PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848120

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848120
South America Sugar Substitute - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
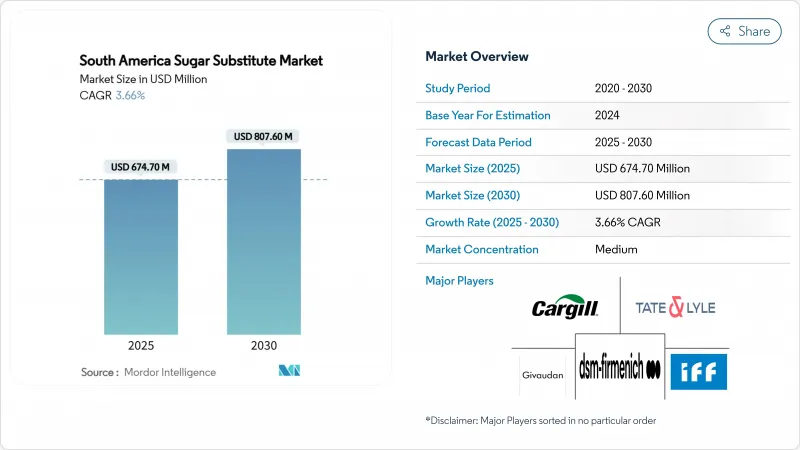
The South America sugar substitute market reached USD 674.7 million in 2025 and is projected to reach a market size of USD 807.6 million by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 3.66%.
Healthy-eating trends, rapid urbanization, and steady investments in product reformulation continue to underpin market expansion. Momentum is especially strong for naturally sourced molecules, as food and beverage formulators respond to clean-label purchasing criteria, while multinational soft-drink and dairy brands reformulate legacy recipes to comply with voluntary sugar-reduction pledges. In parallel, pharmaceutical manufacturers are adopting polyols to improve palatability in pediatric and geriatric dosage forms and to protect moisture-sensitive actives. Strategic sourcing programs that favor cane-based feedstocks, combined with South America's maturing biotech fermentation capacity, are lowering production costs, narrowing price gaps with refined sugar, and further boosting adoption. At the same time, trade liberalization within Mercosur is expanding cross-border supply networks for stevia leaf, erythritol, and monk-fruit extracts, amplifying competitive intensity within the region.
South America Sugar Substitute Market Trends and Insights
Adoption of natural sweeteners due to clean-label demand
Food processors are adding stevia glycosides, monk-fruit mogrosides, and fermented erythritol to shorten ingredient lists and replace chemical-sounding additives. National supermarket chains in the region now dedicate prominent shelf space to products labeled "100% natural sweetened," reinforcing mainstream visibility. Ingredient manufacturers have responded by scaling leaf-extraction and precision-fermentation plants near sugarcane hubs in Sao Paulo state, cutting freight distances and greenhouse-gas emissions. Continuous investment in purity-enhancement technologies has reduced off-notes that historically limited usage levels. As a result, the South America sweetener market is witnessing higher inclusion rates across dairy, cereal, and ready-to-drink categories. The growing consumer demand for clean-label products has accelerated research and development in natural sweetener extraction methods. Manufacturing facilities are implementing advanced filtration systems and enzymatic processes to improve the taste profile of these alternatives while maintaining their natural appeal.
Growing health consciousness and shift toward low-calorie diets
Post-pandemic consumer surveys indicate that calorie count ranks among the top three front-of-pack attributes influencing purchase decisions in Brazil and Colombia. Beverage multinationals have consequently lowered average sugar concentration per serving, substituting a blend of sucralose and steviol glycosides to preserve taste while delivering zero-calorie benefits. Meal-replacement brands are similarly replacing maltodextrin fillers with functional polyols that provide sweetness alongside fewer digestible carbohydrates. Mass-media health campaigns from regional ministries are accelerating these preferences, positioning low-calorie sweeteners as an accessible tool for weight management. The increasing prevalence of diabetes and obesity in South American countries has further intensified consumer demand for sugar alternatives. Additionally, government initiatives promoting sugar reduction in processed foods have compelled manufacturers to reformulate their products using sugar substitutes .
