PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850295

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850295
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The tuberculosis diagnostics market stood at USD 2.58 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 3.44 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.87% CAGR.
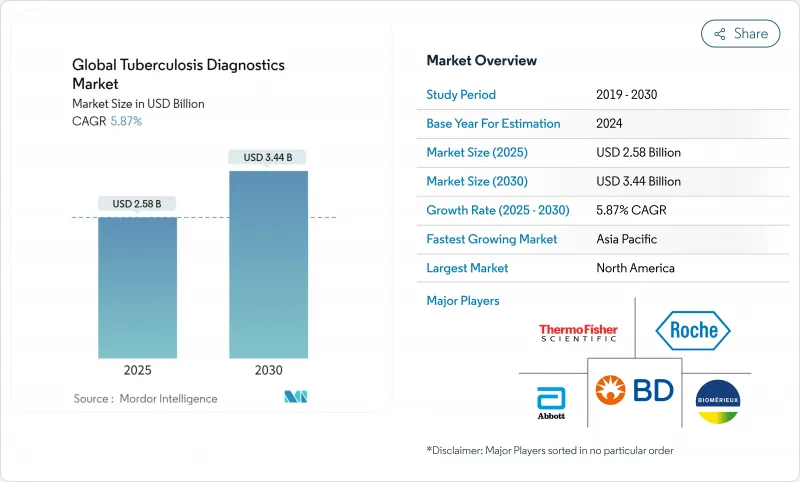
Accelerated demand stems from the roughly 4 million tuberculosis cases that go undetected every year and from the December 2024 WHO approval of Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra, a rapid molecular test that can confirm infection and drug resistance in a single visit. Laboratories are abandoning weeks-long culture protocols in favor of nucleic-acid amplification platforms, which have become the centerpiece of most national testing algorithms. AI-guided digital microscopy and portable point-of-care assays-such as Tulane University's lab-in-tube device that returns results in under an hour at a cost below USD 3-are widening access in community clinics and mobile units. Asia-Pacific is on track for the quickest expansion as high-burden countries shift from smear microscopy to molecular testing, while North America maintains the largest revenue base thanks to entrenched laboratory infrastructure. Competitive intensity stays moderate: Cepheid alone has installed more than 20,000 GeneXpert systems in high-burden nations, yet cartridge supply constraints and a multibillion-dollar funding gap flagged by U.S. public-health agencies threaten to slow broader scale-up Cepheid.
Global Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market Trends and Insights
Rising Prevalence of Drug-Resistant TB Strains
Drug-resistant cases climbed to 465,000 in 2024, yet only 43% were correctly diagnosed, intensifying the call for rapid molecular susceptibility testing. Germany's 5.7% multidrug-resistant incidence and Cote d'Ivoire's 22% rifampicin resistance among retreatment cases show how resistance patterns differ by geography. Xpert MTB/XDR delivers actionable drug profiles in 90 minutes, while Abbott's RealTime MTB RIF/INH assay achieves 94.8% sensitivity for rifampicin and 88.3% for isoniazid, letting clinicians tailor therapy promptly. Nations are also piloting targeted next-generation sequencing to map resistance comprehensively, moving diagnostic workflows from culture-dependent to molecular-first approaches.
WHO Endorsement & National Roll-Outs of NAAT Platforms
WHO's March 2024 guideline update placed molecular rapid tests at the front of all diagnostic algorithms and introduced targeted sequencing advice for drug-resistant surveillance WHO. India's Initiative for Promoting Affordable and Quality TB Tests boosted Xpert uptake tenfold and cut prices by up to 50%, scaling from 56 to 211 labs in five years. Uganda, by decentralizing NAATs to district hospitals, shortened median time to treatment initiation and raised same-day confirmations NEJM.
High Cost of Molecular Tests & Cartridges
Traditional desktop platforms can exceed USD 19,000, whereas Tulane's lab-in-tube device costs under USD 800 and keeps per-test pricing below USD 3 Tulane. Economic analyses in Brazil and India showed Diaskintest at USD 22.6 and USD 41.0 per correct case, while TSPOT.TB delivered greater effectiveness at incremental costs of USD 55-74. Cepheid's cost-price cartridge offer narrows the gap, yet a sustainable reimbursement model remains critical for widespread adoption.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Funding & Global Health Initiatives
- Emergence of AI-Powered Microscopy & Digital Radiology Triage
- Shortage of Skilled Laboratory Infrastructure
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
NAATs garnered 36.45% of tuberculosis diagnostics market share in 2024, benefitting from WHO's instruction to prioritize molecular tools over smear microscopy. Although culture methods remain essential for comprehensive drug profiling, interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) are the fastest climber at 6.54% CAGR through 2030 as QIAreach QuantiFERON-TB shows 99% sensitivity and 94% specificity versus prior IGRA versions. Automated smear platforms now achieve 96.7% accuracy and 91.94% sensitivity, reducing manual workload. AI-supported radiography secures AUCs of 0.951-0.975 on external datasets, raising confidence in imaging triage. Beyond sputum, sonication-based tongue-swab assays and finger-sweat drug monitoring are widening specimen options, indicative of how the tuberculosis diagnostics market continues to diversify test formats.
