PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851080

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851080
Hemophilia - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The hemophilia market size was valued at USD 14.56 billion in 2025 and is forecast to advance to USD 19.25 billion by 2030, recording a 5.74% CAGR during the period.
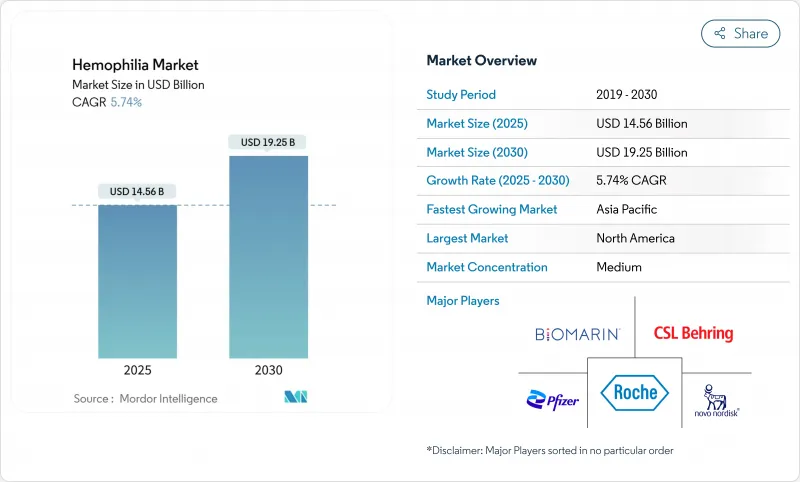
Expanding diagnosis, favorable reimbursement, and commercialization of transformative options such as extended half-life (EHL) recombinant factors and single-dose gene therapies are reshaping the hemophilia market landscape. Uptake of non-factor agents for inhibitor patients, intensifying competition among manufacturers, and broadening newborn-screening programs also contribute to sustainable demand. Headline risks stem from gene-therapy durability questions, persistent plasma-collection shortages, and payer budget constraints. Yet, overall momentum remains positive as payers increasingly recognize the long-run cost offsets offered by innovative prophylactic approaches.
Global Hemophilia Market Trends and Insights
Rising Diagnosed Prevalence & Life-Expectancy Improvements
Identification of hemophilia cases has risen sharply, taking the global diagnosed population to roughly 1.1 million in 2025 after sustained expansion of testing capacity in emerging economies. China reduced its average diagnosis lag from 13.3 years to 0.4 years between 2008 and 2018, illustrating the pace of improvement. Higher life expectancy is tied to broader prophylaxis adoption; CDC surveillance shows mortality declines in patients managed through hemophilia treatment centers. Countries with structured care networks now deliver near-normal life expectancy, reinforcing steady demand for advanced therapies.
Launch of Extended Half-Life (EHL) Recombinant Factors
ALTUVIIIO enables once-weekly dosing, reducing infusion counts by half compared with standard factors. Clinical data show 65% of users experience zero bleeds during prophylaxis, and European approval with 10-year exclusivity adds regulatory confidence. EHL factors cut cold-chain burdens, improve joint outcomes and bolster adherence, while maintaining surgical safety comparable to legacy products.
High Treatment Cost & Payer Budget Pressure
Annual US costs range from USD 213,874 to USD 869,940 per patient, straining budgets. Gene therapies intensify scrutiny with list prices near USD 3.5 million. Plasma-supply shortages add further inflationary pressure in Europe, while Chinese urban patients bear out-of-pocket costs topping 30% of disposable income, limiting prophylaxis uptake. Brazil's annual spend averages USD 450,831 per patient, totaling USD 5.19 billion nationally in 2025.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Commercial Availability of One-Time Gene Therapies
- Favorable Reimbursement & National Hemophilia Programs
- Care-Access Gaps in Low-/Middle-Income Countries
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hemophilia A contributed 75.12% of hemophilia market share in 2024 due to its higher prevalence of roughly 1 in 5,000 male births. Hemophilia B is growing faster because factor IX's longer half-life supports durable gene-therapy efficacy; HEMGENIX enabled 94% of patients to stop prophylaxis over four years. The hemophilia industry sees complementary progress in non-factor agents that address unmet needs across both subtypes.
Momentum in hemophilia A derives from EHL factors such as ALTUVIIIO and non-factor molecules like emicizumab, which together improve adherence and bleed control. Parallel breakthroughs in hemophilia B create a balanced pipeline where gene-therapy success stories stimulate investment while established factor concentrates preserve treatment flexibility. Hemophilia C and other rare factor deficiencies represent a smaller but clinically significant segment, with factor VII deficiency studies in Japan demonstrating effective management with recombinant activated factor VII, achieving 45.7% excellent and 33.6% effective hemostatic responses. Overall, the convergence of traditional and advanced modalities maintains dynamic competition within the broader hemophilia market.
Replacement therapy retained 63.41% of the hemophilia market size in 2024, valued at USD 9.23 billion, reflecting its entrenched role in daily care. Yet gene therapy posts the highest CAGR to 2030, propelled by single-infusion curative potential that appeals to younger cohorts. Non-factor prophylactics expand quickly as physicians shift inhibitor patients from bypassing agents to convenient subcutaneous regimens.
