PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848081

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848081
Mycotoxin Testing - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The global mycotoxin testing market size is expected to reach a size of USD 2.13 billion in 2025 and is projected to expand to USD 3.08 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 7.67% during the forecast period.
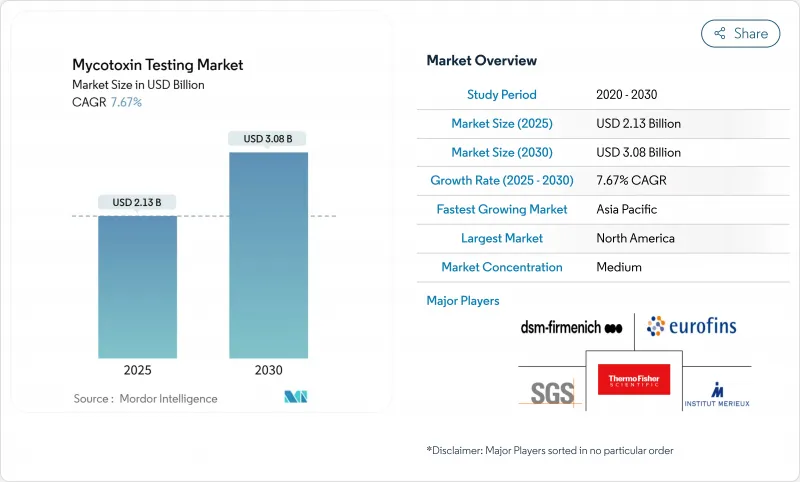
This growth trajectory reflects the escalating regulatory pressure following high-profile contamination incidents, including France's rejection of Turkish dried figs due to aflatoxin levels exceeding legal limits by 20 times in December 2024 and the tragic death of 450 dogs in Malawi from aflatoxin-contaminated maize. Chromatography-based platforms remain the benchmark for confirmatory analysis, yet rapid test kits are gaining ground as processors seek point-of-use screening. Climate-linked shifts in fungal prevalence, such as the surge in Fusarium toxins, further underpin routine testing demand. Global laboratories scale capacity in response to the European Union's Regulation 2023/915 and the United States' LAAF mandates, while Asia-Pacific laboratories add accredited instrumentation to serve rising export volumes according to FDA (Food and Drug Administration .
Global Mycotoxin Testing Market Trends and Insights
Stringent Food Safety Regulations
Regulatory tightening has fundamentally reshaped testing requirements, with the EU's Regulation 2023/915 consolidating maximum contaminant levels and introducing binding limits for T-2 and HT-2 toxins effective July 2024. The FDA's expansion of its Mycotoxins in Domestic and Imported Human Foods Compliance Program to include T-2/HT-2 toxins and zearalenone monitoring represents a parallel enforcement escalation. These regulatory shifts create cascading compliance costs that favor larger testing laboratories with advanced analytical capabilities. The implementation of limit of quantification requirements differentiating screening from confirmatory methods has particularly advantaged chromatography-based testing over traditional approaches. Australia's integration of food safety requirements into the Biosecurity Import Conditions system effective June 2025 exemplifies the global trend toward streamlined yet more rigorous import controls according to the Australian Department of Agriculture.
Increased Contamination Incidents in Grains, Nuts, and Processed Foods
Driven by climate-induced contamination patterns, testing demand has surged. In 2022, Serbia reported that 73.2% of its maize samples surpassed EU aflatoxin B1 limits, with peak levels hitting 527 µg/kg, as noted by MDPI (Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute). The European Food Safety Authority has broadened testing protocols, identifying emerging risks like engineered nanomaterials and rare earth elements infiltrating food chains. Highlighting the ongoing fungal threats, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare flagged multiple mold detection incidents in 2024-2025, including in sweet potato products and rice cakes. There's a growing recognition of the link between temperature and humidity fluctuations and mycotoxin levels, with elevated warmth and moisture leading to heightened contamination. This heightened climate sensitivity has shifted the focus towards proactive testing strategies, moving away from mere reactive contamination management.
High Cost of Advanced Testing Equipment and Reagents
Advanced LC-MS/MS systems, pivotal for mycotoxin testing, demand hefty investments surpassing USD 500,000. This figure doesn't account for the annual reagent expenses, which can soar to USD 100,000, especially in high-throughput labs. Adding to the industry's woes, the FDA is reportedly eyeing a 17% budget cut for FY 2026. Such a move could halt the Proficiency Testing Program for food labs, jeopardizing quality control and inflating compliance costs for private entities. Furthermore, crafting certified reference materials for intricate matrices-like corn/peanut blended vegetable oil-demands significant outlays in method validation and inter-laboratory studies. These financial and operational challenges are further compounded by the need for continuous training of laboratory personnel to handle advanced systems effectively. Additionally, the lack of uniform global regulations for mycotoxin testing creates inconsistencies in testing standards, complicating international trade. As cost pressures mount, many are turning to rapid testing alternatives, albeit often at the expense of analytical precision in favor of quicker results.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancements in Testing Technologies
- Expansion of Certified Testing Laboratories in Emerging Markets
- Shortage of Skilled Technicians for Handling Complex Instruments
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, chromatography-based technologies held a commanding 37.34% market share, bolstered by regulatory mandates for confirmatory analyses and the heightened precision required for trace-level detections. Meanwhile, rapid test kits emerged as the industry's fastest-growing segment, boasting a 9.12% CAGR projected through 2030, underscoring a pronounced shift towards point-of-use testing. Waters Corporation's launch of the waters_connect Data Intelligence software in November 2024 highlights the industry's pivot, steering chromatographic platforms towards cloud-centric business intelligence and heightened audit readiness. While immunoassay methods remain the go-to for primary screenings, there's a noticeable uptick in the adoption of spectroscopy and biosensor methods for real-time monitoring.
