PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848065

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848065
Indonesia Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
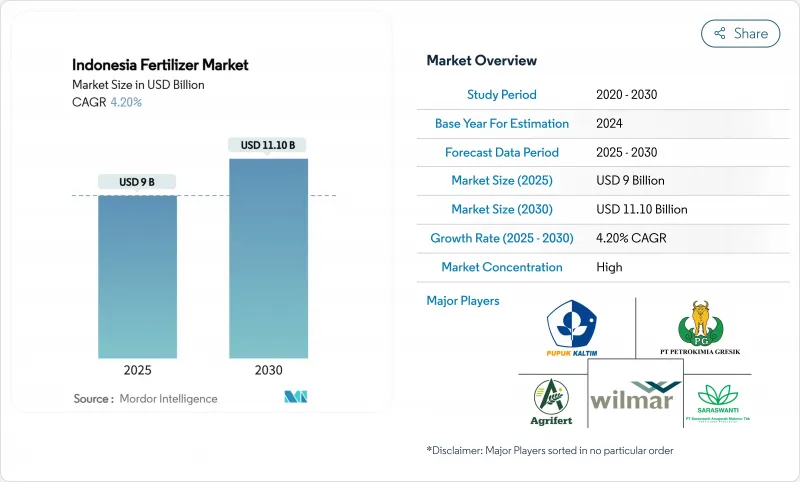
The Indonesia fertilizer market size stands at USD 9 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 11.1 billion by 2030, expanding at a 4.2% CAGR.
Strong public funding for input subsidies and the replanting of aging oil-palm estates forms the backbone of demand across the Indonesia fertilizer market. A government allocation of 9.5 million metric tons of subsidized product under the Highest Retail Price scheme stabilizes consumption even when natural-gas prices spike, compressing producer margins. New NPK blending projects worth more than USD 1 billion enhance domestic value addition and keep the Indonesia fertilizer market on track to serve regional export demand.
Competitive dynamics reflect extreme market concentration, with the top 5 companies, including PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT), PT Petrokimia Gresik, Wilmar International Limited, PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk, and Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group), maintaining significant positions through integrated palm oil operations. This concentration creates both operational efficiency and strategic vulnerability, as supply disruptions from major producers can significantly impact national food security.
Indonesia Fertilizer Market Trends and Insights
Government Fertilizer Subsidy (HET) Expansion
As per the Indonesian ministry, the 2025 budget earmarked 9.5 million metric tons of subsidized fertilizer, 4.6 million metric tons of urea, 4.2 million metric tons of NPK, and 500,000 metric tons of organic keeping prices at IDR 2,250/kg (USD 0.14) for urea and IDR 2,300/kg (USD 0.15) for NPK, levels far below commercial quotations This guaranteed volume underpins the Indonesia fertilizer market even as fiscal outlays approach USD 3.3 billion, roughly 2.8% of GDP. By linking deliveries to the e-RDKK farmer database, authorities minimize leakages and channel nutrients to priority crops. Suppliers also gain visibility on quarterly offtake, allowing smoother production scheduling and working-capital planning.
Rice And Corn Self-Sufficiency Programs
President Prabowo targets rice self-sufficiency by 2026 and corn self-sufficiency within three years, spurring wider adoption of balanced NPK over single-nutrient products across new cultivation zones in Sulawesi and Kalimantan. Higher planting density and double-cropping schedules lift per-hectare nutrient requirements, offsetting future efficiency gains from precision farming. Seed packages issued under the Kartini Tani program include fertilizer recommendations, nudging farmers toward integrated soil fertility management. Private distributors report that demand for zinc-enriched NPK has tripled in the eastern islands since mid-2024.
Natural-Gas Price Volatility Raising Urea Costs
Regasified LNG now trades at USD 16.77 per MMBtu versus USD 6 under the previous subsidy, adding USD 50-70 to the cost of every metric ton of urea and squeezing margins for domestic manufacturers. Producers seek long-term gas contracts indexed to Brent-minus formulas to stabilize input costs. Several plants are evaluating carbon-capture linked blue ammonia pathways to unlock concessional finance and hedge against fossil fuel volatility.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- New NPK Blending Plants Under Pupuk Indonesia
- Palm-Oil Plantation Replanting Cycle
- Environmental Pressure on Peatland Nutrient Runoff
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Straight fertilizers led with 54% of the Indonesia fertilizer market share in 2024, a position anchored by urea's 60% slice of nitrogen volume and by the government's HET-backed allocation of 4.6 million metric tons for the 2025 season. Abundant local ammonia feedstock keeps urea costs low, while wide dealer networks push product into remote rice and corn belts that consume the bulk of nitrogen inputs under the swasembada pangan plan. Calcium ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate fill soil-specific niches, and in-country ammonia synthesis largely feeds domestic demand, reinforcing leadership for nitrogenous grades within the Indonesia fertilizer market size.
