PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850952

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1850952
Geotextile - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The geotextiles market size is estimated at USD 4.70 billion in 2025 and is forecast to climb to USD 7.69 billion by 2030, reflecting a CAGR of 10.34% over the period.
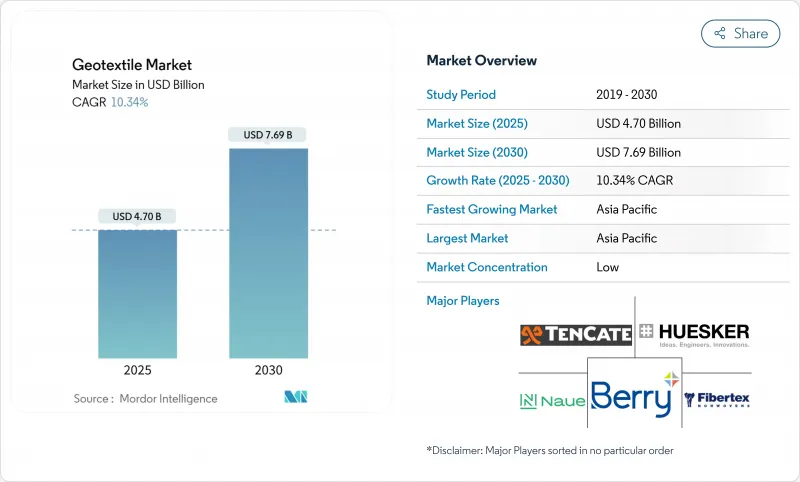
The strong expansion is rooted in the material's ability to boost infrastructure resilience while supporting circular-economy targets, so the geotextiles industry increasingly sits at the intersection of civil engineering, environmental stewardship and resource efficiency. Even after adjusting for inflation, the absolute spending on new roads, railbeds and flood-control systems is widening the addressable market faster than previously projected, implying sustained procurement pipelines for suppliers. In parallel, manufacturer investments in higher-throughput lines signal confidence that demand elasticity outweighs short-term raw-material volatility. A fresh inference from recent contract awards is that public agencies now bundle performance-based specifications with recycled-content clauses, effectively making geotextiles a proxy for sustainability goals instead of a purely technical item.
Global Geotextile Market Trends and Insights
Construction Sector Expansion Fuels Geotextile Adoption
Persistent growth in transportation budgets is pushing geotextile specifications from optional to standard practice on highway contracts. Field data from the Federal Highway Administration show that 78% of new U.S. highway projects already integrate at least one geotextile layer, and agency engineers report aggregate savings of up to one-fifth on sub-base volumes. The pattern is similar in rail, where American Society of Civil Engineers papers document a two-digit improvement in ballast stability when separation fabrics are used. A fresh inference is that cost predictability, not just headline savings, is driving faster contractor uptake because material quantities become easier to model once geotextiles are part of the design.
Mining Sector Integration Enhances Operational Sustainability
Copper and lithium producers in Chile, Australia and South Africa are embedding geotextiles into tailings-storage facilities to limit seepage and reduce freshwater withdrawals. Operators now specify sensor-ready non-woven layers that feed real-time data into dam-integrity dashboards, a capability that shortens inspection cycles and satisfies increasingly stringent disclosure rules. The industry's willingness to pilot higher-spec products indicates that compliance risk, rather than commodity price swings, is shaping procurement priorities. An observed secondary effect is the creation of local fabrication units near major mine clusters, hinting at an emerging decentralised supply model for the geotextiles industry.