Artificial intelligence's integration with conventional analytical techniques is carving out a competitive edge. Notably, machine learning algorithms are refining hyperspectral imaging's accuracy for mycotoxin detection in cereal grains, as highlighted by MDPI (Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute). Innovations in nanotechnology and microfluidics are propelling the momentum of other technologies, such as novel biosensor platforms and portable detection devices. Furthermore, advancements like time-resolved fluorescence immunoassays, which now detect aflatoxin B1 at an impressive 0.3 µg/kg limit, underscore the industry's relentless pursuit of heightened sensitivity across all platforms.
The Mycotoxin Testing Market Report is Segmented by Technology Type (Chromatography-Based, Immunoassay-Based, Rapid Test Kits, Spectroscopy and Biosensor-Based, and Other Technologies), Mycotoxin Type (Aflatoxins, Ochratoxin A, Patulin, Fusarium Toxins, and Other Mycotoxins), Tested Commodity (Food, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
In 2024, North America secured a commanding lead with a 34.89% market share, thanks to stringent FDA enforcement and a robust testing infrastructure. Demonstrating its dedication, the FDA has set aside USD 15 million in its FY 2025 budget, zeroing in on microbiological and chemical safety. Canada's 2024-2025 departmental plan prioritizes regulatory modernization and boosts laboratory capacity for disease detection, reinforcing the region's testing infrastructure.
The Asia-Pacific region, however, is making waves, projecting a notable 9.45% CAGR through 2030. Japan's swift action on mold detection, following several contamination incidents in 2024-2025, underscores the region's dedication to food safety. India's FSSAI has extended foreign facility registration requirements to September 2024, signaling the shifting regulatory landscape in emerging markets.
Europe benefits from harmonized regulations under EU Regulation 2023/915, yet Brexit has complicated trade dynamics between the UK and the EU. Meanwhile, the European Environment Agency warns of mycotoxin exposure due to shifting climate conditions, stressing the urgency for adaptive testing strategies. In South America, key grain-producing regions are battling climate-induced contamination issues. Concurrently, the Middle East and Africa are bolstering their testing infrastructures to meet export standards.
- Eurofins Scientific SE
- SGS S.A.
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- Institut Merieux
- DSM-Firmenich AG
- Neogen Corporation
- SCIEX
- Symbio Labs
- TUV SUD
- Fera Science Limited
- Charm Sciences
- ALS Limited
- Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- Waters Corporation
- Microbac Laboratories, Inc.
- Shimadzu Corporation
- Randox Laboratories
- Romer Labs
- Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- Bruker
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing awareness among consumers about food safety
- 4.2.2 Stringent food safety regulations
- 4.2.3 Increased contamination incidents in grains, nuts, and processed foods
- 4.2.4 Advancements in testing technologies
- 4.2.5 Expansion of certified testing laboratories in emerging markets
- 4.2.6 Increased adoption of rapid testing kits
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of advanced testing equipment and reagents
- 4.3.2 Lack of standardized testing regulations
- 4.3.3 Limited access to accredited labs in developing regions
- 4.3.4 Shortage of skilled technicians for handling complex instruments
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Technology Type
- 5.1.1 Chromatography-based
- 5.1.2 Immunoassay-based
- 5.1.3 Rapid Test Kits
- 5.1.4 Spectroscopy and Biosensor-based
- 5.1.5 Other Technologies
- 5.2 By Mycotoxin Type
- 5.2.1 Aflatoxins
- 5.2.2 Ochratoxin A
- 5.2.3 Patulin
- 5.2.4 Fusarium Toxins
- 5.2.5 Other Mycotoxins
- 5.3 By Tested Commodity
- 5.3.1 Food
- 5.3.1.1 Meat and Poultry
- 5.3.1.2 Dairy
- 5.3.1.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.3.1.4 Processed Food
- 5.3.1.5 Other Food
- 5.3.2 Pet Food and Animal Feed
- 5.3.1 Food
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.2 Germany
- 5.4.2.3 Spain
- 5.4.2.4 France
- 5.4.2.5 Italy
- 5.4.2.6 Russia
- 5.4.2.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials (if available), Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Eurofins Scientific SE
- 6.4.2 SGS S.A.
- 6.4.3 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.4.4 Institut Merieux
- 6.4.5 DSM-Firmenich AG
- 6.4.6 Neogen Corporation
- 6.4.7 SCIEX
- 6.4.8 Symbio Labs
- 6.4.9 TUV SUD
- 6.4.10 Fera Science Limited
- 6.4.11 Charm Sciences
- 6.4.12 ALS Limited
- 6.4.13 Agilent Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.14 Waters Corporation
- 6.4.15 Microbac Laboratories, Inc.
- 6.4.16 Shimadzu Corporation
- 6.4.17 Randox Laboratories
- 6.4.18 Romer Labs
- 6.4.19 Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.
- 6.4.20 Bruker
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




