PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850045

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850045
Magnetic Resonance Imaging - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The MRI market size is projected at USD 10.16 billion in 2025 and is expected to reach USD 13.67 billion by 2030, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.10 % over the forecast period.
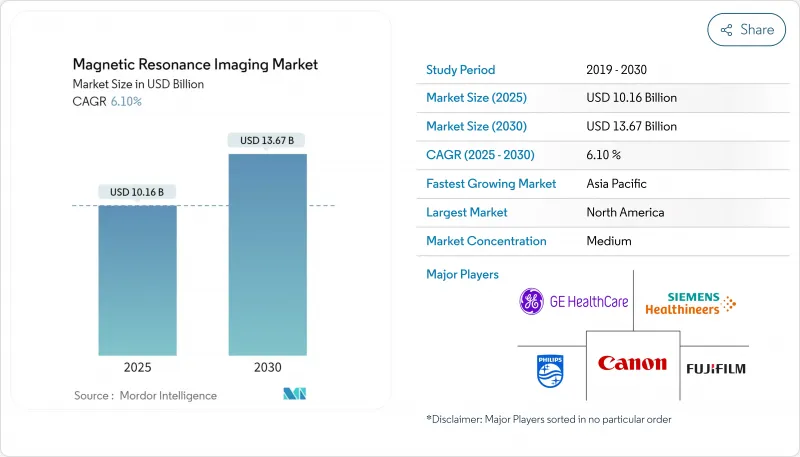
This outlook underscores how magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is becoming an essential pillar of modern diagnostics within the broader MRI industry.
The MRI market size supporting global healthcare continues to climb as clinicians integrate MRI into routine diagnostic pathways for neurology, oncology, and cardiology. Hospitals value the modality's superior soft-tissue contrast, which delivers clearer answers when disease signs remain ambiguous on other scans. Economic incentives favor MRI because it does not expose patients to ionizing radiation, a growing concern among regulators and providers alike. Capital investment remains steady, showing confidence that scanners will stay busy across multiple specialities. Software-driven gains, especially artificial-intelligence-based reconstruction, now influence purchasing decisions as much as gradient strength. Portable and ultra-low-field devices create new access points inside intensive-care units and emergency rooms. One fresh takeaway is that payers' evolving reimbursement policies are nudging administrators to balance image quality with setting-of-care economics.
Regional growth patterns reveal Asia-Pacific expanding at an impressive 8.80 % CAGR between 2025 and 2030, while North America holds the largest MRI market share at 34 % in 2024. Manufacturers segment their offerings accordingly, emphasizing cost-effective helium-light magnets in emerging markets yet focusing on workflow automation in mature economies. Workforce shortages, such as the 18.1 % vacancy rate for certified technologists reported in the United States, temper scan-room throughput even where hardware capacity is abundant. Training programs bundled with equipment purchases aim to ease this bottleneck. Insurance expansion, especially in China and India, is shifting MRI from tertiary referral imaging toward a frontline diagnostic tool. The trend implies that distribution strategies aligned with local staffing and reimbursement realities will shape future revenue streams.
Global Magnetic Resonance Imaging Market Trends and Insights
Rising Global Burden of Chronic and Age-Related Diseases
Neurological disorders and cancer dominate MRI use because they require detailed anatomical and functional information. Aging populations in developed regions drive higher imaging rates, and MRI's ability to reveal early microstructural changes promotes earlier therapeutic intervention. In oncology, diffusion-weighted and dynamic contrast-enhanced techniques help characterize tumors without invasive biopsies, resulting in MRI commanding roughly 41% of all neurological imaging volumes today. Large cancer centers routinely adopt whole-body MRI for staging, leading to consistent demand for high-channel coils and advanced post-processing software. As institutions pivot toward preventive screening, repeat imaging creates predictable volume growth. An emerging inference is that reliable early detection converts occasional MRI users into regular patients, reinforcing scanner utilization.
