PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850290

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850290
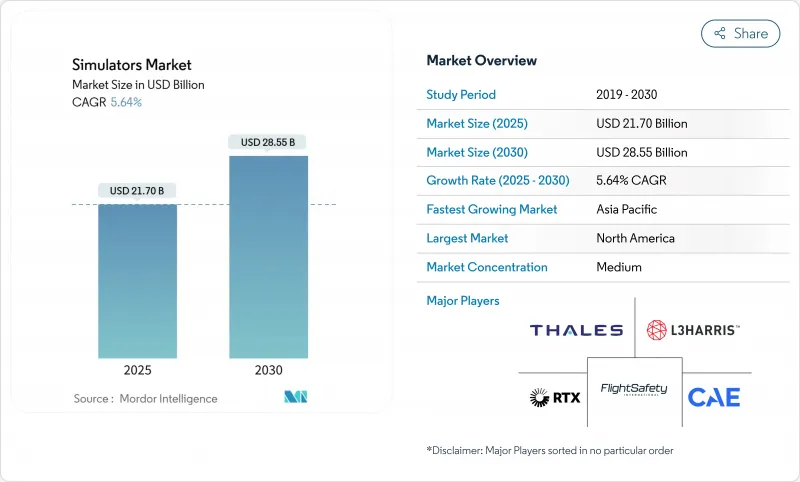
Simulators - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The simulators market stood at USD 21.70 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 28.55 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.64% CAGR.
Growth stemmed from accelerating defense-modernization cycles, tightening aviation-training rules, and adopting service-oriented delivery models that lower user entry costs. Military buyers continued to dominate spending, yet commercial airlines, drone operators, and process-industry firms broadened demand as digital-twin and AI-powered debrief tools proved their value. Platform interoperability upgrades mandated by NATO and the US Indo-Pacific Command created a replacement wave. At the same time, supply-chain bottlenecks in precision servomotors and UHD projectors prolonged lead times, favoring larger vendors that hold multi-year contracts with defense agencies. Wet-lease and simulation-as-a-service offerings further democratized access, enabling smaller air carriers and emerging-market militaries to train on high-fidelity devices without large capital outlays.
Global Simulators Market Trends and Insights
NATO and Indo-Pacific modernization programs drive LVC integration
The NATO Standardization Agreement 4603 and the US Indo-Pacific Command's Pacific Multi-Domain Training and Experimentation Capability linked previously isolated ranges, forcing vendors to embed High-Level Architecture gateways and Distributed Interactive Simulation bridges inside new devices.Canada, Australia, and Japan followed suit by stipulating network-ready simulators in recent tenders, expanding a procurement pool beyond traditional flight training into cyber, maritime, and space mission rehearsal.
EASA/FAA Evidence-Based Training mandates reshape pilot certification
The European Union Aviation Safety Agency finalized Evidence-Based Training guidance that moves airlines from task-list syllabi to competency-driven scenarios, increasing the number of Level-D simulator hours per type rating. The US Federal Aviation Administration mirrored this approach through its Simulation and Training Engineering Support program, which is valued at about USD 2.3 billion.Device utilisation rates rose, creating steady aftermarket demand for software upgrades and data analytics packages documenting competency evidence.
Interoperability gaps constrain multinational training exercises
Coalition Warrior Interoperability trials in 2023 revealed that NATO DIS and HLA traffic overloaded tactical networks when connected to Asia-Pacific Federation Object Models, degrading fidelity during fast-jet scenarios. The NATO Modelling & Simulation Centre of Excellence (M&S COE) published a new federation object model, but retrofitting legacy systems remains expensive for smaller nations, delaying joint-exercise scheduling.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Asia's UAV-logistics expansion accelerates drone-training demand
- Defense cost-reduction initiatives accelerate virtual training adoption
- Hardware supply-chain disruptions extend procurement timelines
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The airborne segment generated 42.58% of 2024 revenue, confirming its central role in the simulators market. Carrier pilot shortages, evidence-based recurrent training, and new aircraft introductions kept order books full. The maritime segment, while smaller, is forecast to expand at a 6.42% CAGR as navies replace classroom bridge trainers with network-ready, high-motion devices that support littoral combat scenarios. Kongsberg's DP3 anchor-handling simulator sale to an offshore client highlighted this shift. Land-based armored-vehicle trainers continued to benefit from the US Army's Synthetic Training Environment program, yet growth remained moderate compared with seaborne applications.
Maritime buyers requested embedded solutions that allow crews to train while ships stay on task. L3Harris fielded on-board consoles that integrate with operational sensors, reducing downtime and mission disruption. Colleges and merchant-marine academies also invested in integrated engine rooms and navigation suites, signaling a broadening user base beyond defense.
Live-Virtual-Constructive (LVC) methods owned a 35.17% revenue share in 2024 as NATO and the US Air Force mandated multi-domain synthetic environments for force-generation readiness. Devices now replicate air, maritime, land, cyber, and space elements inside a single federation, pushing buyers to upgrade legacy hardware and middleware. However, the gaming and serious-games subset will chart a 8.03% CAGR, the strongest rate of any technique, as defense ministries adopt commercial game engines for affordability and agility.
