PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850385

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850385
Marine Propulsion Engine - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market size is estimated at USD 38.71 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 43.93 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 2.54% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
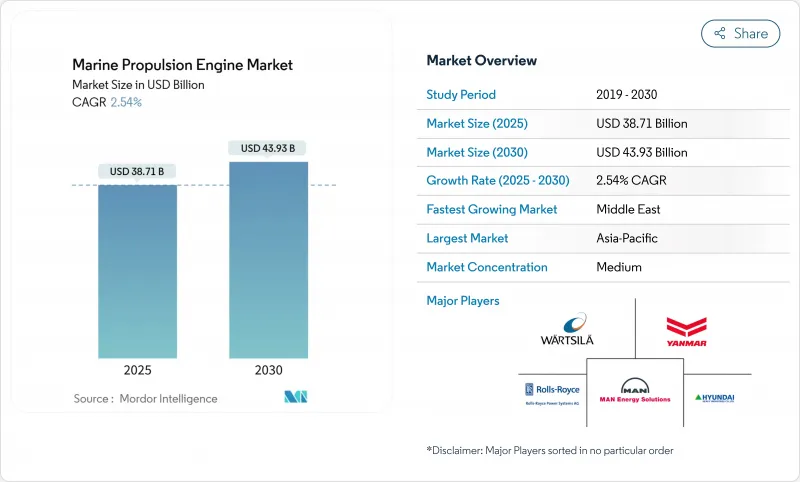
Demand is anchored in the commercial cargo fleet's capacity renewal cycle, yet momentum increasingly shifts toward alternative fuels as the IMO Net-Zero Framework pushes owners to cut greenhouse-gas intensity by 80% before 2050. Early adoption of LNG and methanol dual-fuel engines, fueled by robust Asia-Pacific orderbooks and European policy incentives, is reinforcing the technology transition.
Global Marine Propulsion Engine Market Trends and Insights
IMO Tier III & EEXI Compliance Push Retrofits
Shipping companies face mandatory 75% nitrogen-oxide cuts inside Emission Control Areas, a requirement that now applies to the Mediterranean as of May 2025. The new rules intersect with EEXI energy-efficiency thresholds, triggering a retrofit opportunity that covers roughly 35% of global tonnage. SCR and EGR packages dominate near-term procurement, illustrated by MAN's methanol retrofit kits slated for 2026 roll-out. Owners without compliant engines risk restricted port access, making retrofit timelines a boardroom priority. Capital allocation, therefore, increasingly shifts toward upgrade programs rather than pure maintenance budgets, reshaping the aftermarket revenue mix.
Asia-Pacific Container & LNG New-Build Boom
Chinese, South Korean and Japanese shipyards secured a torrent of container and LNG carrier contracts, pushing regional yard utilization to multi-year highs. Evergreen's USD 3 billion order for eleven LNG-fueled 24,000 TEU vessels typifies the volume surge. First-quarter 2024 data recorded 78 LNG new-building orders, up 129% year on year. Engine makers are therefore juggling capacity constraints alongside heightened demand for dual-fuel platforms. This pipeline supports long-run visibility for the marine propulsion engine market as Asia-Pacific yards convert design slots into deliveries through 2028.
Fuel-Price Volatility Complicates Engine Choice
VLSFO averaged USD 630 per ton in 2024 but EU-ETS fees can lift European voyage costs to an effective USD 795 per ton by 2025. Bio-blend mandates inflate fuel budgets further, while e-methanol trades above USD 1,300 per ton, undermining near-term parity with fossil alternatives. Owners hedge risk through dual-fuel installations, accepting higher upfront expenditure for operational flexibility. Yet volatility discourages smaller operators from long-horizon capex, causing uneven fleet modernization across size classes. Analysts warn that misaligned regional regulations could push compliance costs above fuel spend by 2031, eroding competitiveness for aging tonnage.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- LNG/Methanol Dual-Fuel Uptake
- Port-Entry Zero-Emission Zones
- High Capex for SCR/EGR After-Treatment
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Diesel engines retained 66.12% of the marine propulsion engine market share in 2024, underscoring their entrenched support network and cost competitiveness. Dual-fuel designs that accept LNG, methanol and ammonia are bridging technology gaps, allowing shipowners to comply with new emission standards without abandoning diesel baselines. Fuel-cell systems, although a niche at present, record the highest 2.76% CAGR and attract pilots in ferries, cruise yachts and auxiliary power modules. The marine propulsion engine market size for dual-fuel units is forecast to rise in tandem with bunker infrastructure roll-outs, especially in Northern Europe and East Asia.
