PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910623

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1910623
Liver Diseases Therapeutics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2026 - 2031)
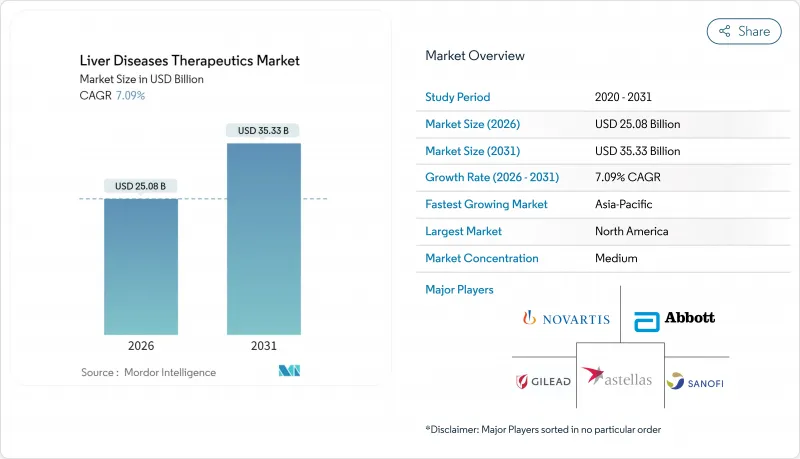
The Liver Diseases Therapeutics Market is expected to grow from USD 23.42 billion in 2025 to USD 25.08 billion in 2026 and is forecast to reach USD 35.33 billion by 2031 at 7.09% CAGR over 2026-2031.
Robust demand is underpinned by breakthrough regulatory approvals, the rising global prevalence of viral hepatitis and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), and technological leaps in RNA-based delivery platforms. Manufacturers prioritise precision medicine, integrating companion diagnostics that stratify patients by viral genotype, fibrosis stage, or metabolic profile to maximise treatment benefit. Meanwhile, hospital formulary committees face escalating budget pressures as multi-drug regimens reach five-digit annual costs, prompting negotiations around risk-sharing contracts linked to sustained virologic response or histology-confirmed fibrosis reversal.
Global Liver Diseases Therapeutics Market Trends and Insights
Rise in the Incidence of Liver Diseases
Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks as the third-leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, while chronic liver disease affects more than 4.5 million Americans each year. This epidemiological surge stimulates sustained uptake of antivirals, immunotherapies, and disease-modifying antifibrotics. Asia-Pacific carries a heavier viral hepatitis burden, whereas Western economies confront rising MASLD linked to obesity and diabetes. Aging populations compound disease prevalence because hepatic regenerative capacity declines with age. National payer systems respond by broadening screening programmes that detect disease earlier, expanding the addressable pool for curative therapies and boosting the liver disease therapeutics market.
Increase in Alcohol Consumption & Obesity-Driven MASLD
MASLD touches roughly 25% of the global population, making it the fastest-growing indication for liver transplantation. Clinical evidence from 2024 shows metabolic-syndrome patients possess triple the risk of advancing to stage 3-4 fibrosis, and concurrent alcohol use accelerates disease by seven years. Dual-pathway drugs, including FGF21 agonists and PPAR modulators, are now in late-phase trials. Regulators embrace adaptive designs that test combination regimens, acknowledging MASLD's multifactorial nature. In the United States alone, MASLD-related spending exceeds USD 103 billion annually, prompting insurers to accept premium pricing for therapies that avert progression to end-stage disease.
Adverse Events & Long-Term Safety Concerns of Therapies
Immunosuppressive regimens elevate infection risk by 40%; new antifibrotic agents mandate cardiac and renal monitoring. FDA now demands five-year post-marketing safety studies for NASH drugs. Complex dosing schedules undermine adherence, and physicians adopt conservative prescribing until long-term real-world data mature. To curb attrition, sponsors are investing in predictive toxicology and microphysiological liver models that flag safety liabilities earlier in drug development.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rising Government Vaccination & Screening Initiatives
- Breakthrough Approvals for NASH-Specific Drugs
- Stringent, Multi-Regional Regulatory Approval Timelines
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Anti-viral therapies retained 36.12% share of the liver disease therapeutics market in 2025, propelled by pan-genotypic direct-acting antivirals that sustain 95% cure rates. Chronic hepatitis B suppression for 296 million carriers assures durable revenue. Meanwhile, antifibrotic/antisteatotic agents are projected to log a 10.22% CAGR to 2031, benefitting from Resmetirom's first-in-class approval and a ballooning MASLD population. Immunosuppressants maintain a niche for autoimmune hepatitis, whereas oncology-focused immunotherapies increasingly supplant cytotoxic chemotherapies. Combination regimens blending metabolic correctors with anti-inflammatory agents are expanding prescribing patterns, lifting the liver disease therapeutics market size.
The competitive narrative is evolving as pipeline dispersion intensifies; more than a dozen dual-pathway candidates have entered Phase II within 18 months. Pay-for-performance contracts tied to non-invasive fibrosis regression scores bolster market uptake, especially among integrated health systems. As late-line antiviral resistance remains rare, lifecycle management pivots to fixed-dose combinations that lessen pill burden and shield franchises from generic erosion.
