PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850396

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850396
5G Infrastructure - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The 5G infrastructure market reached USD 15.55 billion in 2025 and is on course to attain USD 54.06 billion by 2030, translating into a 28.30% CAGR.
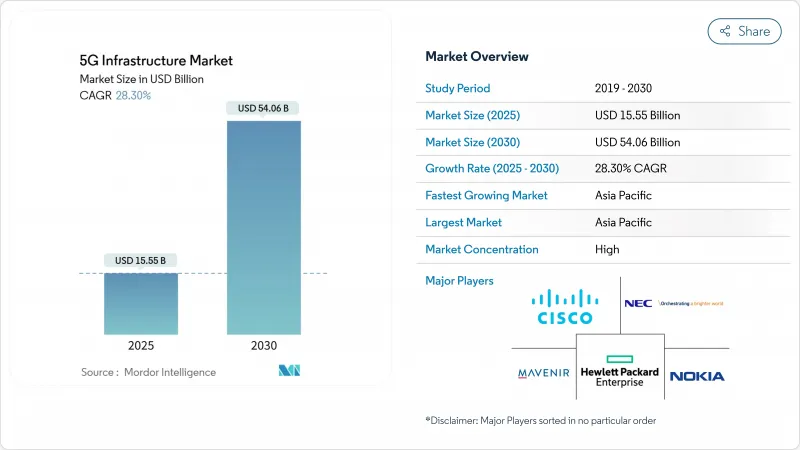
The current expansion pivots on operators replacing earlier non-standalone rollouts with fully programmable standalone platforms that support network slicing, edge computing and private network creation. Capital is shifting from pure coverage toward software-defined functions that shorten service launch cycles, improve automation and lower lifetime operating costs. Demand is reinforced by private-network interest from manufacturing, mobility and energy, alongside fixed-wireless access (FWA) deployments that extend high-speed broadband into rural zones. Meanwhile, spectrum policy is unlocking fresh mid-band capacity, and vendor road maps are converging around cloud-native Open RAN designs that let carriers avoid single-supplier dependence and monetize APIs more quickly.
Global 5G Infrastructure Market Trends and Insights
Increasing Machine-to-Machine and IoT Device Density
Standalone 5G allows each cell site to handle as many as 50,000 connected devices, a prerequisite for Industry 4.0 production lines and massive sensor grids. Hyundai Motor's RedCap-enabled factory network proved that reduced-capability devices can lower power budgets without losing coverage. Edge computing is moving compute resources closer to machines, keeping latency within millisecond windows that robotics and predictive-maintenance schemes require. Private-network proofs in automotive, healthcare, and heavy industry validate the revenue upside that comes from device-dense environments rather than consumer handsets. This driver underpins sustained spending on small cells and edge data centers over the forecast window.
Surge in Mobile Data Consumption
Monthly mobile traffic continues to set new highs as cloud gaming, extended-reality video, and AI-enhanced streaming demand consistent multi-gigabit links. Three UK boosted backbone throughput to 9 Tbit/s after end-2024 peaks surpassed 2 Tbit/s. In China, regulators expect national traffic to quadruple by 2030, moving operators toward capacity architectures that remain efficient under day-long loads. Healthcare pilots, such as real-time tele-ultrasound demonstrations, underline the value of uplink capacity for mission-critical imagery. FWA uptake in India and the United States is also redirecting traffic from smartphones to CPE units, pushing carriers to redesign backhaul for home-first video habits.