Propylene Price Volatility Threatens Margin Stability
Contract prices for polypropylene feedstock have shown double-digit intra-year swings, compressing producer margins and complicating fixed-price bids. Smaller mills with limited hedging capacity are shifting toward make-to-order models, which pass cost volatility downstream but risk eroding market share when buyers prioritise lead-time certainty. The ripple effect is that alternative polymers such as high-density polyethylene are gaining incremental share in containment applications, not due to technical superiority but because of more predictable input costs. One fresh inference is that procurement officers may start indexing contracts to polymer baskets rather than single monomers to balance price risk.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Environmental Regulations Drive Material Innovation
- European Landfill Directive Elevates Geosynthetic Demand
- Engineering Skills Gap Hampers Technical Implementation
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The polypropylene segment accounts for the largest geotextiles market share at 57.30% in 2024, with the market size in this material forecast to climb at an 11.30% CAGR through 2030. Its popularity stems from chemical resistance and a favourable strength-to-weight ratio, attributes recently confirmed by laboratory aging tests under elevated temperature and ultraviolet exposure that showed retained tensile strength above specification thresholds. A fresh inference is that the ongoing shift to circular design will further cement polypropylene's lead, because stabiliser packages compatible with mechanical recycling are already commercially available.
Polyester holds a significant share prized for high tensile modulus in reinforcement mats but held back by constrained rPET supply. Supply-chain stress is encouraging diversification into blends that mix virgin polyester with bio-sourced fibres, balancing performance and procurement risk. Polyethylene captures close to one-eighth of volume, targeting chemical-containment niches where stress-crack resistance matters more than modulus. Emerging natural and biodegradable polymers make up the balance and, though costlier, secure purchase orders in sensitive ecosystems where removal after service life is difficult. The logical inference is that dual-material specifications, combining a durable synthetic layer with a biodegradable sacrificial layer, could open new mid-price adoption avenues.
Woven geotextiles command a 45% market share in 2024, driven by superior load-distribution in road sub-bases. Their market size is expected to expand steadily as public agencies prioritise long design lives. New shuttle-loom configurations have increased productive width, lowering installation overlaps and labour hours. A current inference is that the wider rolls may tilt cost-benefit analyses in favour of woven fabrics even in applications traditionally dominated by non-wovens.
Non-woven geotextiles grow faster, at an 11.50% CAGR, and increasingly integrate into stormwater filtration systems. Needle-punched variants address differential settlement without sacrificing permeability, bridging a performance gap that once limited use beneath rail ballast. Knitted fabrics, supply ultra-high strength for geogrid-geotextile composites where directional reinforcement is prized. Manufacturers are bundling knitted layers with non-woven filters into multi-layer laminates, an approach that delivers three functions in one installation step. That trend implies buyers may soon specify "systems" rather than "fabrics", altering how market statistics are compiled.
The Geotextiles Market Report Segments the Industry by Material (Polypropylene, Polyester, and More), Fabric Type (Woven, Non-Woven, and Knitted), Function (Separation, Drainage, and More), Application (Road Construction and Pavement Repair, Erosion, and More), and Geography (Asia-Pacific, North America, Europe, South America, and Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific leads with a 39.5% geotextiles market share in 2024. China generates significant of regional demand, marrying aggressive infrastructure expansion with stricter environmental codes. India contributes one-quarter and benefits from its Quality Control Order scheduled for April 2025, which is expected to raise baseline technical standardsJapan, South Korea, and Australia collectively contribute a significant portion to the regional expenditure, deploying sophisticated earthquake- and cyclone-resilient designs that often rely on composite geotextiles. The remainder rests with Southeast Asia, where public-private partnerships are catalysing first-time adoption. An emerging inference is that domestic capacity additions will convert Asia-Pacific from a net importer to a balanced trade zone by decade-end.
North America, dominated by the United States, where BABA rules require domestic manufacture for federally funded projects from March 2025. Canada holds one-fifth of the regional pie, leveraging geotextiles for cold-region roads and mining applications, while Mexico's share grows with industrial-park construction along the near-shoring corridor. Adoption of sensor-embedded fabrics is highest here, an indicator that digital infrastructure strategies are translating into premium product demand. A fresh inference is that U.S. highway re-authorisation cycles lock in multi-year procurement visibility, allowing mills to operate at higher utilisation rates than global averages.
Europe contributes significantly to total sales, with Germany, France, and the UK playing a major role in this contribution, propelled by stringent emissions protocols that favour recycled and low-carbon geotextiles. Southern Europe focuses on erosion-control projects linked to drought resilience, while Eastern states channel EU cohesion funds into rail and road rehabilitation. Manufacturers such as Sioen Industries publicise circular-economy achievements, suggesting brand differentiation is shifting from cost to sustainability metrics. The inference is that once economic conditions improve, deferred maintenance backlogs could trigger a second-wave demand surge.