Rapid innovation defines the premium end of the segment. TECO 2030's high-speed hydrogen ferry prototype proves that fuel cells can reach 35 knots while supporting 160 nautical-mile range, a benchmark for coastal passenger services. Luxury yacht builders are experimenting with cryogenic storage and methanol reformers to extend zero-carbon cruising. Yet hydrogen handling rules remain in flux, and insurance premiums for gaseous fuel cargoes are still elevated. These barriers protect diesel's majority share in deep-sea trades where global availability, simplicity and decades of operating data continue to outweigh environmental penalties.
Commercial cargo vessels accounted for 57.37% of the marine propulsion engine market size in 2024, buoyed by a surge in container and bulk demand after pandemic disruptions. Fleet owners prioritized dual-fuel engines to secure CII-compliant operations on Asia-Europe loops. Passenger categories, covering cruise ships and ferries, outpace overall growth at 2.41% CAGR as governments impose fjord and port emission caps that favor electric or hybrid packages. The marine propulsion engine industry also benefits from spill-over orders in the defense segment where silent running and multi-fuel readiness are operational must-haves.
Cruise lines now embed battery modules and methanol capability as standard on newbuilds to meet corporate ESG targets. Norway's fjord rule alone spurred orders for electric fjord ferries, while California's At-Berth extension pushes North American operators toward shore-power compliance. These developments raise auxiliary power requirements, inflating market value even as engine counts per hull decline. Cargo owners, by contrast, invest in fuel flexibility to hedge both price and availability risk, cementing a two-track investment pattern that splits the market between efficiency-driven freighters and regulation-driven passenger craft.
The Marine Propulsion Engine Market Report is Segmented by Engine Type (Diesel, Dual-Fuel, Gas Turbine, and More), Application (Passenger, Commercial Cargo, and Defense), Ship Type (Container Ship, Tanker, Bulk Carrier, and More), Fuel Type (Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), Marine Diesel/Gas Oil, and More), Power Range (Up To 1 000 KW, 1 001 KW To 5 000 KW, and More) and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific commanded 43.36% of 2024 revenue, anchored by China's near-monopoly on high-volume commercial shipbuilding and South Korea's LNG carrier specialization. Regional support extends from policy incentives, such as China's VAT rebates on export tonnage, to supply-chain depth that includes foundries, crankshaft forges and a dense vendor ecosystem. Dual-fuel capability adoption accelerates here because owners can marry low-cost hull production with the latest propulsion packages before delivery, shortening payback periods. Advanced R&D clusters in Japan propel ammonia-ready designs that promise gradual emission abatement without immediate bunkering network overhauls.
Europe remains the crucible for regulatory innovation, shaping technology demand through instruments like FuelEU Maritime, the EU Emissions Trading System and expanding Emission Control Areas. Norwegian fjord zero-emission mandates create an immediate retrofit and new-build pipeline for electric and hydrogen solutions, while Mediterranean ECA designation extends compliance pressures to bulk and tanker traffic that historically skirted Northern rules. Engine suppliers leverage European yards' specialist focus to test fuel-cell and carbon-capture prototypes under commercial voyage conditions, learning that subsequently informs Asia-Pacific volume deployments.
The Middle East and Africa, though only around one tenth of the revenue contributor in 2024, charts the fastest 3.37% CAGR as QatarGas and ADNOC invest in LNG and methanol infrastructure to anchor export chains. Sovereign-backed shipbuilding expansions, such as Hanwha Philly Shipyard's scale-up to ten vessels per year, pull global best-practice know-how into the region. North America's growth centers on defense procurement, reinforced by the Jones Act cabotage shield that drives domestic yard backlog even at higher cost. South America and Africa progress in spurts linked to port modernization and offshore energy investment, but financing hurdles and limited technical clusters slow technology uptake.