Increasing Reimbursement Coverage and Government Support
Recent Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) proposals added six new CPT codes covering MRI safety protocols, embedding formerly unbilled activities into payable workflows . Private insurers such as UnitedHealthcare set site-of-service rules that channel many exams into lower-cost outpatient facilities, shaping magnet placement strategies. Minimum reimbursable field strength, now pegged at 0.3 T, accelerates replacement cycles for older 0.2 T systems. Administrators therefore find clearer financial justification for mid-field or higher-strength upgrades. With safety activities monetized and site selection clarified, hospitals gain budgeting certainty. The practical takeaway is that coding precision now directly influences equipment lifecycles and facility planning.
High Cost of MRI Systems
Purchase prices range from USD 150,000 for basic low-field devices to USD 3 million for advanced 3 T units. Site preparation-covering magnetic shielding, vibration control, and structural reinforcement-adds substantial expense. Operational costs such as helium refills and service contracts lengthen payback periods. Helium-light or sealed magnets lower lifetime costs, reshaping total-cost-of-ownership evaluations. Leasing options and vendor-managed services help smaller hospitals acquire higher-spec equipment without large upfront capital. This cost pressure stimulates interest in portable MRI solutions that bypass construction expenses. A logical inference is that economic considerations can promote lower-field or modular technology even in clinically demanding environments.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Technological Breakthroughs in MRI
- Expanding Clinical Indications for MRI
- Shift Toward Patient-Centric, Non-Ionizing Diagnostic Alternatives
- Shortage of Certified MRI Technologists
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Closed MRI systems held 78% MRI market share in 2024, reflecting their dominance in high-field clinical imaging. Portable scanners, advancing at an 8.10% CAGR through 2030, bring neuro-imaging directly to bedside settings. Hyperfine's FDA-cleared 0.064 T Swoop connects to standard power, enabling rapid stroke assessments without patient transport. AI-driven denoising offsets low-field signal limits, sustaining diagnostic quality. Hospitals increasingly deploy mixed fleets-high-field units for comprehensive studies and portable devices for time-critical triage-improving resource allocation. This hybrid approach reinforces the trend that architecture choice now hinges on clinical workflow requirements rather than image quality alone.
Mid-field systems (1.0 T-1.5 T) commanded 48 % MRI market size in 2024, balancing cost and performance for routine exams. Ultra-high-field magnets (>3 T) grow fastest at 7.20 % CAGR, offering superior resolution for neuroscience and oncology. United Imaging's FDA-cleared 5 T system indicates regulatory momentum for clinical use of higher field strengths. Ultra-low-field ( <0.5 T) devices meet point-of-care needs where portability outweighs signal-to-noise limitations. Reimbursement criteria mandating a minimum 0.3 T field strength hasten the retirement of older 0.2 T scanners. Clinicians now select field strength based on disease pathway requirements rather than a universal standard.
The MRI Market Report Segments the Industry Into by Architecture (Closed MRI Systems, Open MRI Systems, and More), by Field Strength (Low Field, High Field, and More), by Mobility (Fixed Room Systems and Mobile Trailer-Based Systems), by Application (Oncology, Neurology, and More), End User (Hospitals, Diagnostic Imaging Centers, and More), and by Geography. The Market Sizes and Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America led with 34% MRI market share in 2024, supported by mature reimbursement frameworks and early technology uptake. CMS added CPT codes for MRI safety, formalizing tasks such as implant screening and magnet safety checks. Labor shortages persist, with an 18.1% technologist vacancy prompting automation investments. FDA clearances for innovations such as GE HealthCare's SIGNA MAGNUS head-only 3 T scanner reinforce the region's product-leadership status. Providers increasingly rely on AI-driven workflow solutions to offset staffing gaps. This dynamic shows that regulation, labor, and innovation collectively sustain regional momentum.
Asia-Pacific is forecast to post the fastest regional CAGR of 8.80% between 2025 and 2030. Infrastructure spending in China and India boosts scanner installations, while Japan and South Korea adopt ultra-high-field systems for research and advanced clinical work. China's 2024 Medical Device and Supply Chain Innovation White Paper emphasizes differentiated innovation and cost control. Expanding public insurance, notably India's Ayushman Bharat, enlarges the patient base eligible for MRI. Vendors offer tiered products, pairing helium-light magnets for basic access with premium platforms for metropolitan centers. The pattern shows dual-track expansion: widening geographic coverage and deepening clinical sophistication simultaneously.