- ACE Geosynthetics
- AFITEXINOV
- AGRU America Inc.
- Asahi Kasei Advance Corporation
- Berry Global Inc.
- Carthage Mills
- CMC
- Fibertex Nonwovens A/S
- Freudenberg Performance Materials
- HUESKER International
- Industrial Fabrics, Inc.
- KayTech
- Mattex Geosynthetics
- Naue GmbH & Co. KG
- Officine Maccaferri Spa
- Owens Corning
- Solmax
- TenCate Geosynthetics
- Thrace Group
- TYPAR Geosynthetics
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Growing Usage of Geotextiles in Construction Industry
- 4.2.2 Increase Usage of Geotextiles in Mining Activities
- 4.2.3 Stringent Regulatory Framework for Environmental Protection
- 4.2.4 Mandatory Capping Layers in Europe Landfill Directive Boosting Geosynthetic Liners
- 4.2.5 Saudi NEOM and Giga-Projects Driving Desert Soil-Stabilisation Solutions in GCC region
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Volatile Propylene Contract Prices
- 4.3.2 Polyester Supply Tightness from rPET Allocation to Beverage Packaging
- 4.3.3 Engineering-Skills Gap Curtailing Design-Build Adoption in Emerging Economies
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.5.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.5.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.5.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.5.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.5.5 Degree of Competition
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value)
- 5.1 By Material
- 5.1.1 Polypropylene
- 5.1.2 Polyester
- 5.1.3 Polyethylene
- 5.1.4 Other Materials
- 5.2 By Fabric Type
- 5.2.1 Woven
- 5.2.2 Non-woven
- 5.2.3 Knitted
- 5.3 By Function
- 5.3.1 Separation
- 5.3.2 Drainage
- 5.3.3 Filtration
- 5.3.4 Reinforcement
- 5.3.5 Protection
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Road Construction and Pavement Repair
- 5.4.2 Erosion
- 5.4.3 Drainage
- 5.4.4 Railworks
- 5.4.5 Agriculture
- 5.4.6 Other Applications (Mining Operations, Coastal and Waterway Protection,etc.)
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.1.1 China
- 5.5.1.2 India
- 5.5.1.3 Japan
- 5.5.1.4 South Korea
- 5.5.1.5 Thailand
- 5.5.1.6 Malaysia
- 5.5.1.7 Indonesia
- 5.5.1.8 Vietnam
- 5.5.1.9 Rest of Asia
- 5.5.2 North America
- 5.5.2.1 United States
- 5.5.2.2 Canada
- 5.5.2.3 Mexico
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 Germany
- 5.5.3.2 France
- 5.5.3.3 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Nordics
- 5.5.3.7 Russia
- 5.5.3.8 Turkey
- 5.5.3.9 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Argentina
- 5.5.4.3 Colombia
- 5.5.4.4 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 Qatar
- 5.5.5.4 South Africa
- 5.5.5.5 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.6 Egypt
- 5.5.5.7 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 Asia-Pacific
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ACE Geosynthetics
- 6.4.2 AFITEXINOV
- 6.4.3 AGRU America Inc.
- 6.4.4 Asahi Kasei Advance Corporation
- 6.4.5 Berry Global Inc.
- 6.4.6 Carthage Mills
- 6.4.7 CMC
- 6.4.8 Fibertex Nonwovens A/S
- 6.4.9 Freudenberg Performance Materials
- 6.4.10 HUESKER International
- 6.4.11 Industrial Fabrics, Inc.
- 6.4.12 KayTech
- 6.4.13 Mattex Geosynthetics
- 6.4.14 Naue GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.4.15 Officine Maccaferri Spa
- 6.4.16 Owens Corning
- 6.4.17 Solmax
- 6.4.18 TenCate Geosynthetics
- 6.4.19 Thrace Group
- 6.4.20 TYPAR Geosynthetics
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment
- 7.2 Rising Awareness about Water Conservation in the Manufacturing Sector