- MAN Energy Solutions
- Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- Wartsila Corp.
- Caterpillar Inc.
- Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
- Cummins Inc.
- Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery
- Daihatsu Diesel
- Yanmar Co.
- GE Marine
- Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- Volvo Penta
- ABB Turbocharging & Motion
- Siemens Energy Marine
- Doosan Engine
- STX Engine
- Weichai Heavy-Duty Engine
- Jiangsu CSSC Diesel
- Honda Marine
- Scania AB
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 IMO Tier III & EEXI mandates accelerate engine retrofits
- 4.2.2 Surge in Asia-Pacific new-build orders for container & LNG carriers
- 4.2.3 Rapid uptake of LNG / methanol dual-fuel designs
- 4.2.4 Port-entry zero-emission auxiliary propulsion zones
- 4.2.5 Digital-twin predictive-maintenance lowers total cost of ownership
- 4.2.6 Defense CODAD / CODAG procurement boom
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Fuel-price volatility complicates engine selection
- 4.3.2 High capex for SCR, EGR & after-treatment systems
- 4.3.3 Limited green-methanol / ammonia bunkering network
- 4.3.4 Rare-earth magnet supply risk for electric motors
- 4.4 Value-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value (USD))
- 5.1 By Engine Type
- 5.1.1 Diesel
- 5.1.2 Dual-Fuel (LNG, Methanol, Ammonia ready)
- 5.1.3 Gas Turbine
- 5.1.4 Hybrid-Electric
- 5.1.5 Fuel-Cell
- 5.1.6 Nuclear (Naval)
- 5.2 By Application
- 5.2.1 Passenger
- 5.2.2 Commercial Cargo
- 5.2.3 Defense / Coast Guard
- 5.3 By Ship Type
- 5.3.1 Container Ship
- 5.3.2 Tanker
- 5.3.3 Bulk Carrier
- 5.3.4 Offshore Support Vessel
- 5.3.5 Naval Ship
- 5.3.6 Passenger / Cruise
- 5.4 By Fuel Type
- 5.4.1 Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO)
- 5.4.2 Marine Diesel/Gas Oil
- 5.4.3 LNG
- 5.4.4 Methanol
- 5.4.5 Ammonia/Hydrogen
- 5.5 By Power Range (kW)
- 5.5.1 Up to 1 000 kW
- 5.5.2 1 001 kW to 5 000 kW
- 5.5.3 5 001 kW to 10 000 kW
- 5.5.4 10 001 kW to 20 000 kW
- 5.5.5 Above 20 000 kW
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Spain
- 5.6.3.5 Russia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 UAE
- 5.6.5.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.4 South Africa
- 5.6.5.5 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.6 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (Includes Global Level Overview, Market Level Overview, Core Segments, Financials as Available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for Key Companies, Products and Services, SWOT Analysis, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 MAN Energy Solutions
- 6.4.2 Rolls-Royce Power Systems
- 6.4.3 Wartsila Corp.
- 6.4.4 Caterpillar Inc.
- 6.4.5 Hyundai Heavy Industries Engine & Machinery
- 6.4.6 Cummins Inc.
- 6.4.7 Mitsubishi Heavy Industries Marine Machinery
- 6.4.8 Daihatsu Diesel
- 6.4.9 Yanmar Co.
- 6.4.10 GE Marine
- 6.4.11 Kawasaki Heavy Industries
- 6.4.12 Volvo Penta
- 6.4.13 ABB Turbocharging & Motion
- 6.4.14 Siemens Energy Marine
- 6.4.15 Doosan Engine
- 6.4.16 STX Engine
- 6.4.17 Weichai Heavy-Duty Engine
- 6.4.18 Jiangsu CSSC Diesel
- 6.4.19 Honda Marine
- 6.4.20 Scania AB
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




