PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848129

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848129
Pulmonary Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The pulmonary drugs market size is valued at USD 18.55 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 24.62 billion by 2030, reflecting a 5.83% CAGR.
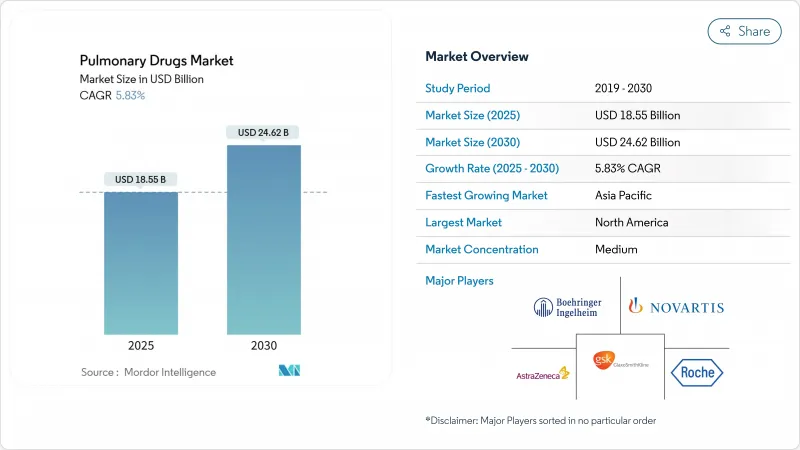
Rising respiratory disease prevalence, an aging global population, and steady innovation in inhaled and biologic therapies are the main engines of growth. Demand also tracks worsening air quality, with the World Health Organization reporting that nearly the entire world lives in areas exceeding particulate-matter limits. At the same time, patient adherence technologies and eco-friendly propellants broaden product appeal, while patent expirations spur both generic competition and life-cycle management strategies. North America leads revenue generation, but Asia-Pacific shows stronger momentum as healthcare access expands and urban pollution intensifies.
Global Pulmonary Drugs Market Trends and Insights
Growing Burden of Respiratory Diseases
Air pollution drives mounting morbidity and mortality, causing 4.2 million deaths each year worldwide and accounting for one-quarter of COPD fatalities. Emerging economies feel the heaviest impact because industrial activity often outpaces regulatory oversight. Economic costs accumulate through lost productivity and greater hospital utilization, heightening the need for chronic pharmacologic management. COPD prevalence reached 12.5 million cases in the United States by 2020, with marked variation by race and age. The resulting demand fuels sustained expansion of the pulmonary drugs market as payers prioritize preventive care and exacerbation reduction.
Aging Global Population
Older adults exhibit diminished lung elasticity and weaker immune response, making them prone to chronic respiratory conditions. In the United States, 51.4% of adults live with multiple chronic illnesses, and respiratory disease often overlaps cardiovascular and metabolic disorders. That comorbidity pattern encourages use of fixed-dose combination inhalers that limit pill burden and simplify regimens. Developed regions already experience rapid population aging, but emerging countries are following close behind, enlarging the future patient pool. This demographic wave underpins long-run volume growth for the pulmonary drugs market.
Stringent Regulatory Framework
Heightened pharmacovigilance has lengthened review cycles. The FDA recently attached Guillain-Barre warnings to RSV vaccines, signaling more conservative risk-benefit thresholds for respiratory products. Manufacturing audits also intensified; quality citations against multiple active-ingredient plants caused temporary production halts. While such vigilance protects patients, it increases development cost and can slow product launches, particularly affecting smaller innovators and emerging-market manufacturers. Larger firms may benefit from lower competitive entry, but their compliance spending continues to rise.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technological Advancements in Inhalation Therapies
- Rising Adoption of Biologic Therapies
- Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Combination inhalers generated 28.65% of pulmonary drugs market size in 2024, reinforcing clinician preference for multi-mechanism control of airflow limitation. Triple-therapy products like Breztri met Phase III asthma endpoints in 2025, signalling broader label opportunities and deeper formulary penetration. Beta-2 agonists and anticholinergics continue as backbone components inside these fixed-dose platforms, sustaining mature revenue bases. Monoclonal antibodies, though currently smaller in volume, clock a 7.53% CAGR, propelled by approvals in eosinophilic COPD and severe asthma. Corticosteroid monotherapies face modest growth as safety concerns shift interest toward targeted biologics. Anti-leukotrienes and antihistamines preserve niche use in pediatric and allergy-linked cases, while pipeline agents targeting novel inflammatory mediators foreshadow future competitive cycles. The diverse therapeutic arsenal underscores why the pulmonary drugs market remains competitive yet opportunity-rich.
Combination-therapy dominance also shapes manufacturing investment as firms upgrade fill-finish lines to accommodate dual canisters and triple-moiety dry-powder blends. Branded leaders hedge against generic erosion by bundling device innovations such as dose counters and adherence trackers. Meanwhile, monoclonal antibody producers scale up single-use bioreactors to reduce batch contamination risk and comply with evolving good-manufacturing-practice rules. The strategic mix of small-molecule inhalers and injectable biologics leaves purchasers juggling formulary rebates, which in turn shifts contracting power toward wholesalers well versed in complex negotiation.
