PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848146

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848146
Organic Soy Protein - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The organic soy protein market is estimated to be USD 0.73 billion in 2025 and is forecast to rise to USD 1.14 billion by 2030, advancing at a 9.50% CAGR.
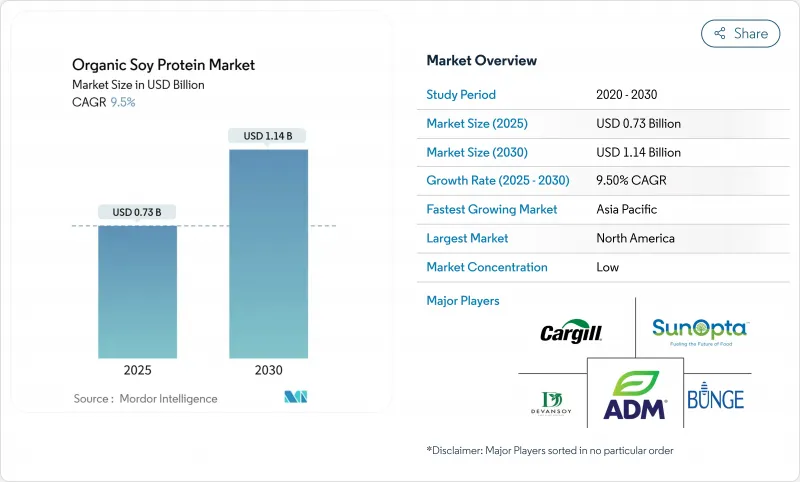
Rising demand for plant-based protein, supportive FDA health-claim regulations, and continuous innovation in extraction technology underpin this momentum. Manufacturers reformulate mainstream foods with soy protein to meet clean-label expectations, while supply-chain realignment toward South American crushing hubs lowers processing costs and improves margin resilience. Firms also leverage soy protein's complete amino-acid profile to fill nutritional gaps in sports nutrition, medical foods, and infant formula. Regulatory clarity from the FDA's 2025 draft guidance on labeling plant-based alternatives further accelerates new-product launches that prominently feature soy protein. The increasing consumer awareness of sustainable protein sources and environmental concerns has positioned organic soy protein as a preferred choice in the market. Additionally, the growing adoption of organic soy protein in plant-based meat alternatives and dairy substitutes continues to expand market opportunities.
Global Organic Soy Protein Market Trends and Insights
Rising demand for clean label and organic products
Consumer scrutiny of food ingredient lists has intensified the shift toward recognizable, minimally processed components, positioning soy protein as a preferred alternative to synthetic additives in food formulation. The USDA organic certification process, while requiring 3-year transition periods and higher production costs, generates price premiums of USD 6-9 per bushel for organic soybeans compared to conventional varieties. The certification cost burden, ranging from USD 400,000 to USD 890,000 for relabeling compliance, creates barriers for smaller processors while benefiting established players with scale advantages according to FDA (Food and Drug Administration). Processing innovations that eliminate hexane extraction, such as aqueous extraction methods, address consumer concerns about chemical residues while maintaining protein functionality. The trend toward clean label formulations particularly benefits soy protein isolates, which offer neutral taste profiles that enable manufacturers to reduce artificial flavoring while maintaining product palatability.
Growing popularity of plant-based protein
The plant-based protein market has evolved from niche health food applications to mainstream food manufacturing, with soy protein offering a complete amino acid profile that provides advantages in formulation compared to other plant proteins. The Asia-Pacific region shows significant market growth potential due to traditional consumption patterns of soy-based foods and halal certification benefits. Soy protein's environmental benefits, including reduced land and water usage compared to animal protein production, align with companies' environmental, social, and governance (ESG) commitments. Food manufacturers increasingly utilize soy protein to meet protein content requirements under FDA labeling guidelines for plant-based alternatives. Recent technological developments in processing methods, such as high hydrostatic pressure treatments, have enhanced soy protein's functional properties, enabling its use in premium plant-based products where texture and mouthfeel are essential.