Emerging multiplex strategies combine modalities to hit 97.9% sensitivity, though specificity is constrained at 4.9%, exposing the need for algorithmic refinement. New biomarkers in breath and plasma are meeting WHO triage targets, signalling potential replacement tests for skin screening in high-burden settings. As novel assays mature, culture methods are likely to migrate toward centralized surveillance while rapid molecular tools dominate frontline case finding within the tuberculosis diagnostics industry.
Tuberculosis Diagnostics Market is Segmented by Diagnostic Test Type (Culture Based Test, Smear Microscopy, and More), by Rechnology (Culture-Based, Molecular Diagnostics (PCR/NAAT) and More), by End-User (Hospital/Clinics, Diagnostics/Research Laboratory, and Other End Users), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, and South America. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America represented 38.89% of the tuberculosis diagnostics market in 2024, aided by comprehensive insurance coverage and consistent CDC laboratory upgrades CDC. Asia-Pacific is forecast to expand at 6.74% CAGR thanks to India's one-third share of global burden and policy shifts from smear microscopy to NAAT. Europe posted 38,993 cases across 29 EU/EEA nations in 2023; Ukrainian refugee screening recorded 12.8 per 100,000 incidence with 26% multidrug resistance, prompting intensified entry screening. South America benefits from national Xpert scale-up; Brazil's roll-out added 9.7% notifications and catalyzed multisector coordination Lancet Regional Health-Americas. The Middle East and Africa see uneven progress: while Nigeria's AI-linked vans record 1.75 times higher positivity in hotspots, only 4% of labs can run Line Probe Assays. Diaskintest is cheaper than tuberculin in Brazil and India, but TSPOT.TB delivers higher accuracy at added expense, underscoring divergent procurement choices
List of Companies Covered in this Report:
- Cepheid (Danaher)
- Roche
- Beckton Dickinson
- Abbott Laboratories
- Hologic
- QIAGEN
- Thermo Fisher Scientific
- bioMerieux
- Siemens Healthineers
- Beckman Coulter Diagnostics
- FUJIFILM
- SD Biosensor
- Molbio Diagnostics
- Oxford Immunotec
- Meridian Bioscience
- LumiraDx
- Tauns Laboratories
- QuantuMDx
- Luminex (DiaSorin)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising prevalence of drug-resistant TB strains
- 4.2.2 WHO endorsement & national roll-outs of NAAT platforms
- 4.2.3 Government funding & global health initiatives
- 4.2.4 Emergence of AI-powered microscopy & digital radiology triage
- 4.2.5 Decentralised near-POC molecular platforms
- 4.2.6 Subscription-based diagnostics-as-a-service models
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High cost of molecular tests & cartridges
- 4.3.2 Shortage of skilled laboratory infrastructure
- 4.3.3 Supply-chain fragility for single-source cartridges
- 4.3.4 Competition from emerging non-sputum biomarkers
- 4.4 Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts
- 5.1 By Test Type (Value)
- 5.1.1 Culture-based Tests
- 5.1.2 Smear Microscopy
- 5.1.3 Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAAT)/PCR
- 5.1.4 Interferon-Gamma Release Assays (IGRA)
- 5.1.5 Tuberculin Skin Test (Mantoux)
- 5.1.6 Radiographic & Imaging Tests
- 5.1.7 Other Tests
- 5.2 By Technology (Value)
- 5.2.1 Culture-based
- 5.2.2 Molecular Diagnostics (PCR/NAAT)
- 5.2.3 Immunoassays (IGRA/LAM)
- 5.2.4 Radiology/X-ray
- 5.2.5 AI-enhanced Digital Microscopy
- 5.2.6 Others
- 5.3 By End-User (Value)
- 5.3.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.3.2 Diagnostic Laboratories
- 5.3.3 Academic & Research Institutes
- 5.3.4 Others
- 5.4 By Geography (Value)
- 5.4.1 North America
- 5.4.1.1 United States
- 5.4.1.2 Canada
- 5.4.1.3 Mexico
- 5.4.2 Europe
- 5.4.2.1 Germany
- 5.4.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.4.2.3 France
- 5.4.2.4 Italy
- 5.4.2.5 Spain
- 5.4.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.4.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.3.1 China
- 5.4.3.2 India
- 5.4.3.3 Japan
- 5.4.3.4 South Korea
- 5.4.3.5 Australia
- 5.4.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.4.4 South America
- 5.4.4.1 Brazil
- 5.4.4.2 Argentina
- 5.4.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.4.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.5.1 GCC
- 5.4.5.2 South Africa
- 5.4.5.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.4.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)}
- 6.3.1 Cepheid (Danaher)
- 6.3.2 Roche Diagnostics
- 6.3.3 Becton, Dickinson and Company
- 6.3.4 Abbott Laboratories
- 6.3.5 Hologic Inc.
- 6.3.6 Qiagen N.V.
- 6.3.7 Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc.
- 6.3.8 BioMerieux SA
- 6.3.9 Siemens Healthineers
- 6.3.10 Beckman Coulter Diagnostics
- 6.3.11 Fujifilm Holdings Corporation
- 6.3.12 SD Biosensor
- 6.3.13 Molbio Diagnostics
- 6.3.14 Oxford Immunotec
- 6.3.15 Meridian Bioscience
- 6.3.16 LumiraDx
- 6.3.17 Tauns Laboratories
- 6.3.18 QuantuMDx
- 6.3.19 Luminex (DiaSorin)
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-Need Assessment