High Upfront RAN Densification and Fiber Back-Haul Costs
Small-cell bills from USD 10,000 to USD 50,000 and macro-cell outlays that reach USD 200,000 per site make dense 5G footprints capital heavy, especially where mmWave is mandated. Fiber back-haul can add 30% to project budgets, and scarce digs in suburban corridors slow trenching schedules. Global telecom CAPEX dipped in 2023, the first drop since 2017, making CFOs cautious about accelerated rollouts. Network-sharing deals deliver up to 40% savings but reduce each partner's ability to market premium differentiation. Spectrum licence fees above USD 1 billion per operator further compress balance sheet headroom.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Spectrum Auctions Accelerating Mid-Band Rollouts
- Telco Capex Pivot to Cloud-Native Open RAN Architectures
- Delayed Standardisation for Network-Slicing Monetisation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
RAN equipment generated the largest slice of the 5G infrastructure market, delivering 37% revenue in 2024 as carriers rolled out dense macro and small-cell grids. That initial hardware wave will keep RAN important, yet core networks outpace other layers with a 32.36% CAGR because software-defined control decides future monetisation. The 5G infrastructure market size for core platforms is set to increase sharply as standalone rollouts mandate dual-mode packet cores that virtualise user plane and control plane functions. Vodafone Spain and Three UK highlight how cloud-native cores let operators expose APIs for edge, security and quality-on-demand products
In the second half of the decade, operators view the converged core as the engine for private-network slices, low-latency industrial services, and real-time analytics. RAN spend will taper as coverage milestones are met, whereas lifecycle refresh and feature add-ons keep core invoices growing. Transport and xHaul budgets also rise because distributed units must feed line-rate traffic into data-centre cores. Consequently, the 5G infrastructure market will witness supplier jockeying where optical and routing vendors position themselves as strategic rather than tactical partners.
Mid-band commanded 46% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024 because it blends propagation reach with multi-hundred-MHz bandwidth that supports massive MIMO arrays. Operators from Chicago to Berlin use 3.5 GHz radios to cover suburban rings without overspending on cells. mmWave, however, shows the fastest 33.58% CAGR by serving FWA households and event venues. This trajectory means the 5G infrastructure market size linked to mmWave radios, repeaters and advanced beamforming silicon will climb quickly, especially in the United States, Japan and South Korea.
Low-band below 1 GHz stays vital for wide-area IoT coverage but struggles with gigabit targets, keeping it a supplement, not a star. mmWave deployment faces line-of-sight and foliage loss, yet high-gain antennas and AI-aided beam steering are closing some gaps. Regulators that bundle mid-band and high-band blocks in the same licence round help carriers align the spectrum mix with differentiated service tiers.
The 5G Infrastructure Market is Segmented by Communication Infrastructure (5G Radio Access Networks, 5G Core Networks, Transport / XHaul [Front, Mid, Back-Haul], and More), Spectrum Band (Low-Band, Mid-Band, and More), Network Architecture (Non-Standalone [NSA] and More), Core Network Technology (Software-Defined Networking [SDN] and More), End-User Vertical (Consumer Electronics, and More), and Geography.
Geography Analysis
Asia Pacific held 24% of 5G infrastructure market share in 2024, driven by China's 4.4 million base stations and India's race to connect 30 million FWA subscribers by 2027. The region will expand at a 32.27% CAGR as South Korea sustains 97% population coverage and Japan adds suburban densification. Rural programmes in Indonesia, Vietnam, and the Philippines will lean on shared-tower models, while Australia advances with hybrid satellite-5G back-ups for remote mining operations.
North America shows coverage maturity above 80% of people yet reinvigorated spending in 2025 after a 2023 dip. Ericsson logged 54% year-over-year regional growth in Q4 2024, signalling that standalone cores, edge zones, and large enterprise deals are moving budgets again. US carriers bundle FWA with fibre to capture underserved suburbs, and Canada allocates fresh mid-band spectrum to accelerate indigenous-community connectivity.
Europe trails on standalone penetration but targets a EUR 164 billion economic boost by 2030 from harmonised regulation. Germany's 96% coverage illustrates what cohesive awards achieve, whereas the United Kingdom must rebuild performance after vendor bans slowed equipment swaps. Latin America steps into commercial phase with 29 operators live; regional connections should reach 425 million by 2030 as spectrum fees fall and cloud players finance neutral-host towers.