Micronutrient fertilizers post the quickest climb, advancing at an 8.1% CAGR to 2030 as precision farming spreads from Java to Sumatra and supports export-oriented horticulture. Complex NPK sales also rise steadily because 2 million metric tons of new blending capacity lifts national nameplate output to 14 million metric tons, curbing reliance on imports and tailoring micronutrient coatings by micro-region. Phosphatic and potash grades remain exposed to freight swings because Indonesia imports almost all DAP, MAP, and MOP, while secondary nutrients gain traction in acidic soils across Kalimantan and Sumatra that limit long-term plantation yields.
The Indonesia Fertilizer Market Report is Segmented by Type (Complex Fertilizers and Straight Fertilizers {Nitrogenous Fertilizers, Phosphatic Fertilizers, Potash Fertilizers, and More}), and by Crop Type (Grains and Cereals, Pulses and Oilseeds, Commercial Crops, Fruits and Vegetables, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- PT Petrokimia Gresik
- Wilmar International Limited
- Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group)
- PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk
- Yara International ASA
- EuroChem Group AG
- ICL Group Ltd.
- OCI Global N.V.
- PT Meroke Tetap Jaya
- PT Jadi Mas
- PT Dupan Anugerah Lestari
- PT Pupuk Sriwidjaya Palembang
- PT Pupuk Kujang Cikampek
- PT Pupuk Iskandar Muda
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Government fertilizer subsidy (HET) expansion
- 4.2.2 Rice and corn self-sufficiency programs
- 4.2.3 New NPK blending plants under Pupuk Indonesia
- 4.2.4 Palm-oil plantation replanting cycle
- 4.2.5 Growth in export-oriented horticulture needing specialty nutrients
- 4.2.6 Early adoption of drone-based precision fertilization in Java
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Subsidy budget cuts creating supply gaps
- 4.3.2 Natural-gas price volatility raising urea costs
- 4.3.3 Proliferation of counterfeit fertilizers in informal channels
- 4.3.4 Environmental pressure on peatland nutrient runoff
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Complex Fertilizers
- 5.1.2 Straight Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.1 Nitrogenous Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.1.1 Urea
- 5.1.2.1.2 Calcium Ammonium Nitrate (CAN)
- 5.1.2.1.3 Ammonia
- 5.1.2.1.4 Ammonium Nitrate
- 5.1.2.1.5 Ammonium Sulfate
- 5.1.2.1.6 Other Nitrogenous Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.2 Phosphatic Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.2.1 Mono-ammonium Phosphate (MAP)
- 5.1.2.2.2 Di-ammonium Phosphate (DAP)
- 5.1.2.2.3 Triple Super-phosphate (TSP)
- 5.1.2.2.4 Other Phosphatic Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.3 Potash Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.3.1 Muriate of Potash (MOP)
- 5.1.2.3.2 Other Potash Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.4 Secondary Nutrient Fertilizers
- 5.1.2.5 Micronutrients
- 5.2 By Crop Type
- 5.2.1 Grains and Cereals
- 5.2.2 Pulses and Oil Seeds
- 5.2.3 Commercial Crops
- 5.2.4 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.2.5 Turf and Ornamental Crops
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 PT Pupuk Kalimantan Timur (PKT)
- 6.4.2 PT Petrokimia Gresik
- 6.4.3 Wilmar International Limited
- 6.4.4 Agrifert Marketing Pte Ltd (Kuok Group)
- 6.4.5 PT Saraswanti Anugerah Makmur Tbk
- 6.4.6 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.7 EuroChem Group AG
- 6.4.8 ICL Group Ltd.
- 6.4.9 OCI Global N.V.
- 6.4.10 PT Meroke Tetap Jaya
- 6.4.11 PT Jadi Mas
- 6.4.12 PT Dupan Anugerah Lestari
- 6.4.13 PT Pupuk Sriwidjaya Palembang
- 6.4.14 PT Pupuk Kujang Cikampek
- 6.4.15 PT Pupuk Iskandar Muda
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