Adopting serious-games platforms created a pipeline of entry-level suppliers that license Unreal or Unity frameworks and layer military content, driving down price points. This shift improved accessibility in emerging economies where full-motion LVC devices remain cost-prohibitive.
The Simulators Market Report is Segmented by Platform (Airborne, Land, and Maritime), Technique (Synthetic Environment Simulation, and More), Solution (Hardware, Software, and Services), Application (Commercial Pilot and Crew Training, and More), End Use (Commercial and Military), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America secured 37.42% of global revenue in 2024 after the US Department of Defense allocated USD 833 billion for FY 2025, including substantial simulator procurement and R&D funding. Canada's P-8A patrol aircraft and Cormorant helicopter mid-life programs added further volume through bundled simulator buys. Federal Aviation Administration contracts supported civil growth, and Lockheed Martin's THAAD and F-35 upgrade efforts kept device makers busy with missile defense and stealth fighter trainers.
Asia-Pacific emerged as the fastest-growing theatre, tracking a 6.28% CAGR to 2030. Japan's FY 2025 defense budget prioritised unmanned systems, AI, and cyber, all reliant on virtual testbeds.As illustrated by Simaero's six-bay centre in Changsha, China's civil aviation expansion continued. Taiwan's eVTOL medical initiative and Australia's AUKUS submarine training pipeline added specialised naval and rotorcraft demand, widening the regional solution mix.
Europe held steady on the back of NATO interoperability mandates. EASA's Evidence-Based Training rule increased airline simulator hours, and member states such as Romania embedded modelling-and-simulation targets inside national defence strategies. The UK Ministry of Defence promoted open-standards adoption to de-risk procurement cost, while Germany modernised naval and rotary-wing trainers, keeping order pipelines consistent despite macroeconomic headwinds.
- CAE, Inc.
- Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- FlightSafety International Inc.
- L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- Thales Group
- Rheinmetall AG
- Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- BAE Systems plc
- Lockheed Martin Corporation
- KNDS N.V.
- FAAC Incorporated
- Exail SAS
- Moog Inc.
- Siemens Digital Industries (Siemens AG)
- Frasca International, Inc.
- Pacific Simulators 2010 Ltd.
- Indra Sistemas, S.A.
- TRU Simulation + Training Inc.
- Zen Technologies Limited
- Motion Systems
- HAVELSAN A.S.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 NATO and Indo-Pacific modernization programs mandate LVC networking
- 4.2.2 EASA/FAA Evidence-Based Training rules require more Level-D simulator hours
- 4.2.3 Asia's UAV-logistics boom lifts demand for low-cost drone-pilot simulators
- 4.2.4 Global defense ministries target 25% cost-reduction in live training
- 4.2.5 Digital-twin and AI-based debrief tools penetrate operator-training simulators
- 4.2.6 Emerging-market airlines adopt wet-lease sim-as-a-service models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Interoperability gaps between NATO DIS, HLA, and Asia-Pacific FOM architectures
- 4.3.2 Precision servomotor and UHD-projector shortages inflate hardware lead times
- 4.3.3 Conflict-zone governments reallocate training funds to live munitions
- 4.3.4 High CAPEX inhibits small flight schools in South America and Africa
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory and Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Platform
- 5.1.1 Airborne
- 5.1.2 Land
- 5.1.3 Maritime
- 5.2 By Technique
- 5.2.1 Live, Virtual, and Constructive (LVC) Simulation
- 5.2.2 Synthetic Environment Simulation
- 5.2.3 Gaming/Serious-Games Simulation
- 5.3 By Solution
- 5.3.1 Hardware
- 5.3.2 Software
- 5.3.3 Services
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Commercial Pilot and Crew Training
- 5.4.2 Military and Defense Training
- 5.4.3 Research and Testing/R&D
- 5.5 By End-Use Industry
- 5.5.1 Commercial
- 5.5.2 Military
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 France
- 5.6.3.3 Germany
- 5.6.3.4 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 CAE, Inc.
- 6.4.2 Collins Aerospace (RTX Corporation)
- 6.4.3 FlightSafety International Inc.
- 6.4.4 L3Harris Technologies, Inc.
- 6.4.5 Thales Group
- 6.4.6 Rheinmetall AG
- 6.4.7 Kongsberg Gruppen ASA
- 6.4.8 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.9 Lockheed Martin Corporation
- 6.4.10 KNDS N.V.
- 6.4.11 FAAC Incorporated
- 6.4.12 Exail SAS
- 6.4.13 Moog Inc.
- 6.4.14 Siemens Digital Industries (Siemens AG)
- 6.4.15 Frasca International, Inc.
- 6.4.16 Pacific Simulators 2010 Ltd.
- 6.4.17 Indra Sistemas, S.A.
- 6.4.18 TRU Simulation + Training Inc.
- 6.4.19 Zen Technologies Limited
- 6.4.20 Motion Systems
- 6.4.21 HAVELSAN A.S.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-Space and Unmet-Need Assessment