- Airspan Networks Inc.
- AT&T Inc.
- Casa Systems Inc.
- Cisco Systems Inc.
- CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- Corning Inc.
- Dell Technologies Inc.
- Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- Fujitsu Limited
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- Intel Corporation
- Juniper Networks Inc.
- Mavenir Systems Inc.
- NEC Corporation
- Nokia Corporation
- Oracle Corporation
- Parallel Wireless Inc.
- Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- Ribbon Communications Inc.
- Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- Verizon Communications Inc.
- ZTE Corporation
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Increasing machine-to-machine and IoT device density
- 4.2.2 Surge in mobile data consumption
- 4.2.3 Government spectrum auctions accelerating mid-band rollouts
- 4.2.4 Telco capex pivot to cloud-native open RAN architectures
- 4.2.5 Emerging demand for private 5G in brownfield industrial sites
- 4.2.6 Fixed-wireless access (FWA) substituting fiber in rural markets
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High upfront RAN densification and fiber back-haul costs
- 4.3.2 Delayed standardization for network-slicing monetization
- 4.3.3 National-security restrictions on Chinese vendors
- 4.3.4 Skilled-labor shortages for mmWave deployment
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Investment and Funding Trends
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.4 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
- 4.8.5 Threat of Substitute Products
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Communication Infrastructure
- 5.1.1 5G Radio Access Network (RAN)
- 5.1.2 Transport / xHaul (Front-, Mid-, Back-haul)
- 5.1.3 Core Network (Cloud-native 5GC)
- 5.2 By Spectrum Band
- 5.2.1 Low-Band (less than 1 GHz)
- 5.2.2 Mid-Band (1-6 GHz)
- 5.2.3 High-Band / mmWave (above 24 GHz)
- 5.3 By Network Architecture
- 5.3.1 Non-Standalone (NSA)
- 5.3.2 Standalone (SA)
- 5.4 By Core Network Technology
- 5.4.1 Software-Defined Networking (SDN)
- 5.4.2 Network Function Virtualization (NFV)
- 5.4.3 Multi-access Edge Computing (MEC)
- 5.4.4 Network Slicing
- 5.5 By End-user Vertical
- 5.5.1 Consumer Electronics
- 5.5.2 Automotive and Mobility
- 5.5.3 Industrial Manufacturing
- 5.5.4 Healthcare and Life Sciences
- 5.5.5 Energy and Utilities
- 5.5.6 Public Safety and Defense
- 5.5.7 Smart Cities and Infrastructure
- 5.5.8 Other Verticals (Retail, Media, Agriculture)
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 Germany
- 5.6.3.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Spain
- 5.6.3.6 Russia
- 5.6.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 APAC
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 Japan
- 5.6.4.3 South Korea
- 5.6.4.4 India
- 5.6.4.5 Australia
- 5.6.4.6 Rest of APAC
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Airspan Networks Inc.
- 6.4.2 AT&T Inc.
- 6.4.3 Casa Systems Inc.
- 6.4.4 Cisco Systems Inc.
- 6.4.5 CommScope Holding Company Inc.
- 6.4.6 Corning Inc.
- 6.4.7 Dell Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.8 Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson
- 6.4.9 Fujitsu Limited
- 6.4.10 Hewlett Packard Enterprise Development LP
- 6.4.11 Huawei Technologies Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.12 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.13 Juniper Networks Inc.
- 6.4.14 Mavenir Systems Inc.
- 6.4.15 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.16 Nokia Corporation
- 6.4.17 Oracle Corporation
- 6.4.18 Parallel Wireless Inc.
- 6.4.19 Qualcomm Technologies Inc.
- 6.4.20 Qucell Networks Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Rakuten Symphony Inc.
- 6.4.22 Ribbon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.23 Samsung Electronics Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.24 Verizon Communications Inc.
- 6.4.25 ZTE Corporation
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