Asthma contributed 42.56% of pulmonary drugs market share in 2024 due to its high prevalence and guideline-mandated long-term controller therapy. Biologics addressing Type 2 inflammation build on this base, offering step-up options for uncontrolled disease. COPD remains sizeable but still sees high unmet need for disease-modifying interventions, a gap partially closed by the 2024 approval of ensifentrine. Allergic rhinitis advances fastest at an 8.99% CAGR, supported by combo nasal sprays that merge antihistaminic and corticosteroid activity for rapid symptom relief. Pulmonary arterial hypertension commands premium pricing despite fewer patients, making it disproportionately lucrative. Cystic fibrosis treatments benefit from orphan incentives, though the overall pulmonary drugs market size in that subsegment stays limited by population. Emerging indications such as idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis inch forward as research unravels fibrosis-driving pathways, attracting early-stage venture funding.
Geographic treatment patterns differ: asthma biologic uptake climbs steadily in the United States and Germany, while COPD triple inhaler adoption outpaces elsewhere due to hospital-driven protocols. In Asia-Pacific, rhinitis therapy growth rides rising urban allergen exposure. Such regional nuances push manufacturers to tailor educational campaigns, reimbursement dossiers, and supply chains, reflecting the nuanced segmentation landscape inside the pulmonary drugs market.
The Pulmonary Drugs Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Beta-2 Agonists, and More), Indication (Asthma, COPD, and More), Route of Administration (Inhaled, Oral, and More), Distribution Channel (Hospital Pharmacies, and More), Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, The Middle East and Africa, and South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained 38.54% of 2024 revenue, buoyed by high biologic uptake and favorable reimbursement structures. U.S. Medicare redesigns for 2025 introduce negotiated ceiling prices, increasing payer leverage yet promising broader affordability once drugs qualify for negotiation. Canadian provinces expand biologic coverage, though tendering keeps net prices under pressure. The region also drives device innovation, with several FDA-de novo clearances for smart inhalers shaping clinical expectations.
Europe remains a core market characterized by universal coverage and stringent cost-effectiveness rules. Germany, the United Kingdom, and France collectively command the largest slice of regional spending, underpinned by aging demographics and strong environmental policies aimed at cutting particulate emissions. Pan-EU initiatives streamline approval pathways, easing multi-country launches and shortening time-to-market. However, reference-pricing frameworks limit high list prices, directing manufacturers toward outcomes-based contracts, particularly for biologics.
Asia-Pacific records the fastest 6.54% CAGR through 2030. Rapid urbanization and coal-heavy power generation worsen air-quality metrics, expanding the patient pool. China invests in local production of inhaled generics to curb import dependence, although premium biologics still rely on multinational supply. India's domestic industry scales up dry-powder inhaler output, supporting both export and local demand. Japanese guidelines widen indications for triple therapy, spurring prescription growth, while Australia funds remote-monitoring pilots to serve rural COPD patients. Southeast Asian countries improve reimbursement, yet affordability remains a hurdle, leaving room for tiered-pricing strategies across the pulmonary drugs market.
- AstraZeneca
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Boehringer Ingelheim
- Roche
- Novartis
- Pfizer
- Sanofi
- Merck
- Teva Pharmaceutical Industries
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Chiesi Farmaceutici
- Circassia Group Plc
- Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma
- Viatris
- Cipla
- Grifols
- Sunovion Pharmaceuticals
- Mylan
- Takeda Pharmaceuticals
- Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Burden of Respiratory Diseases
- 4.2.2 Aging Global Population
- 4.2.3 Technological Advancements in Inhalation Therapies
- 4.2.4 Increasing Environmental Risk Factors
- 4.2.5 Rising Adoption of Biologic Therapies
- 4.2.6 Expansion of Digital Health and Remote Monitoring Solutions
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Stringent Regulatory Framework
- 4.3.2 Adverse Effects and Safety Concerns
- 4.3.3 Escalating Pricing and Reimbursement Pressures
- 4.3.4 Patent Expiry and Generic Competition
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Drug Class
- 5.1.1 Beta-2 Agonists
- 5.1.2 Anticholinergic Agents
- 5.1.3 Oral & Inhaled Corticosteroids
- 5.1.4 Anti-Leukotrienes
- 5.1.5 Antihistamines
- 5.1.6 Monoclonal Antibodies
- 5.1.7 Combination Drugs
- 5.1.8 Other Drug Classess
- 5.2 By Indication
- 5.2.1 Asthma
- 5.2.2 COPD
- 5.2.3 Allergic Rhinitis
- 5.2.4 Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- 5.2.5 Cystic Fibrosis
- 5.2.6 Other Indications
- 5.3 By Route of Administration
- 5.3.1 Inhaled
- 5.3.2 Oral
- 5.3.3 Injectable/IV/Sub-Cutaneous
- 5.3.4 Intranasal
- 5.3.5 Other Route of Administrations
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.4.2 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.4.3 Other Distribution Channels
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 AstraZeneca PLC
- 6.3.2 GlaxoSmithKline PLC
- 6.3.3 Boehringer Ingelheim GmbH
- 6.3.4 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- 6.3.5 Novartis AG
- 6.3.6 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.7 Sanofi SA
- 6.3.8 Merck & Co., Inc.
- 6.3.9 Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd.
- 6.3.10 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.11 Chiesi Farmaceutici S.p.A.
- 6.3.12 Circassia Group Plc
- 6.3.13 Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.
- 6.3.14 Viatris Inc.
- 6.3.15 Cipla Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Grifols S.A.
- 6.3.17 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.18 Mylan NV
- 6.3.19 Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Ltd.
- 6.3.20 Vertex Pharmaceuticals Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