Viral hepatitis contributed 42.35% of liver disease therapeutics market share in 2025 due to sheer patient volume and life-saving curative regimens. WHO elimination targets sustain procurement funding, and domestic production efforts in China and India lower per-course costs by 65%, broadening access and reinforcing the liver disease therapeutics market. MASLD, however, will post an 11.28% CAGR as obesity climbs worldwide. Steatotic liver disease's multifactorial pathogenesis encourages combination therapy architectures that elevate average selling prices.
Alcohol-related liver disease receives fresh attention following FDA Breakthrough Therapy status for larsucosterol, which demonstrated 25% reduction in 90-day mortality in severe alcoholic hepatitis. Autoimmune liver diseases, although representing a smaller segment, achieve premium reimbursement for biologic agents that delay transplant need. Rare genetic and paediatric disorders benefit from orphan incentives that speed approvals and permit higher pricing benchmarks, cushioning research risk.
The Liver Disease Therapeutics Market Report is Segmented by Treatment Type (Anti-Viral Drugs, Immunosuppressants, and More), Disease Type (Viral Hepatitis A-E, and More), Drug Class (Small-Molecule Orals, and More), Route of Administration (Oral, Injectable), End User (Hospitals, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America captured 42.10% of revenue in 2025, underpinned by rapid adoption of newly approved NASH drugs and broad insurance coverage for pan-genotypic HCV antivirals. The presence of academic centres accelerates enrolment in late-phase trials, and tax credits support R&D. Yet ballooning therapy prices heighten scrutiny from pharmacy benefit managers that negotiate indication-based rebates.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing territory at a 12.45% CAGR to 2031. China alone houses 80 million chronic hepatitis B patients, and national reimbursement now covers first-line tenofovir generics, expanding the treated population. Japan's fast-track review system shortens approval timelines for breakthrough biologics, while South Korea's biotech tax incentives spur domestic RNAi pipelines.
Europe witnesses steady, slower growth as health technology assessment agencies seek cost-effectiveness before authorising new entries. EMA alignment with FDA scientific advice has smoothed parallel submissions, but price-volume agreements can delay country-level launches by more than a year. Middle East & Africa and South America together account for minor share of global revenue; however, multilateral donor programmes and tiered pricing models improve access to WHO-preferred therapies, gradually enlarging the liver disease therapeutics market.
- Abbott Laboratories
- Abbvie
- Astellas Pharma
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals
- Bristol-Myers Squibb
- Roche
- Gilead Sciences
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Merck
- Novartis
- Pfizer
- Sanofi
- Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.
- Endo International
- Provectus Biopharmaceuticals
- Intercept Pharmaceuticals
- Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Eiger BioPharmaceuticals Inc.
- Ionis Pharmaceuticals
- Aligos Therapeutics Inc.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rise in the Incidence of Liver Diseases
- 4.2.2 Increase In Alcohol Consumption & Obesity-Driven MASLD
- 4.2.3 Rising Government Vaccination & Screening Initiatives
- 4.2.4 Breakthrough Approvals for Nash-Specific Drugs
- 4.2.5 Ai-Powered, Non-Invasive Diagnostics Enabling Early Detection
- 4.2.6 Combination RNAi-Immunotherapy Pipelines Accelerating Cures
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Adverse Events & Long-Term Safety Concerns of Therapies
- 4.3.2 Stringent, Multi-Regional Regulatory Approval Timelines
- 4.3.3 Escalating Therapy Costs & Reimbursement Hurdles
- 4.3.4 Limited Clinically Validated Biomarkers Delaying Adoption
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value in USD)
- 5.1 By Treatment Type
- 5.1.1 Anti-viral Drugs
- 5.1.2 Immunosuppressants
- 5.1.3 Targeted Therapy & Small Molecules
- 5.1.4 Chemotherapy Drugs
- 5.1.5 Antifibrotic/Antisteatotic Agents
- 5.1.6 Vaccines
- 5.1.7 Immunoglobulins
- 5.2 By Disease Type
- 5.2.1 Viral Hepatitis (A-E)
- 5.2.2 Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ARLD)
- 5.2.3 Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) / MASH
- 5.2.4 Autoimmune Liver Diseases
- 5.2.5 Genetic & Pediatric Disorders
- 5.2.6 Other Disease Types
- 5.3 By Drug Class
- 5.3.1 Small-molecule Orals
- 5.3.2 Biologics & Monoclonal Antibodies
- 5.3.3 RNA-based Therapeutics
- 5.3.4 Cell & Gene Therapy
- 5.4 By Route of Administration
- 5.4.1 Oral
- 5.4.2 Injectable
- 5.5 By End User
- 5.5.1 Hospitals
- 5.5.2 Ambulatory Surgery Centers
- 5.5.3 Specialty Clinics
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Australia
- 5.6.3.5 South Korea
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.3.2 AbbVie Inc.
- 6.3.3 Astellas Pharma Inc.
- 6.3.4 Alnylam Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.5 Bristol-Myers Squibb Co.
- 6.3.6 F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Gilead Sciences Inc.
- 6.3.8 GlaxoSmithKline plc
- 6.3.9 Merck & Co. Inc.
- 6.3.10 Novartis AG
- 6.3.11 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.3.12 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.13 Takeda Pharmaceutical Co.
- 6.3.14 Endo International plc
- 6.3.15 Provectus Biopharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.16 Intercept Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.17 Madrigal Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.18 Eiger BioPharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.19 Ionis Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.3.20 Aligos Therapeutics Inc.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