Europe remains a heavyweight in the MRI industry owing to universal health coverage and strong research networks. Adoption rates vary, with Northern and Western Europe embracing new technologies faster than Southern and Eastern regions. The Max Planck Institute operates 9.4 T and 14.1 T scanners to further neuro-biological discovery . EMA harmonization promotes seamless regulatory approval across member states, expediting technology diffusion. Siemens Healthineers' investment in a UK superconducting-magnet facility underscores Europe's manufacturing relevance. Value-based-care models encourage abbreviated MRI protocols that deliver efficiency without sacrificing care quality. The result is balanced growth that couples scientific leadership with broad access.
- Siemens Healthineers
- GE HealthCare Technologies, Inc.
- Koninklijke Philips
- Canon
- Fujifilm Holdings Corp.
- United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd.
- Shenzhen Anke High-Tech Co., Ltd.
- Esaote S.p.A.
- Hyperfine, Inc.
- Bruker
- FONAR Corporation
- Neusoft
- Aurora Healthcare U.S.
- Medonica Co., Ltd.
- Time Medical Systems
- Aspect Imaging Ltd.
- IMRIS (Deerfield Imaging)
- Paramed Medical Systems
- Synaptive Medical
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising global burden of chronic and age-related diseases
- 4.2.2 Increasing reimbursement coverage and government support for high-value imaging modalities
- 4.2.3 Technological breakthroughs in MRI
- 4.2.4 Steady growth in healthcare spending and modernization of hospital & outpatient imaging infrastructure worldwide
- 4.2.5 Expanding clinical indications for MRI
- 4.2.6 Shift toward patient-centric, non-ionizing diagnostic alternatives
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of MRI Systems
- 4.3.2 Safety and compatibility concerns for patients
- 4.3.3 Shortage of Certified MRI Technologists
- 4.3.4 Limited Accessibility in Middle Income Countries
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory & Reimbursement Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Architecture
- 5.1.1 Closed MRI Systems
- 5.1.2 Open MRI Systems
- 5.1.3 Portable / Point-of-Care MRI Systems
- 5.2 By Field Strength
- 5.2.1 Low-Field (<=0.5 T) MRI Systems
- 5.2.2 Mid-Field (1.0 T - 1.5 T) MRI Systems
- 5.2.3 High-Field (3 T) MRI Systems
- 5.2.4 Ultra-High & Very-High (>3 T) MRI Systems
- 5.3 By Mobility
- 5.3.1 Fixed Room Systems
- 5.3.2 Mobile Trailer-based Systems
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Neurology
- 5.4.2 Oncology
- 5.4.3 Cardiology
- 5.4.4 Musculoskeletal
- 5.4.5 Gastroenterology & Hepatology
- 5.4.6 Other Applications
- 5.5 By End User
- 5.5.1 Hospitals
- 5.5.2 Diagnostic Imaging Centers
- 5.5.3 Ambulatory Surgery Centers
- 5.5.4 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Italy
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Australia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 Middle East
- 5.6.4.1 GCC
- 5.6.4.2 South Africa
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5 South America
- 5.6.5.1 Brazil
- 5.6.5.2 Argentina
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Business Segments, Financials, Headcount, Key Information, Market Rank, Market Share, Products and Services, and analysis of Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Siemens Healthineers AG
- 6.4.2 GE HealthCare Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.3 Koninklijke Philips N.V.
- 6.4.4 Canon Medical Systems Corp.
- 6.4.5 Fujifilm Holdings Corp.
- 6.4.6 United Imaging Healthcare Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Shenzhen Anke High-Tech Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Esaote S.p.A.
- 6.4.9 Hyperfine, Inc.
- 6.4.10 Bruker Corporation
- 6.4.11 FONAR Corporation
- 6.4.12 Neusoft Medical Systems Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Aurora Healthcare U.S.
- 6.4.14 Medonica Co., Ltd.
- 6.4.15 Time Medical Systems
- 6.4.16 Aspect Imaging Ltd.
- 6.4.17 IMRIS (Deerfield Imaging)
- 6.4.18 Paramed Medical Systems
- 6.4.19 Synaptive Medical
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




