PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848330

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1848330
Anti Malarial Drugs - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The anti-malarial drugs market size reached USD 1.08 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 1.35 billion by 2030 at a 4.53% CAGR.
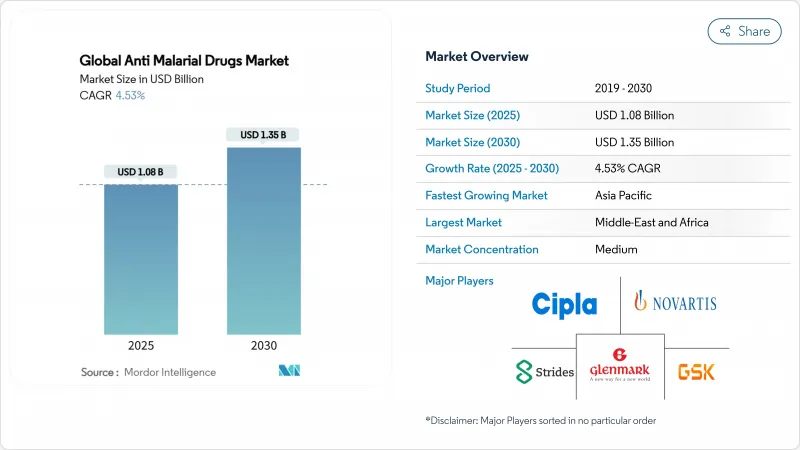
This progression shows a shift from volume-led growth to value-driven innovation as companies introduce next-generation compounds that fight emerging resistance while preserving affordability for endemic countries. Artemisinin resistance spreading through East Africa is forcing portfolio diversification, spurring research into spiroindolone and endoperoxide analogues. Plasmodium falciparum continues to dominate clinical demand, yet improved diagnostics are revealing a larger burden from P. knowlesi. Geographic revenue still favors high-income regions where prophylaxis and R&D spending drive premium pricing. Inside endemic areas, digital procurement platforms and radical cure therapies are reshaping supply chains and treatment choices.
Global Anti Malarial Drugs Market Trends and Insights
Endemic Disease Burden In Tropical Regions
Persistent transmission in tropical climates sustains baseline demand even when purchasing power is low. Sub-Saharan Africa recorded 597,000 malaria deaths in 2023, equal to 94% of the global total, yet contributed a smaller share of revenue because pricing relies on donor procurement. Ethiopia logged 7.3 million cases and 1,157 deaths in 2024 during supply chain disruptions that limited medicine availability. Urban invasion by Anopheles stephensi is altering transmission patterns, requiring new therapeutic strategies that go beyond rural programs. This concentrated burden assures continuous consumption in endemic countries, but revenue growth remains capped by affordability frameworks.
Government-Led Malaria Control Initiatives And Funding
National plans such as Indonesia's 2030 elimination roadmap and India's 2023-27 strategic plan translate policy ambition into predictable drug tenders. Cross-border surveillance along India-Bhutan and India-Nepal corridors aggregates procurement volumes and lowers unit costs. Yet WHO cautions that projected aid reductions in 2025 could affect services across 64 endemic countries, disrupting supply chains and destabilizing the anti-malarial drugs market. Funding swings therefore create cyclic demand, benefiting suppliers able to flex production in line with donor cycles.
Increasing Drug Resistance In Endemic Areas
Kelch-13 469Y mutations now identified in Uganda, Tanzania, Rwanda, and the Democratic Republic of Congo confirm partial artemisinin resistance beyond its Southeast Asian origin. Rising resistance shortens product lifecycles, compels costly reformulation, and may sideline smaller producers unable to fund R&D. WHO's new recommendation for multiple first-line therapies raises the logistical burden on health systems that must stock several options simultaneously.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Advancements In Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies
- Expansion Of Global Health Financing Mechanisms
- Proliferation Of Counterfeit And Substandard Medications
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Artemisinin derivatives controlled 46.43% of anti-malarial drugs market share in 2024, anchored by global treatment guidelines. Spiroindolones, represented by Novartis's cipargamin, are advancing at a 6.56% CAGR because they retain potency against artemisinin-resistant strains. Antifolates and aryl amino-alcohols keep niche relevance in combinations and prevention. Endoperoxide analogues are in early pipelines that aim to mimic peroxide-based activity without cross-resistance.
The transition indicates strategic hedging against single-mechanism failure. Other drug types such as FIKK kinase inhibitors and chromatin remodelers are under exploration, offering new pathways to disrupt parasite biology [SCiencedaily.com]. Regulatory lead times remain long, so larger firms with deeper capital are best placed to carry these assets through approval.
Plasmodium falciparum accounted for 63.12% of the anti-malarial drugs market size in 2024. Improved PCR diagnostics are uncovering a faster rise in P. knowlesi, which now grows at a 6.99% CAGR, particularly in Malaysia and parts of Indonesia where human-macaque interface drives zoonotic spillover. Plasmodium vivax retains high demand because its liver hypnozoites necessitate radical cure regimens.
Species-tailored therapies are beginning to penetrate. Brazil's and Thailand's introduction of single-dose radical cure for vivax signals movement toward precision medicine in malaria care. Broader adoption hinges on diagnostic accuracy in primary care settings.