Availability of other plant-based proteins
The plant protein market has seen increased competition against soy protein, particularly from pea protein, which offers benefits such as being allergen-free and having a neutral taste that simplifies food formulation. This shift is part of a broader market trend where companies like Bunge are expanding their protein portfolios to include faba, lentil, and mung proteins to address diverse functional and nutritional needs. Investment trends show increased funding for alternative protein sources rather than traditional soy applications, which may constrain soy protein's growth in new market segments. Regulatory developments support this diversification, as demonstrated by Health Canada's guidelines on pea protein safety and the FDA's draft labeling requirements for plant-based alternatives, which create uniform standards across protein sources. While soy protein historically held a cost advantage in processing, this gap has narrowed as alternative protein production has increased, though soy protein retains its position in areas requiring complete amino acid profiles and established regulatory compliance, especially in infant nutrition.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Increased application in sports and functional nutrition
- Increasing use of soy protein in infant formula
- Rising soy allergies in consumers
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Protein concentrates dominate the market with a substantial 48.17% share in 2024, maintaining their position as the preferred choice in the protein ingredients segment. Their widespread adoption is primarily driven by cost-effectiveness compared to other protein forms. These concentrates are particularly valuable in conventional food applications where moderate protein content is sufficient. The ability of protein concentrates to meet functional requirements while keeping production costs manageable makes them attractive to food manufacturers. Additionally, their versatility and ease of incorporation into various food products contribute to their continued market leadership.
Isolates represent the fastest-growing segment with a 10.29% CAGR through 2030, driven by their use in sports nutrition and infant formula applications where protein purity exceeds 90% . The production process requires approximately 3 tons of defatted soybeans to produce 1 ton of isolate, with premium pricing compensating for higher manufacturing costs. New processing methods, such as gas-supported screw-pressed techniques, enhance isolate functionality while reducing environmental impact compared to hexane extraction. FDA regulations support isolate market growth by permitting specific health claims for products containing at least 6.25 grams of soy protein per serving. The market shows a trend toward premium products, with isolates gaining value in applications where functional properties justify higher costs, while concentrates remain dominant in cost-sensitive food manufacturing.
The Organic Soy Protein Market is Segmented by Form (Concentrates, Isolates, and Textured/Hydrolyzed), Application (Food and Beverages, Supplements, Animal Feed, and Personal Care and Cosmetics), Grade (Food Grade, and Non-Food Grade), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America holds 38.65% share of the global soy protein market in 2024, supported by established processing infrastructure and regulatory frameworks. The region's integrated supply chains connect soybean production with processing facilities, though transportation infrastructure limitations in production areas increase logistics costs. The FDA's health claim approvals for soy protein products and USDA organic certification programs create market opportunities, despite higher production costs. North American market maturity encourages premium application development, exemplified by Green Bison Soy Processing's (ADM-Marathon joint venture) investments in renewable diesel integration.
Asia-Pacific demonstrates the highest growth rate at 11.78% CAGR through 2030, primarily due to China's focus on domestic protein production and traditional acceptance of soy-based foods. China's 90% dependency on soybean imports presents supply vulnerabilities, which the government addresses through domestic production incentives and protein alternatives. Singapore's regulatory leadership in cultivated meat and plant-based alternatives, combined with regional investments in alternative protein research, supports market growth. China's shift from U.S. to Brazilian soybean imports due to tariffs influences regional supply chain strategies.
Europe prioritizes domestic protein production through policy initiatives and funding programs to reduce import reliance. Germany's EUR 38 million investment in sustainable protein development demonstrates regional commitment. The market favors sustainably sourced soy protein products, while facing competition from regional alternatives like pea and faba proteins. Brazil, as the global soybean production leader, encounters infrastructure limitations affecting processing development. The Middle East and Africa show potential for growth due to increasing populations and protein demand, but face processing infrastructure and regulatory constraints.
- Archer Daniels Midland Company
- SunOpta Inc.
- Devansoy Inc.