Regulatory restrictions on usage limits and labeling of artificial sweeteners
Chile caps acesulfame-K usage in carbonated drinks at 350 mg/L, lower than Codex Alimentarius benchmarks, forcing localized reformulation that can raise formulation complexity and cost according to the Chile Ministry of Health. Uruguay mandates front-label identifications such as "contains non-nutritive sweeteners," which may deter older consumers skeptical of synthetic additives. Labeling stipulations that require a quantitative declaration of each high-intensity sweetener further complicate space-constrained packaging design. Some nutraceutical exporters also face additional analytical testing at customs to verify compliance, lengthening lead times and adding to working-capital requirements, according to the Chile Ministry of Health. These regulatory frameworks vary significantly across regions, creating operational challenges for manufacturers seeking global market expansion. The inconsistent regulations between countries often necessitate multiple product formulations, increasing production costs and reducing operational efficiency.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising prevalence of diabetes and obesity across the region
- Government initiatives promoting healthier lifestyles and sugar reduction
- Cultural preference for traditional sugar-based foods and beverages
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Sales of high-intensity molecules such as aspartame, sucralose, and steviol glycosides reached 64.20% of revenue in 2024, making them the largest contributor to the South America sweetener market. Over the forecast window, stable cost profiles, high sweetness potency, and extensive safety dossiers will keep these molecules in mainstream beverage, confectionery, and pharmaceutical formulations. Brands also favor sucralose for its heat stability during UHT processing, while new stevia Reb M solutions are demonstrating improved sensory performance. Nevertheless, sugar polyols are projected to post an 8.10% CAGR, outpacing overall category growth, on the back of rising application in chewing gum, chocolate coatings, and diabetic bakery goods.
Formulators closely monitor evolving regulatory attitudes. While aspartame gained renewed attention after global toxicology reviews, regional authorities retained existing acceptable daily intake levels, providing short-term stability for beverage and tabletop-sweetener volumes. Sucralose continues to gain share in blended systems, often paired with acesulfame-K to mask temporal bitterness. Meanwhile, entrepreneurial brands are leveraging erythritol's favorable glycemic impact to capture health-conscious consumers.
Synthetic molecules such as sucralose and aspartame captured 48.90% of the South America sweetener market share in 2024, owing to their predictable quality parameters and mature sourcing networks. They remain preferred in mainstream CSD lines, large-scale ice-cream production, and powder soft-drink mixes where consistent flavor, supply reliability, and competitive cost outweigh natural positioning. However, biotechnologically fermented ingredients are forecast for the fastest growth at an 8.80% CAGR between 2025 and 2030. Advances in precision fermentation of Reb M stevia and novel rare sugar synthesis have increased yields, lowered solvent usage, and reduced unit costs.
Plant-derived ingredients such as monk fruit extracts continue to enjoy a "natural halo," but supply constraints stemming from limited agricultural acreage in Asia and complex extraction processes temper their scalability. As fermentation technologies mature, however, the line between natural and synthetic blurs, shifting narratives toward "nature-identical" positioning. Top beverage brands increasingly communicate carbon-footprint metrics on-pack, with biotech-fermented Reb M demonstrating lower land use compared with traditional stevia leaf farming.
The South America Sugar Substitute Market is Segmented by Type (High-Intensity Sweeteners, and Sugar Polyols), by Origin (Plant Derived, Synthetic, and Biotechnologically Fermented), by Form (Powder, and Liquid), by Application (Food, Beverages, Pharmaceuticals, and Other Applications), and by Geography (Brazil, Argentina, and Rest of South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Cargill, Incorporated
- Tate & Lyle PLC
- Ingredion Incorporated
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- GLG Life Tech Corporation
- Roquette Freres S.A.
- Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
- Celanese Corporation
- Merisant Company
- Tereos S.A.
- Kerry Group plc
- Sudzucker AG
- DSM-Firmenich AG
- International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc.
- Evolva Holding SA
- Givaudan SA
- Corbion N.V.
- Apura Ingredients, Inc.
- Sensient Technologies Corporation
- Axiom Foods, Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Adoption of Natural Sweeteners Due To Clean Label Demand
- 4.2.2 Growing Health Consciousness and Shift Toward Low-Calorie Diets
- 4.2.3 Rising Prevalence of Diabetes and Obesity Across The Region
- 4.2.4 Rising Use of Sugar Substitutes in Processed Foods
- 4.2.5 Rising Shift to Lower-Carbon Footprint Ingredients
- 4.2.6 GGovernment Initiatives Promoting Healthier Lifestyles and Sugar Reduction
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Regulatory Restrictions on Usage Limits and Labeling of Artificial Sweeteners
- 4.3.2 Cultural Preference for Traditional Sugar-Based Foods and Beverages
- 4.3.3 Higher Cost of Natural and Low-Calorie Sweeteners Compared to Conventional Sugar
- 4.3.4 Taste and Aftertaste Concerns Affecting Consumer Acceptance
- 4.4 Supply Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 High-Intensity Sweeteners
- 5.1.1.1 Acesulfame Potassium
- 5.1.1.2 Advantame
- 5.1.1.3 Aspartame
- 5.1.1.4 Neotame
- 5.1.1.5 Saccharin
- 5.1.1.6 Sucralose
- 5.1.1.7 Stevia
- 5.1.1.8 Monk Fruit
- 5.1.1.9 Other High-Intensity Sweeteners
- 5.1.2 Sugar Polyols
- 5.1.2.1 Sorbitol
- 5.1.2.2 Xylitol
- 5.1.2.3 Maltitol
- 5.1.2.4 Erythritol
- 5.1.2.5 Other Sugar Polyols
- 5.1.1 High-Intensity Sweeteners
- 5.2 By Origin
- 5.2.1 Plant-Derived
- 5.2.2 Synthetic
- 5.2.3 Biotechnologically Fermented
- 5.3 By Form
- 5.3.1 Powder
- 5.3.2 Liquid
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Food
- 5.4.1.1 Bakery and Cereals
- 5.4.1.2 Confectionery
- 5.4.1.3 Dairy and Dairy Alternatives
- 5.4.1.4 Sauces, Condiments and Dressings
- 5.4.1.5 Other Food Applications
- 5.4.2 Beverage
- 5.4.2.1 Carbonated Soft Drinks
- 5.4.2.2 RTD Tea and Coffee
- 5.4.2.3 Sports and Energy Drinks
- 5.4.2.4 Other Beverages
- 5.4.3 Pharmaceuticals
- 5.4.4 Other Applications
- 5.4.1 Food
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.3 Rest of South America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials, Strategic Info, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cargill, Incorporated
- 6.4.2 Tate & Lyle PLC
- 6.4.3 Ingredion Incorporated
- 6.4.4 Archer Daniels Midland Company
- 6.4.5 GLG Life Tech Corporation
- 6.4.6 Roquette Freres S.A.
- 6.4.7 Ajinomoto Co., Inc.
- 6.4.8 Celanese Corporation
- 6.4.9 Merisant Company
- 6.4.10 Tereos S.A.
- 6.4.11 Kerry Group plc
- 6.4.12 Sudzucker AG
- 6.4.13 DSM-Firmenich AG
- 6.4.14 International Flavors & Fragrances, Inc.
- 6.4.15 Evolva Holding SA
- 6.4.16 Givaudan SA
- 6.4.17 Corbion N.V.
- 6.4.18 Apura Ingredients, Inc.
- 6.4.19 Sensient Technologies Corporation
- 6.4.20 Axiom Foods, Inc.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK




