PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851095

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851095
5G Enterprise - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The 5G Enterprise Market size is estimated at USD 6.73 billion in 2025, and is expected to reach USD 26.02 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 31.06% during the forecast period (2025-2030).
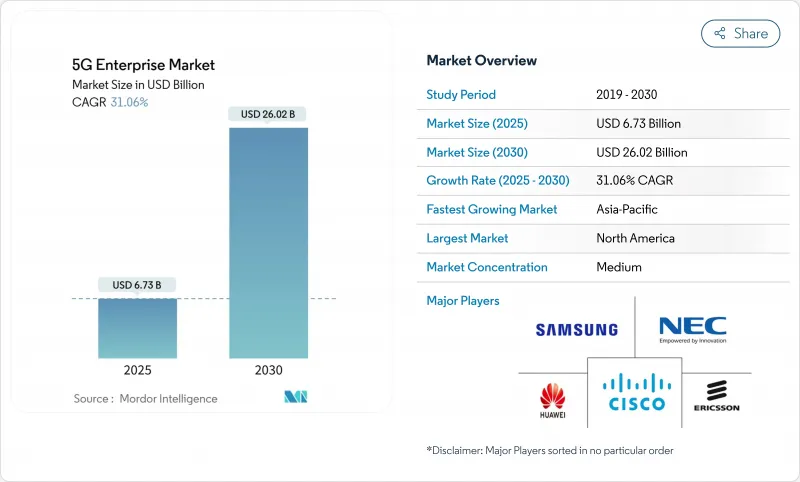
This expansion springs from enterprises treating 5G as the digital backbone for automation, analytics, and immersive applications. Robust interest in standalone 5G, already offered by 47 mobile operators, is speeding up adoption of features such as network slicing and ultra-reliable low-latency communications. Private deployments and edge architectures are removing performance bottlenecks, while unlicensed and shared spectrum access is lowering entry barriers. Early industrial rollouts show measurable productivity gains, and satellite-5G partnerships now span 43 countries, broadening coverage footprints. Even so, high capital outlays, brown-field integration complexity, and a pronounced shortage of cross-disciplinary 5G/OT talent temper the near-term uptake.
Global 5G Enterprise Market Trends and Insights
Release of Unlicensed/Shared Spectrum Transforms Enterprise Access
Regulators opening mid-band frequencies have made private 5G viable for firms that once shied away from spectrum fees. In the United States, the Citizens Band Radio Service has already supported more than 250,000 industrial device activations, encouraging similar frameworks in Europe's 3.8-4.2 GHz band. Siemens anticipates deployments moving from pilots to scale during 2025 as harmonization progresses. Greater flexibility allows factories, logistics hubs, and energy sites to customize coverage footprints, improving uptime and security. Shared spectrum also stimulates a growing ecosystem of network-in-a-box vendors that package radios, edge cores, and management tools as turnkey kits. The cumulative effect is a wider funnel of prospects entering the 5G enterprise market, accelerating time to revenue for suppliers.
Edge Computing and Network Slicing Redefine Enterprise Architectures
Enterprises are refactoring networks so that latency-sensitive workloads sit within meters of connected assets. Operators such as T-Mobile illustrate the concept through priority slices for first responders. Forty-seven operator groups are now standardizing APIs that expose slice configuration to developers, lowering orchestration effort. Combining dedicated slices with on-premises compute nodes helps manufacturers push decision loops below 1 ms, enabling synchronous robotics and vision inspection. A Wray Castle study indicates network slicing can boost overall spectrum utilisation by 40%. These gains feed directly into OpEx savings, reinforcing the value proposition of private-edge architecture inside the 5G enterprise market.
High CAPEX and Integration Complexity Slow Adoption
Standalone 5G cores, multi-band radios, and industrial gateways can push a mid-sized brown-field deployment into multi-million-dollar territory. A 2024 Kyndryl survey showed many firms deferring projects until they blueprint migration paths for legacy SCADA and MES layers. Open RAN promises vendor diversity yet introduces fresh interoperability testing, as flagged by the Open RAN Integration Playbook. Network-as-a-Service models are emerging to smooth cash-flow peaks by shifting spend from capex to OpEx, but clarity around service-level commitments still varies. This financial and technical inertia trims early growth in segments with razor-thin margins.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Industrial IoT Accelerates Manufacturing Transformation
- Net-Zero Mandates Drive Energy-Optimized Deployments
- Scarcity of 5G/OT Engineering Talent Creates Implementation Bottleneck
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
The 5G Radio Access Network segment generated the largest slice of revenue in 2024 at 36.00%, reflecting its indispensable role in linking endpoints. This foundational investment gave operators and integrators a head starts in monetizing coverage obligations. Rising enterprise need for deterministic performance now shifts attention to cloud-native 5G cores, which are on course for a 32.69% CAGR. The 5G enterprise market size for core solutions is projected to expand sharply as standalone deployments move beyond trials. Network function virtualization lets firms bolt on low-code policy engines, converged charging, and AI-driven assurance, driving higher ARPU per site.