- Sonic Biochem
- Bunge Limited
- Cargill, Incorporated.
- Foodchem International Corporation
- GROUPE BERKEM
- The Scoular Company
- Laybio
- ORGANIC PROTEIN
- Wilmar International Ltd.
- Shiv Health Foods LLP (Prowise)
- Eklavya Biotech Private Limited
- Chaitanya Agro Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- International Flavors & Fragrances Inc
- Sun Nutrafoods
- Bioway Organic Ingredients CO., LTD.
- FUJI OIL CO., LTD.
- Farbest Brands (Farbest-Tallman Foods Corporation)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Demand for Clean Label and Organic Products
- 4.2.2 Growing Popularity of Plant-Based Protein
- 4.2.3 Increased Application in Sports and Functional Nutrition
- 4.2.4 Increasing Use of Soy Protein in Infant Formula
- 4.2.5 Support from Government and Organic Certification Bodies
- 4.2.6 Expansion of Vegan and Flexitarian Diets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Availability of Other Plant-Based Proteins
- 4.3.2 Rising Soy Allergies in Consumers
- 4.3.3 High Cost of Organic Certification and Production
- 4.3.4 Price Volatility and Import Dependency
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Form
- 5.1.1 Concentrates
- 5.1.2 Isolates
- 5.1.3 Textured/Hydrolyzed
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Food and Beverages
- 5.2.1.1 Bakery and Confectionery
- 5.2.1.2 Snacks
- 5.2.1.3 Dairy and Dairy Alternative Products
- 5.2.1.4 Meat/Poultry/Seafood and Meat Alternative Products
- 5.2.1.5 Beverages
- 5.2.1.6 Other Food Applications
- 5.2.2 Supplements
- 5.2.2.1 Sport/Performance Nutrition
- 5.2.2.2 Baby Food and Infant Formula
- 5.2.2.3 Elderly Nutrition and Medical Nutrition
- 5.2.3 Animal Feed
- 5.2.4 Personal Care and Cosmetics
- 5.2.1 Food and Beverages
- 5.3 By Grade
- 5.3.1 Food Grade
- 5.3.2 Non-Food Grade
- 5.4 By Geography
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 Italy
- 5.4.2.4 France
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Netherlands
- 5.4.2.7 Poland
- 5.4.2.8 Belgium
- 5.4.2.9 Sweden
- 5.4.2.10 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 Australia
- 5.4.3.5 Indonesia
- 5.4.3.6 South Korea
- 5.4.3.7 Thailand
- 5.4.3.8 Singapore
- 5.4.3.9 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Colombia
- 5.4.4.4 Chile
- 5.4.4.5 Peru
- 5.4.4.6 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 South Africa
- 5.4.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.4.5.3 United Arab Emirates
- 5.4.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.4.5.5 Egypt
- 5.4.5.6 Morocco
- 5.4.5.7 Turkey
- 5.4.5.8 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Ranking Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global-level Overview, Market-level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Archer Daniels Midland Company
- 6.4.2 SunOpta Inc.
- 6.4.3 Devansoy Inc.
- 6.4.4 Sonic Biochem
- 6.4.5 Bunge Limited
- 6.4.6 Cargill, Incorporated.
- 6.4.7 Foodchem International Corporation
- 6.4.8 GROUPE BERKEM
- 6.4.9 The Scoular Company
- 6.4.10 Laybio
- 6.4.11 ORGANIC PROTEIN
- 6.4.12 Wilmar International Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Shiv Health Foods LLP (Prowise)
- 6.4.14 Eklavya Biotech Private Limited
- 6.4.15 Chaitanya Agro Biotech Pvt. Ltd.
- 6.4.16 International Flavors & Fragrances Inc
- 6.4.17 Sun Nutrafoods
- 6.4.18 Bioway Organic Ingredients CO., LTD.
- 6.4.19 FUJI OIL CO., LTD.
- 6.4.20 Farbest Brands (Farbest-Tallman Foods Corporation)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




