PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850035

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850035
Data Center Blade Server - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
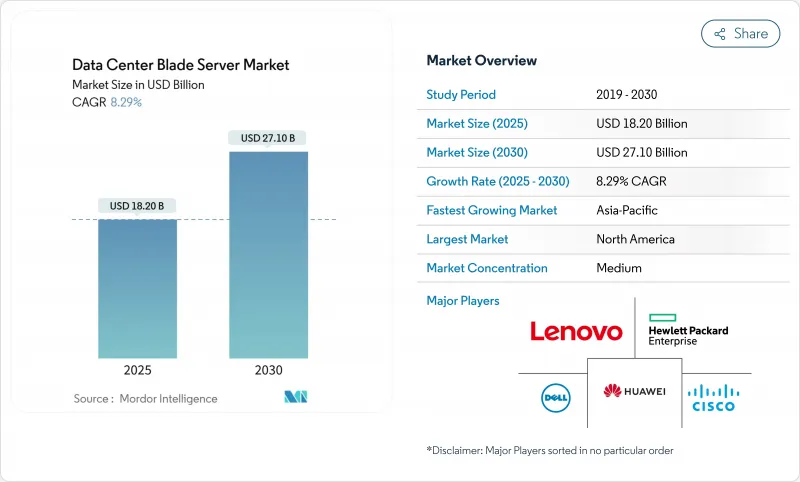
The Data Center Blade Server market is valued at USD 18.2 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 27.10 billion by 2030, expanding at an 8.29% CAGR.
Rising deployment of AI and machine-learning workloads is reshaping compute density requirements, pushing vendors toward composable, disaggregated blade designs that separate compute, storage and networking resources. This architectural shift enables higher utilization and rapid workload re-allocation, while direct liquid cooling, silicon-photonics backplanes and advanced chassis management software help operators manage rack power envelopes that now exceed 30 kW. North America retains scale leadership, yet Asia-Pacific is growing faster on the back of large greenfield builds in India, China and Singapore. Colocation facilities remain the largest customer group, but hyperscalers are setting the technical agenda as they move to purpose-built AI blade systems that deliver higher rack-level efficiency.
Global Data Center Blade Server Market Trends and Insights
Surging Rack-Level Power Density Accommodates AI/ML Workloads
AI inference and training clusters now push rack envelopes from 10-15 kW toward 30-50 kW. The Open Compute Project's OSAI specification targets 250 kW to 1 MW rack architectures, encouraging blade vendors to integrate high-efficiency voltage regulators and direct liquid cooling. Dell's PowerEdge XE9680L demonstrates how chassis-level airflow, cold-plate loops, and AI-specific accelerators can coexist without thermal throttling. The International Energy Agency projects that AI-focused data centers could consume 945 TWh by 2030, which keeps power-efficient blade design at the center of operator strategies
Edge-Cloud Convergence Accelerating Deployment in Micro-Modular DCs
5G rollouts and ultra-low-latency services push compute to the network edge, spawning demand for micro-modular data centers that can ship pre-wired and pre-cooled. Google's patent for modular edge facilities confirms the importance of secure, multitenant rack assemblies with integrated power and heat exchange. Telecom operators are allocating a sizeable share of their USD 600 billion CAPEX plan to such edge sites, giving blade vendors an opening to supply quarter-height nodes tailored for constrained footprints
CapEx Spike from Silicon-Photonics and 800 GbE Backplane Migration
Switching to photonic integrated circuits and 800 GbE fabrics unlocks latency and bandwidth gains but demands new chassis, mid-plane connectors and retimer cards. National agencies acknowledge the efficiency upside yet caution that early deployments bear heavy capital costs, particularly for mid-sized enterprises. Research into memory disaggregation over CXL suggests a multi-year payback, forcing operators to stagger upgrades
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- High Server Consolidation Ratios Lower OPEX and Real-Estate Cost
- Liquid-Cooling Ready Chassis Gaining Regulatory Incentives
- Supplier Concentration in Proprietary Chassis Ecosystems
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Tier 3 facilities owned 42.21% of the Data Center Blade Server market in 2024, as their N+1 redundancy profile aligns with mainstream enterprise SLAs. Tier 4 sites, though smaller in count, are forecast to grow at 12.2% CAGR thanks to fault-tolerance demands from AI training clusters. This momentum positions Tier 4 as the proving ground for 100% liquid-cooled chassis and silicon-photonics interconnects.
Operators of Tier 1 and Tier 2 facilities, typically serving edge aggregation or branch workloads, adopt standardized blades to maintain cost discipline while gaining better automation. The Infrastructure Masons report links 90% of current power growth to AI model training, a load now propagating into even modest sites that must accommodate higher power draw and rack density. As a result, vendors are packaging kits that retrofit lower-tier rooms with containment aisles and rear-door heat exchangers, preserving momentum for the wider Data Center Blade Server market.
Half-height blades delivered 48.41% revenue in 2024, supporting dual-socket CPUs, ample DIMM slots and PCIe expansion for most virtualization and database tasks. They remain the workhorse of enterprise colocation racks. Full-height models continue to serve quad-socket, memory-bound workloads such as in-memory analytics.
