PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850269

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850269
Animal Genetics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Animal Genetics Market size is estimated at USD 6.98 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 9.44 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 6.23% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
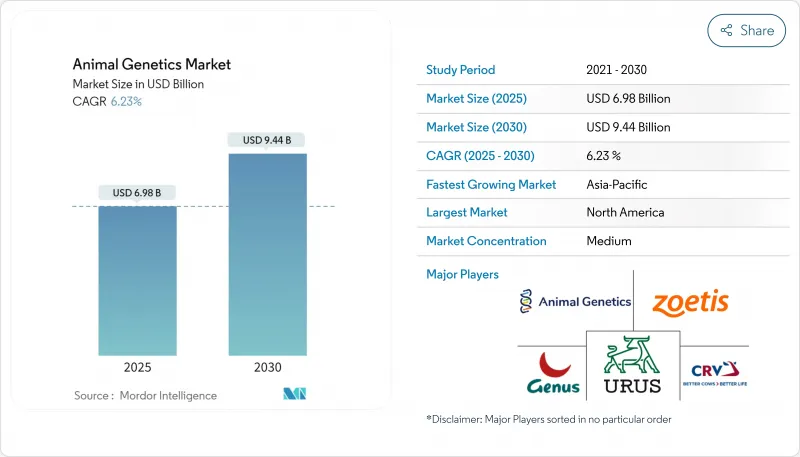
This healthy pace reflects sustained demand for high-quality animal protein, wider use of genomic tools, and the rise of precision breeding that blends genomic selection with conventional husbandry. North America remains the largest regional contributor as advanced laboratories, supportive regulation, and early adoption of artificial insemination and genomic testing keep research cycles short and commercial uptake high. Asia-Pacific is catching up fast, supported by expanding herds, government productivity schemes, and a widening network of in-country genotyping centers that lower access costs. Product-wise, live animals still represent the primary revenue stream, yet genetic material-especially frozen semen and embryos-records quicker growth as logistics, cryopreservation, and digital ordering improve. Technology competition centers on artificial insemination for its proven economics, while CRISPR and related gene-editing tools are moving from experimental to commercial scale as regulatory paths clarify. End-user demand is shifting toward veterinary clinics, where genetic diagnostics are becoming routine for both livestock and companion animals
Global Animal Genetics Market Trends and Insights
Demand for high-yielding disease-resistant livestock breeds
Intensifying pressure on food systems has made genetic disease resistance a core productivity lever. Marker-assisted selection now pinpoints resistance loci quickly, and CRISPR-generated PRRS-resistant pigs demonstrate how precision edits can curb costly outbreaks. Buyers also reward antibiotic-free labels, turning resistance traits into clear price premiums. Breeding firms respond by bundling resistance markers with growth and efficiency traits, while governments channel grants toward projects that cut antimicrobial use. Asia-Pacific producers, exposed to dense farm clusters, view resistance as risk insurance, driving regional demand for verified genetics.
Increased adoption of advanced genetic technologies
Falling sequencing costs and high-throughput SNP arrays have opened genomic testing to mid-scale producers. Integrated prediction models now combine genomic, performance, and environmental records, allowing selection for feed efficiency, heat tolerance, and methane mitigation. Dairy programs, for instance, use rumen microbiome-linked SNP panels to raise nutrient absorption efficiency, lowering feed costs and emissions. Public-private partnerships in Europe and North America co-fund reference populations, ensuring long-term data flow that sustains genetic gain.
High cost of genomic sequencing limiting adoption
While sequencing has become cheaper, upfront equipment outlays and per-sample fees still deter smallholders. Beef enterprises, where genetic gains translate more slowly into cash, adopt cautiously. Output-based pricing schemes and state subsidies partially offset costs, yet access remains uneven. This disparity risks widening performance gaps between industrial players and family farms, nudging policy makers to explore shared lab facilities and tiered service packages.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rapid adoption of sexed-semen technology
- Growth of companion-animal genetic testing
- Shortage of skilled geneticists in breeding co-ops
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The live animal segment generated 62.54% of the animal genetics market in 2024, reflecting the persistent premium that commercial buyers place on proven bulls, boars, rams, and breeding stock with validated production records. Breeders invest in on-farm performance testing, show circuit visibility, and digital pedigree platforms to justify animal prices that often exceed USD 50,000 for elite sires. The trade benefits from improved logistics and quarantine hubs that simplify cross-border movement.
Genetic material, though smaller in absolute value, expands faster at a 6.98% CAGR as cryopreservation advances lower shipment risk and digitized ordering portals connect global buyers to diverse germplasm inventories. Embryo vitrification now achieves post-thaw viability above 90%, widening usage among emerging-market dairies that want rapid genetic leaps without importing live cattle. Semen remains the volume leader for its affordability, but premium embryos and DNA libraries create higher-margin niches. End-product diversity and delivery flexibility position genetic material to outpace overall animal genetics market growth through 2030.
Genetic trait-and-performance testing produced 48.15% of animal genetics market revenue in 2024. The service captures granular data on milk yield, carcass quality, feed conversion, and resilience traits, then integrates them with DNA markers to refine selection indices. Cloud-based dashboards now deliver real-time benchmarking to producers, encouraging iterative improvements each breeding cycle. Demand from integrated pork and poultry operations keeps volume high because small gains in feed efficiency compound across millions of head.
DNA typing and parentage testing, forecast at 7.01% CAGR, benefits from plummeting per-sample sequencing costs and the spread of handheld collection kits that mail specimens to central labs overnight. Companion-animal clinics account for a rising share of samples, but livestock players also employ parentage panels to verify pedigree claims and enforce breed-specific health program compliance. Packages that bundle DNA typing with trait testing help laboratories upsell value-added analytics, strengthening their position within the animal genetics market.
The Animal Genetics Market Report Segments by Animals (Poultry, Porcine, and More), by Animal Genetic Testing Services (DNA Typing, Genetic Trait Tests, and More), by Technology (Artificial Insemination (AI), Embryo Transfer (ET) and More), by End User (Breeding Companies, Livestock Producers/Farms and More) and by Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America remained the largest region, accounting for 37.34% of the animal genetics market share in 2024. Modern laboratory infrastructure, a seasoned AI technician base, and an accommodating regulatory stance reinforce adoption. The FDA's 2025 approval of gene-edited pork signals growing acceptance of precision breeding in the food chain. USDA outlooks project beef, pork, and broiler production to climb 11.1%, 10.0%, and 11.5% respectively by 2034, reinforcing region-wide demand for superior genetics. Universities add further momentum; SubCas9, a compact CRISPR protein discovered in bovine microbiota, promises more targeted edits with fewer off-target risks.
Asia-Pacific is on course for the fastest 7.75% CAGR through 2030. China rolls out national genomic chips for local breeds, while India promotes sexed semen to lift dairy yield per cow. Rising disposable incomes and shifting diets expand demand for meat, eggs, and dairy, prompting investment in genetic upgrades to boost output and cut imports. Public-private partnerships in genomics lower test prices, helping mid-sized farms participate. These efforts collectively push the region's weight in the animal genetics market upward each year of the forecast period.
Europe holds a sizeable position anchored by stringent welfare and sustainability norms that shape breeder strategies. Emphasis lies on balanced selection indices that pair productivity with animal well-being, especially in swine and poultry lines. South America continues to monetize strong pasture resources; Brazil and Argentina see brisk uptake of gene-edited cattle for heat tolerance and hornlessness traits. The Middle East and parts of Africa, though smaller, explore genomics to counter harsh climates and limited feed supplies. Regulatory clarity in Japan and Argentina-where certain gene-edited livestock qualify as non-GMO-could inspire other jurisdictions and smooth cross-border trade in genetic products.
- Genus
- Hendrix Genetics
- Zoetis
- Topigs Norsvin
- Cobb-Vantress Inc.
- Aviagen Group
- CRV Holding BV
- Select Sires
- STgenetics
- Semex Alliance
- Alta Genetics
- Neogen
- ABS Global Inc.
- Genex Co-operative Inc.
- Grimaud Groupe
- Eurogene AI Services
- Sexing Technologies
- Envigo RMS LLC
- Bovine Elite
- Nugenomics Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Demand for high-yielding disease-resistant livestock breeds
- 4.2.2 Increased Adoption of Advanced Genetic Technologies for Large-scale Production and Quality Breeds
- 4.2.3 Rapid adoption of sexed-semen technology in North American bovine AI
- 4.2.4 Growth of companion-animal genetic testing in urban markets
- 4.2.5 Government-subsidized swine herd rebuilding post-ASF in China & Vietnam
- 4.2.6 Expansion of dairy genetics programs targeting A2A2 B-casein in Europe
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of genomic sequencing limiting adoption
- 4.3.2 Shortage of skilled geneticists in breeding co-ops
- 4.3.3 Biosecurity restrictions on cross-border germplasm trade
- 4.3.4 EU ethical & regulatory hurdles for CRISPR gene-edited
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.4 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Product Type (Value)
- 5.1.1 Animal
- 5.1.1.1 Bovine
- 5.1.1.2 Porcine
- 5.1.1.3 Poultry
- 5.1.1.4 Canine
- 5.1.1.5 Equine
- 5.1.1.6 Aquaculture Species
- 5.1.1.7 Others
- 5.1.2 Genetic Material
- 5.1.2.1 Semen
- 5.1.2.2 Embryo
- 5.1.2.3 DNA & Other Germplasm
- 5.1.1 Animal
- 5.2 By Testing Service Type (Value)
- 5.2.1 Genetic Disease Testing
- 5.2.2 Genetic Trait & Performance Testing
- 5.2.3 DNA Typing & Parentage Testing
- 5.2.4 Other Specialised Tests
- 5.3 By Technology (Value)
- 5.3.1 Artificial Insemination (AI)
- 5.3.2 Embryo Transfer (ET)
- 5.3.3 Marker-Assisted & Genomic Selection
- 5.3.4 CRISPR & Gene Editing
- 5.3.5 Other Assisted-Reproduction Technologies
- 5.4 By End User (Value)
- 5.4.1 Breeding Companies & Associations
- 5.4.2 Livestock Producers / Farms
- 5.4.3 Veterinary Hospitals & Specialty Clinics
- 5.4.4 Research & Academic Institutes
- 5.4.5 Others
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Genus PLC
- 6.4.2 Hendrix Genetics BV
- 6.4.3 Zoetis Inc.
- 6.4.4 Topigs Norsvin
- 6.4.5 Cobb-Vantress Inc.
- 6.4.6 Aviagen Group
- 6.4.7 CRV Holding BV
- 6.4.8 Select Sires Inc.
- 6.4.9 STgenetics
- 6.4.10 Semex Alliance
- 6.4.11 Alta Genetics Inc.
- 6.4.12 Neogen Corporation
- 6.4.13 ABS Global Inc.
- 6.4.14 Genex Co-operative Inc.
- 6.4.15 Grimaud Groupe
- 6.4.16 Eurogene AI Services
- 6.4.17 Sexing Technologies
- 6.4.18 Envigo RMS LLC
- 6.4.19 Bovine Elite LLC
- 6.4.20 Nugenomics Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