Replacement therapy benefits from EHL innovations that lower infusion frequency, protecting share even as gene therapy scales. Conversely, payers weigh lifetime cost offsets-gene therapy could negate annual prophylaxis bills that surpass USD 600,000, creating strong incentives for adoption once durability comfort solidifies. Non-factor molecules further diversify choices, reinforcing a multitrack approach where each modality meets distinct clinical needs
The Hemophilia Market Report is Segmented by Disease Type (Hemophilia A, Hemophilia B, and More), Therapy (Replacement Therapy, Gene Therapy, and More), Product Type (Recombinant Coagulation Factor Concentrates and More), Treatment Setting (Prophylaxis and On-Demand), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, Middle East and Africa, South America). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America accounted for 47.59% of global revenue in 2024, anchored by 146 federally funded hemophilia treatment centers that collectively manage more than 52,000 patients. Robust reimbursement frameworks include Medicare coverage for gene therapies and the 340B program that subsidizes drug acquisition. Data from the CDC's Community Counts registry informs best-practice guidelines across 134,000 individuals, accelerating evidence-based adoption of novel agents. Despite available funding, CSL Behring notes slower than anticipated uptake of HEMGENIX, illustrating the nuanced decision pathways that accompany high-cost curative therapies.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest-expanding region, projected at 6.88% CAGR from 2025-2030. China cut diagnosis delays to 0.4 years and increased annual factor consumption as reimbursement broadened. Japan's HIKOBOSHI study shows monthly factor VIII dosing climbed fivefold between 2005 and 2019, reflecting proactive prophylaxis trends. Nonetheless, only 3.2% of Chinese hemophilia A patients access prophylaxis, underscoring financial gaps. Regional working groups push for national registries and coordinated-care programs to harmonize treatment standards.
Europe enjoys mature infrastructure and progressive reimbursement but encounters plasma shortages; the bloc imports around 40% of plasma from the United States and seeks 2 million new donors to stabilize supply. Middle East & Africa and South America face pronounced access deficits; only 8% of African cases are diagnosed, and specialized staff shortages persist. Factor consumption remains well below therapeutic thresholds, sustaining unmet need and positioning these regions as future growth opportunities once infrastructure and reimbursement improve.
- Bayer
- Biomarin Pharmaceutical
- Catalyst Biosciences Inc.
- CSL Ltd. (CSL Behring)
- Roche
- Freeline Therapeutics
- GC Biopharma
- Grifols
- Kedrion Biopharma
- Medexus Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- Novo Nordisk
- Octapharma
- Opko Health
- Pfizer
- Regeneron Pharmaceuticals
- Sangamo Therapeutics
- Sanofi
- Silence Therapeutics plc
- Sobi AB
- Takeda Pharmaceuticals
- UniQure
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising diagnosed prevalence & life-expectancy improvements
- 4.2.2 Launch of extended half-life (EHL) recombinant factors
- 4.2.3 Commercial availability of one-time gene therapies
- 4.2.4 Favorable reimbursement & national hemophilia programs
- 4.2.5 Expansion of non-factor therapies for inhibitor patients
- 4.2.6 Real-world registries enabling precision dosing analytics
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High treatment cost & payer budget pressure
- 4.3.2 Care-access gaps in low-/middle-income countries
- 4.3.3 Durability-uncertainty of single-dose gene therapies
- 4.3.4 Plasma-collection shortages disrupting PD product supply
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Disease Type
- 5.1.1 Hemophilia A
- 5.1.2 Hemophilia B
- 5.1.3 Hemophilia C & Others
- 5.2 By Therapy
- 5.2.1 Replacement Therapy
- 5.2.2 Gene Therapy
- 5.2.3 Non-Factor Therapy
- 5.3 By Product Type
- 5.3.1 Recombinant Coagulation Factor Concentrates
- 5.3.2 Plasma-Derived Factor Concentrates
- 5.3.3 Bypassing & Ancillary Agents
- 5.4 By Treatment Setting
- 5.4.1 Prophylaxis
- 5.4.2 On-Demand
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Competitive Benchmarking
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Bayer AG
- 6.4.2 BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc.
- 6.4.3 Catalyst Biosciences Inc.
- 6.4.4 CSL Ltd. (CSL Behring)
- 6.4.5 F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG
- 6.4.6 Freeline Therapeutics
- 6.4.7 GC Pharma
- 6.4.8 Grifols SA
- 6.4.9 Kedrion SpA
- 6.4.10 Medexus Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.4.11 Novo Nordisk A/S
- 6.4.12 Octapharma AG
- 6.4.13 OPKO Health Inc.
- 6.4.14 Pfizer Inc.
- 6.4.15 Regeneron Pharmaceuticals Inc.
- 6.4.16 Sangamo Therapeutics
- 6.4.17 Sanofi SA
- 6.4.18 Silence Therapeutics plc
- 6.4.19 Sobi AB
- 6.4.20 Takeda Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.21 uniQure NV
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-Space & Unmet-Need Assessment