Quarter-height and micro-blade nodes are the fastest-growing slice at 14.12% CAGR because they fit 16-32 compute sleds per 10U shelf, ideal for limited edge footprints. Vendors now integrate GPU accelerators into these compact sleds, enabling real-time inference at cell-tower sites. Compatibility with Open Rack v3 specifications allows mixed deployment inside the same cabinet, sustaining the Data Center Blade Server market's edge expansion narrative.
Data Center Blade Server Market Report Segments the Industry Into Type (Tier 1, Tier 2, and More), Form Factor(Half-Height Blades, Full-Height Blades, and More), End-User Verticals (BFSI, Manufacturing, and More), Data Center Type(Hyperscalers/Cloud Service Provider, and More) and Geography (Asia-Pacific, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America controlled 42.23% of the Data Center Blade Server market in 2024, fueled by hyperscale campuses in Northern Virginia, Texas and Silicon Valley. The Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory calculated 176 TWh of US data-center electricity use in 2023, raising urgency for liquid-cooled blades that cut facility PUEs. Canada and Mexico add incremental demand through regional sovereign-cloud and disaster-recovery zones.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-growing theater at 12.54% CAGR from 2025-2030. China deploys massive AI cloud clusters, while India needs to expand installed capacity from 1.35 GW to 5 GW by 2030 to keep pace with digital-economy targets. Policy frameworks in Singapore award capacity licenses preferentially to designs that include high-density blades and heat-recovery chillers. Japan and Australia extend the edge footprint along subsea cable landing stations, embedding quarter-height blades for content caching.
Europe shows steady expansion under strict efficiency and data-sovereignty rules. Ecodesign 2019/424 revisions encourage blade chassis that support warm-water cooling above 35 °C, easing integration with district-heat loops. The Middle East and Africa attract investment for cloud on-ramps serving fintech and gaming customers. South America's installations cluster around Brazil's internet exchange hubs, where operators deploy composable blades to meet seasonal traffic peaks. These regional dynamics reinforce the global relevance of the Data Center Blade Server market.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- Dell Technologies
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- IBM Corporation
- Fujitsu Ltd.
- Lenovo Group Ltd.
- NEC Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Super Micro Computer Inc.
- Inspur Group
- Quanta Cloud Technology
- Gigabyte Technology
- Hitachi Ltd.
- AMD (Pensando)
- Nvidia Corp. (Grace Superchip platforms)
- Marvell Technology (DPU-centric blades)
- Broadcom Inc. (Switch-on-Blade)
- Advantech Co. Ltd.
- Silicom Ltd.
- ZTE Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Surging rack-level power density accommodates AI/ML workloads
- 4.2.2 Edge-cloud convergence accelerating deployment in micro-modular DCs
- 4.2.3 High server consolidation ratios lower OPEX and real-estate cost
- 4.2.4 Liquid-cooling ready chassis gaining regulatory incentives (EU, Singapore)
- 4.2.5 Growing hyperscaler preference for composable disaggregated blades
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 CapEx spike from silicon photonics and 800 Gb E backplane migration
- 4.3.2 Supplier concentration in proprietary chassis ecosystems
- 4.3.3 Skill-gap in managing multi-fabric, disaggregated architectures
- 4.3.4 Delayed ORAN/5G monetisation lengthening ROI for telco DCs
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Sustainability Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook (PCIe 6.0, CXL 3.0, silicon photonics)
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Rivalry
- 4.8 Assessment of the Impact on Macro Economic Trends on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUES)
- 5.1 By Data-Center Tier
- 5.1.1 Tier 1 and 2
- 5.1.2 Tier 3
- 5.1.3 Tier 4
- 5.2 By Form Factor
- 5.2.1 Half-height Blades
- 5.2.2 Full-height Blades
- 5.2.3 Quarter-height / Micro-blades
- 5.3 By Application / Workload
- 5.3.1 Virtualisation and Private Cloud
- 5.3.2 High-Performance Computing (HPC)
- 5.3.3 Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning and Data Analytics
- 5.3.4 Storage-centric
- 5.3.5 Edge / IoT Gateways
- 5.4 By Data Center Type
- 5.4.1 Hyperscalers/Cloud Service Provider
- 5.4.2 Colocation Facilities
- 5.4.3 Enterprise and Edge
- 5.5 By End-use Industry
- 5.5.1 BFSI
- 5.5.2 IT and Telecom / CSPs
- 5.5.3 Healthcare and Life-Sciences
- 5.5.4 Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
- 5.5.5 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.6 Government and Defence
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.2 Germany
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 Singapore
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Malaysia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Chile
- 5.6.4.3 Argentina
- 5.6.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 United Arab Emirate
- 5.6.5.2 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Initiatives
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.2 Dell Technologies
- 6.4.3 Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- 6.4.4 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.5 IBM Corporation
- 6.4.6 Fujitsu Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Lenovo Group Ltd.
- 6.4.8 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.9 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.10 Super Micro Computer Inc.
- 6.4.11 Inspur Group
- 6.4.12 Quanta Cloud Technology
- 6.4.13 Gigabyte Technology
- 6.4.14 Hitachi Ltd.
- 6.4.15 AMD (Pensando)
- 6.4.16 Nvidia Corp. (Grace Superchip platforms)
- 6.4.17 Marvell Technology (DPU-centric blades)
- 6.4.18 Broadcom Inc. (Switch-on-Blade)
- 6.4.19 Advantech Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.20 Silicom Ltd.
- 6.4.21 ZTE Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




