enabling the emergence of alternatives. Bio-derived malic and fumaric acids are gaining traction in beverage and protein powder applications. The market for organic acids associated with plant-based meats is expected to grow significantly as precision fermentation capacity increases. Producers with expertise in metabolic engineering are diversifying their acid portfolios to reduce dependency on a single acid.
In 2024, synthetic routes accounted for 71.6% of the food acidulants market, reflecting the industry's long-standing dependence on petrochemical infrastructure. However, bio-based alternatives are experiencing significant growth, with a strong 9.4% CAGR (2025-2030), as brands increasingly aim to reduce their Scope 3 emissions. Corbion's circular lactic-acid plant in Thailand serves as a prime example, utilizing renewable feedstocks and closed-loop wastewater recycling to support clients in meeting ESG disclosure requirements.
Bio-based suppliers are not only delivering environmentally friendly solutions but also providing carbon-footprint declarations, enabling them to secure contracts in premium segments such as beverages and baby foods. Although these bio-based options carry an average price premium of 20%, buyers justify the additional cost through improved eco-label positioning. Over time, economies of scale and the implementation of regulatory carbon taxes are expected to reduce pricing disparities, gradually shifting the food acidulants market toward fermentation-based solutions.
The Food Acidulants Market Report is Segmented by Type (Citric Acid, Lactic Acid, Acetic Acid, and More), Source (Bio-based/Natural, Synthetic), Form (Dry/Powder, Liquid/Solution), Application (Beverages, Dairy and Frozen Desserts, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2024, Asia-Pacific held a leading 39.8% share of the food acidulants market, supported by China's extensive beverage and snack industries and India's rapidly growing packaged food sector. The Indian food processing industry plays a crucial role in the nation's economy, characterized by a strong export orientation and substantial growth opportunities. During 2023-24, the sector attracted USD 608 million in foreign direct investment. According to the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, processed food exports accounted for 23.4% of the country's total agricultural exports. Additionally, Southeast Asian processors benefit from regional trade agreements, driving increased intra-ASEAN beverage exports and boosting acidulant demand.
North America, though a mature market, continues to innovate, with clean-label carbonated soft drinks (CSDs) and plant-based meats driving incremental growth. The FDA's intensified oversight through its Human Foods Program has raised documentation requirements, favoring established players with comprehensive toxicological data. Meanwhile, domestic citric acid producers face margin pressures due to corn-price volatility, prompting diversification into alternative carbohydrate sources. In Europe, stringent additive regulations create a compliance barrier that supports premium pricing. While the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has streamlined approvals for naturally fermented acids, enabling easier market entry for bio-based suppliers, the purity standards outlined in Regulation (EU) 2024/2597 necessitate advanced analytical capabilities. Eastern European beverage manufacturers leverage lower operational costs and import acidulants from western facilities to meet EU harmonized standards.
The Middle East and Africa region is experiencing the fastest growth, with a robust CAGR of 8.3% (2025-2030), driven by urbanization, the expansion of quick-service restaurants (QSRs), and rising disposable incomes. Although acidulant usage in fruit-based beverages and shelf-stable dairy products is increasing, cold-chain infrastructure gaps in Sub-Saharan Africa limit growth potential. However, government investments in cold storage infrastructure could unlock additional demand, particularly for lactic-acid-based stabilizers. In South America, regional soft-drink manufacturers are reformulating products in response to sugar taxes, replacing phosphoric acid with malic acid to align with health-conscious consumer preferences. Additionally, Brazil's thriving citrus industry strengthens domestic citric acid production, reducing reliance on imports and enabling competitive pricing across Mercosur markets.
- Adavancein Organics LLP
- Archer Daniels Midland Co.
- Cargill Inc.
- Jungbunzlauer Suisse AG
- Corbion NV
- Brenntag SE
- Bartek Ingredients Inc.
- Jubilant Ingrevia Ltd.
- Eastman Chemical Co.
- Thirumalai Chemicals Ltd.
- Gadot Biochemical Industries Ltd.
- Tate and Lyle Plc
- RZBC Group Co. Ltd.
- Aditya Birla Chemicals
- FBC Industries Inc.
- Vinipul Inorganics India Pvt. Ltd.
- Nippon Shokubai Co. Ltd.
- Vishnupriya Chemicals Pvt. Ltd.
- Musashino Chemical Laboratory, Ltd.
- Vizag Chemicals
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Drivers
- 4.1.1 Growing interest in natural and clean-label ingredients
- 4.1.2 High demand for processed and convenience foods.
- 4.1.3 Shelf-stable plant-based meat demand boosting lactic and fumaric usage
- 4.1.4 Cola brand investments in low-sugar CSDs increasing phosphoric/malic uptake
- 4.1.5 Emphasis on food safety and regulatory compliance.
- 4.1.6 Rising consumer preference for enhanced flavor profiles is driving the demand for food acidulants.
- 4.2 Market Restraints
- 4.2.1 Corn price volatility post Black-Sea disruptions squeezing citric margins
- 4.2.2 Sub-Saharan cold-chain gaps limiting acidulants in chilled dairy drinks
- 4.2.3 U.S. consumer enamel-erosion concerns curbing phosphoric acid in CSDs
- 4.2.4 Stringent regulatory frameworks on food additives are posing challenges to the growth of the food acidulant market
- 4.3 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.4 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.5 Porters Five Forces
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Citric Acid
- 5.1.2 Lactic Acid
- 5.1.3 Acetic Acid
- 5.1.4 Phosphoric Acid
- 5.1.5 Malic Acid
- 5.1.6 Fumaric Acid
- 5.1.7 Succinic Acid
- 5.1.8 Tartaric Acid
- 5.1.9 Others (GDL, Gluconic, etc.)
- 5.2 By Source
- 5.2.1 Bio-based/Natural
- 5.2.2 Synthetic (Petro-/Corn-derived)
- 5.3 By Form
- 5.3.1 Dry/Powder
- 5.3.2 Liquid/Solution
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Beverages
- 5.4.2 Dairy and Frozen Desserts
- 5.4.3 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.4.4 Meat and Seafood
- 5.4.5 Sauces, Dressings and Condiments
- 5.4.6 Infant and Clinical Nutrition
- 5.4.7 Other Processed Foods
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 France
- 5.5.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pcific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 Australia
- 5.5.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 South Africa
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Adavancein Organics LLP
- 6.4.2 Archer Daniels Midland Co.
- 6.4.3 Cargill Inc.
- 6.4.4 Jungbunzlauer Suisse AG
- 6.4.5 Corbion NV
- 6.4.6 Brenntag SE
- 6.4.7 Bartek Ingredients Inc.
- 6.4.8 Jubilant Ingrevia Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Eastman Chemical Co.
- 6.4.10 Thirumalai Chemicals Ltd.
- 6.4.11 Gadot Biochemical Industries Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Tate and Lyle Plc
- 6.4.13 RZBC Group Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Aditya Birla Chemicals
- 6.4.15 FBC Industries Inc.
- 6.4.16 Vinipul Inorganics India Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Nippon Shokubai Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.18 Vishnupriya Chemicals Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.19 Musashino Chemical Laboratory, Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Vizag Chemicals
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




