PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850217

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850217
Mobile Backhaul - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Mobile Backhaul Market size is estimated at USD 34.97 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 70.95 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 15.20% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
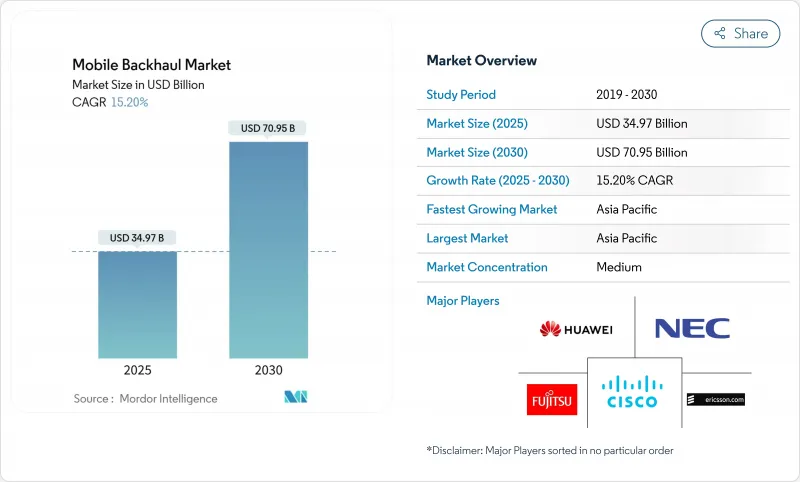
Growth is propelled by escalating smartphone penetration, the sharp rise in video streaming, and dense 5G rollouts that demand 10 Gbps and soon 100 Gbps per cell per site capacity. Operators are swapping copper lines for fiber and high-capacity wireless links, while neutral-host models reduce duplication as 5G investments top USD 1.1 trillion between 2020 and 2025. Open architectures, software-defined transport, and edge compute place new performance and security pressures on backhaul, yet they can lower life-cycle costs through commercial off-the-shelf hardware. Asia Pacific leads with a 35% revenue contribution and shows the fastest regional CAGR at 17.3% as China, Japan, South Korea, and India install millions of small cells. Operators everywhere now blend fiber's scale with microwave, millimeter-wave, and low-Earth-orbit (LEO) satellite hops to fill coverage gaps and accelerate rollouts.
Global Mobile Backhaul Market Trends and Insights
Growing Mobile Data Traffic & Smartphone Adoption
Average monthly data per smartphone is forecast to soar from 21 GB in 2023 to 56 GB by 2029, with video expected to account for 75% of mobile traffic. Regional divergence is emerging: North American users may hit 66 GB per month while Sub-Saharan Africa lingers near 23 GB, forcing operators to engineer country-specific backhaul mixes. Hybrid topologies that splice fiber trunks with high-band microwave hops now dominate urban densification because they meet capacity needs without prolonged street-dig permitting. Small-cell proliferation adds thousands of short-haul links, prompting fresh investment in automated network-management platforms that can tune capacity per site in real time.
Rapid 5G Rollout Driving Capacity Needs
Base-station density is climbing from 4-5 to 40-50 sites per km2 in 5G clusters, multiplying backhaul terminations. China alone is building more than 600,000 5G macro and small cells, a count projected to outstrip 4G by 1.3-1.5 times . Each 5G cell now requires 10 Gbps uplinks and stringent latency of sub-5 ms, accelerating the adoption of 70/80 GHz E-band radios and time-sensitive networking over fiber. Capital stress is nudging many operators toward shared towers and leased dark fiber, lowering up-front costs while ensuring upgrade paths to 100 Gbps interfaces.
High Capex for Fiber & Spectrum Costs
Fiber trenching in dense cities can run beyond USD 100,000 per Kilometer, a figure that climbs sharply where road-opening permits are scarce. Rising electricity prices also double macro-site power draw when 4G and 5G bands overlap, inflating operational overhead. In developing economies, limited access to low-interest financing delays fiber build-outs, forcing carriers to rely on microwave even where long-term economics favor fiber. The result is uneven quality-of-experience across urban and rural divides, hindering digital-inclusion goals.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Cloud-Native & Open RAN Architectures
- Satellite LEO Backhaul for Rural Reach
- SDN Backhaul Cybersecurity Risks
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Fiber-based links constituted 55% of the mobile backhaul market in 2024 due to their unrivalled capacity and low latency. This share translates to the largest deployment slice of the mobile backhaul market size at USD 19.2 billion in 2024. Wireless alternatives, however, are set to post a 16.4% CAGR through 2030, narrowing the gap as urban densification and pop-up events demand rapid turn-ups. Operators mesh 70/80 GHz E-band radios with leased dark fiber trunks, delivering 10 Gbps per hop while avoiding costly civil works.
Hybrid architectures are now standard: fiber remains the preferred medium for core aggregation, but microwave and millimeter-wave serve edge small cells and enterprise venues where permits or geography stall trenching. Emergent W-band and D-band links promise multi-gigabit throughput over 1-2 km, complementing fiber for dense clusters. In sparsely populated regions, operators splice LEO satellite backhaul into microwave rings, creating contiguous coverage without exceeding budget ceilings. This flexibility underpins the long-term competitiveness of the mobile backhaul market.
Microwave radios held 41% of the mobile backhaul market size in 2024, reflecting decades of field-proven reliability. Vendors have pushed spectral efficiency to 16 bps/Hz while adding link-bonding schemes that aggregate non-contiguous channels. Small cells backhaul gear, though only a fraction of revenue today, is set for a 17.4% CAGR as stadiums, malls, and transport hubs adopt indoor 5G.