The Anti-Malarial Drugs Market Report is Segmented by Drug Class (Aryl Amino-Alcohol Compounds, and More), Malaria Type (Plasmodium Falciparum, and More), Mechanism of Action (Treatment for Malaria, Prevention/Chemoprophylaxis, and Radical Cure), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East & Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America's dominant 39.56% share of the anti-malarial drugs market in 2024 came from premium prophylaxis sales to travelers, the military, and research institutions. Imported cases totaled 1,772 in 2024, confirming that non-endemic settings still require reliable treatments. Regulatory leadership by the FDA further anchors R&D investments. Yet reliance on discretionary travel exposes the segment to economic downturns that can quickly dampen pharmacy demand.
Asia-Pacific is forecast to grow at 5.43% CAGR through 2030 as expanding middle-income populations invest in healthcare infrastructure and governments boost case detection. The anti-malarial drugs market size here rises in tandem with integrated surveillance and elimination plans. Funding shortfalls of USD 478 million identified by the Global Fund illustrate ongoing dependency on blended finance. Resistance to artemisinin in the Greater Mekong Subregion drives interest in spiroindolones and triple ACTs. P. vivax dominance ensures radical cure uptake once G6PD testing barriers ease.
Europe, Middle East & Africa, and South America remain heterogeneous. European demand orbits around traveler prophylaxis and basic research, contributing stable but low-growth revenue. Sub-Saharan Africa's disease load secures steady procurement yet caps pricing. African vaccine deployments will coexist with drugs for breakthrough and mixed infections, potentially increasing combination therapy use. South America's Amazon basin is nearing elimination, shifting drug procurement toward follow-up care and imported case management.
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Novartis
- Cipla
- Cadila Healthcare (Zydus Lifesciences)
- Bayer
- Sun Pharmaceuticals Industries
- Sanofi
- Amivas LLC
- Lupin
- Glenmark Pharmaceuticals
- Strides Pharma Science
- Ajanta Pharma
- Alvizia Healthcare
- Lincoln Pharmaceuticals
- Mylan N.V. (Viatris)
- Fosun Pharma (Artequick)
- Hetero Drugs
- Medicines For Malaria Venture (MMV)
- Sigma-Tau Arzneimittel (Eurartesim)
- Shin Poong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Pyramax)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope Of The Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Endemic Disease Burden in Tropical Regions
- 4.2.2 Government-Led Malaria Control Initiatives and Funding
- 4.2.3 Advancements in Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies
- 4.2.4 Expansion of Global Health Financing Mechanisms
- 4.2.5 Integration of Digital Health Tools in Case Management
- 4.2.6 Growing Private-Sector Investment in Novel Antimalarials
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Increasing Drug Resistance in Endemic Areas
- 4.3.2 Proliferation of Counterfeit and Substandard Medications
- 4.3.3 Limited Commercial Incentives for Novel Chemistries
- 4.3.4 Supply Chain Vulnerability to Raw Material Shortages
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Threat Of New Entrants
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power Of Buyers / Consumers
- 4.5.3 Bargaining Power Of Suppliers
- 4.5.4 Threat Of Substitute Products
- 4.5.5 Intensity Of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Drug Class
- 5.1.1 Aryl Amino-Alcohol Compounds
- 5.1.2 Antifolate Compounds
- 5.1.3 Artemisinin Compounds
- 5.1.4 Endoperoxide Analogues
- 5.1.5 Spiroindolone Compounds
- 5.1.6 Other Drug Types
- 5.2 By Malaria Type
- 5.2.1 Plasmodium Falciparum
- 5.2.2 Plasmodium Vivax
- 5.2.3 Plasmodium Malariae
- 5.2.4 Plasmodium Ovale
- 5.2.5 Plasmodium Knowlesi
- 5.3 By Mechanism Of Action
- 5.3.1 Treatment For Malaria
- 5.3.2 Prevention / Chemoprophylaxis
- 5.3.3 Radical Cure (Anti-Relapse)
- 5.4 By Distribution Channel
- 5.4.1 Public Procurement Agencies
- 5.4.2 Hospital Pharmacies
- 5.4.3 Retail Pharmacies
- 5.4.4 Online Pharmacies
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East & Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 GlaxoSmithKline Plc
- 6.3.2 Novartis AG
- 6.3.3 Cipla Limited
- 6.3.4 Cadila Healthcare (Zydus Lifesciences)
- 6.3.5 Bayer AG
- 6.3.6 Sun Pharmaceutical Industries
- 6.3.7 Sanofi S.A.
- 6.3.8 Amivas LLC
- 6.3.9 Lupin Limited
- 6.3.10 Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd
- 6.3.11 Strides Pharma Science Limited
- 6.3.12 Ajanta Pharma
- 6.3.13 Alvizia Healthcare
- 6.3.14 Lincoln Pharmaceuticals
- 6.3.15 Mylan N.V. (Viatris)
- 6.3.16 Fosun Pharma (Artequick)
- 6.3.17 Hetero Drugs
- 6.3.18 Medicines For Malaria Venture (MMV)
- 6.3.19 Sigma-Tau Arzneimittel (Eurartesim)
- 6.3.20 Shin Poong Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. (Pyramax)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