The mobile backhaul market is witnessing a pivot toward integrated access and backhaul (IAB), where a 28 GHz radio simultaneously serves user devices and relays traffic upstream. This reduces rooftop congestion and simplifies zoning. Millimeter-wave chipset advances cut power draw by 30% since 2023, enabling pole-mount and window-mount nodes that require minimum site work. Vendors that bundle self-organizing-network software are winning tenders because they lower truck rolls and optimize link alignment in cluttered environments.
The Mobile Backhaul Market Report is Segmented by Deployment (Wired [Fiber/Optical and Copper/DSL], Wireless [Microwave, Millimetre-Wave, and More]), Equipment Type (Routers and Switches, Microwave Radios, and More), Service Type (Professional Services, Managed Services, and More), Network Architecture (Macro-Cell Backhaul, and More), End-User (Mobile Network Operators, Neutral-Host and Tower Companies, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific commands 35% of the mobile backhaul market, expanding at 17.3% CAGR thanks to outsized 5G investments, state subsidies, and dense urban populations. China, Japan, and South Korea already blanket major cities with standalone 5G, driving steep demand for 10 Gbps microwave hops that skirt excavation bottlenecks. India's recent spectrum auctions have unleashed a fiber-laying spree along highways and into tier-2 cities, while operators also pilot satellite-plus-microwave hybrids for Himalayan and island coverage. Government schemes that underwrite rural fiber further sustain momentum.
North America, while smaller by volume, leads innovation in virtualized RAN and dark-fiber aggregation. Verizon and T-Mobile bolstered their optical footprints by acquiring regional fiber players in 2024, locking in scalable backhaul to support fixed-wireless access rollouts. The Federal Communications Commission's USD 9 billion 5G Fund incentivizes cell-site upgrades in remote counties, channeling investments toward microwave and satellite backhaul where terrain hampers trenching. Fixed-mobile convergence accelerates as operators reuse fiber for both gigabit broadband and cell-site uplinks, amplifying return on capital.
Europe's mature markets balance stringent regulatory reviews with a push for pan-EU 5G corridors. Infrastructure-sharing frameworks lower duplicate capex, while public-private partnerships finance cross-border fiber routes vital for low-latency services such as connected freight. Meanwhile, the Middle East fast-tracks smart-city visions that rely on dense small-cell grids, and African carriers tap LEO constellations to backhaul remote coverage islands. Latin America sees 5G launches in 17 countries, with carriers forming consortia to lease submarine-cable capacity and distribute it inland via microwave chains, weaving resilience into national networks.
- Market level overview
- Huawei Technologies Co.
- Ericsson AB
- Nokia Corporation
- ZTE Corporation
- NEC Corporation
- Cisco Systems
- Fujitsu Limited
- Aviat Networks
- Ceragon Networks Ltd.
- BridgeWave Communications
- ATandT Inc.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- Ciena Corporation
- Juniper Networks
- Siklu Communication Ltd.
- Infinera Corporation
- CommScope Holding Company
- Telefonica S.A.
- Intelsat S.A.
- Parallel Wireless
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing mobile data traffic and smartphone adoption
- 4.2.2 Rapid 5G rollout driving capacity needs
- 4.2.3 Cloud-native and Open RAN architectures
- 4.2.4 Satellite LEO backhaul for rural reach
- 4.2.5 Fiber leasing by utilities and private LTE networks
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High capex for fiber and spectrum costs
- 4.3.2 Microwave spectrum licensing complexity
- 4.3.3 Ultra-low-latency synchronisation challenges
- 4.3.4 SDN backhaul cybersecurity risks
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8 Investment Analysis
- 4.9 Impact of COVID-19 on the Market
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Deployment
- 5.1.1 Wired
- 5.1.1.1 Fiber/Optical
- 5.1.1.2 Copper/DSL
- 5.1.2 Wireless
- 5.1.2.1 Microwave
- 5.1.2.2 Millimetre-Wave (E- and V-band)
- 5.1.2.3 Satellite
- 5.1.2.4 Free-Space Optics
- 5.1.1 Wired
- 5.2 By Equipment Type
- 5.2.1 Routers and Switches
- 5.2.2 Microwave Radios
- 5.2.3 Optical Transport Equipment
- 5.2.4 Small-Cell Backhaul Equipment
- 5.2.5 Others
- 5.3 By Service Type
- 5.3.1 Professional Services
- 5.3.2 Managed Services
- 5.3.3 Installation and Integration
- 5.3.4 Maintenance and Support
- 5.4 By Network Architecture
- 5.4.1 Macro-Cell Backhaul
- 5.4.2 Small-Cell Backhaul
- 5.4.3 Cloud RAN/Fronthaul
- 5.5 By End-user
- 5.5.1 Mobile Network Operators
- 5.5.2 Neutral-Host and Tower Companies
- 5.5.3 Internet Service Providers
- 5.5.4 Private Enterprises and Utilities
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Spain
- 5.6.3.5 Italy
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 GCC
- 5.6.5.2 Turkey
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.6.3 Egypt
- 5.6.6.4 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview
- 6.4.1 Market level overview
- 6.4.2 Huawei Technologies Co.
- 6.4.3 Ericsson AB
- 6.4.4 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.5 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.6 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.7 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.8 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.4.9 Aviat Networks
- 6.4.10 Ceragon Networks Ltd.
- 6.4.11 BridgeWave Communications
- 6.4.12 ATandT Inc.
- 6.4.13 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.14 Ciena Corporation
- 6.4.15 Juniper Networks
- 6.4.16 Siklu Communication Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Infinera Corporation
- 6.4.18 CommScope Holding Company
- 6.4.19 Telefonica S.A.
- 6.4.20 Intelsat S.A.
- 6.4.21 Parallel Wireless
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