Transport and backhaul, though smaller in absolute terms, are evolving rapidly. Partnerships such as Ericsson with Juniper and ECI Telecom confirm demand for high-capacity packet transport between cell sites and data centers. E-band and emerging W-band links unlock multi-gigabit throughput, complementing fibre in dense industrial parks. These innovations reduce bottlenecks that once throttled remote-vision analytics. As a result, core and transport segments are becoming tightly coupled, expanding their combined wallet share inside the 5G enterprise market.
Private deployments captured 38.30% of revenue in 2024, reinforcing the preference for on-premises control. With a 36.2% CAGR, the 5G enterprise market size for private deployments is set to multiply, led by factories, hospitals, and logistics yards that value deterministic Quality of Service. A 2024 Digitalization World survey forecasts global private-5G revenues at USD 6 billion by 2027. Contrast that with public 5G, which suits use cases where coverage breadth outweighs micro latency needs.
Hybrid models are also standing out. Enterprises employ public slices for non-sensitive traffic while reserving a campus-wide micro-core for robotics or AGVs. Neutral-host solutions enable venue owners to share infrastructure costs, facilitating rapid multi-tenant coverage. This approach helps operators penetrate new verticals without redeploying full stacks, broadening addressable revenue streams across the 5G enterprise market.
The Enterprise 5G Market Report is Segmented by Communication Infrastructure Type (5G Radio Access Networks [RAN], 5G Core Networks, and More), Deployment Mode (Private 5G Networks, Public 5G Networks, and More), Spectrum Licensing Type (Licensed Spectrum, Unlicensed/Shared, and Mixed Licensing), Enterprise Vertical (IT and Telecommunication, BFSI, and More), and Geography. The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commanded the largest regional footprint at 37.80% revenue share in 2024, anchored by early spectrum releases and active systems-integration ecosystems. The United States sees 76% of manufacturers planning private networks, though a recent policy shift caused an 11% dip in short-term enthusiasm. Public funding proposals worth USD 9 billion aim to extend 5G broadband into rural zones, which will widen the customer base. Canada follows with strong incentives for Industry 4.0 testbeds. Together, these initiatives reinforce leadership even as North American coverage ambitions mature.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest climber with a 33.5% CAGR through 2030. China's 5G+ Smart Factory programs show quantifiable gains in throughput and defect reduction. Japan and South Korea exploit longstanding industrial automation cultures, layering 5G over existing lean-manufacturing cells. India's telecom-sector skills gap tops 2.4 million workers, which policy makers address via reskilling campaigns lightreading. Despite talent constraints, lower equipment prices bolster adoption among mid-tier enterprises.
Europe retains a solid foothold despite coverage gaps. Germany's auction of 3.8-4.2 GHz licenses directly to industry pioneers expanded campus network pilots. Pan-EU harmonization simplifies device certification, although total capital investment slid for the first time in seven years to EUR 57.9 billion. Open RAN and edge cloud projects attract new entrants, fueling competitive variety. GSMA expects 5G to contribute over EUR 160 billion to European GDP by 2030. These figures underscore steady, if uneven, progression.
The Middle East and Africa witness growing momentum led by Saudi Arabia's fresh spectrum auctions, driving vendor revenue up 9% in Q4 2024 for Nokia. Latin America remains in the early adoption phase but benefits from satellite-backed 5G coverage for mining and agriculture. Collectively, global demand diversity positions the 5G enterprise market for broad-based expansion.
- Cisco Systems
- Ericsson
- Huawei Technologies
- Nokia
- NEC Corporation
- Samsung Electronics
- ZTE Corporation
- Qualcomm
- Intel Corporation
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise (Aruba)
- Dell Technologies
- Juniper Networks
- Mavenir
- Rakuten Symphony
- CommScope
- ATandT
- Verizon Communications
- Deutsche Telekom AG
- Siemens AG
- Fujitsu
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Release of unlicensed/shared spectrum for industrial sites
- 4.2.2 Edge computing and network-slicing enable ultra-low-latency apps
- 4.2.3 Industrial-IoT boom in smart manufacturing plants
- 4.2.4 Net-zero mandates drive real-time energy-optimised private 5G
- 4.2.5 Convergence of 5G and TSN for deterministic control in brown-fields
- 4.2.6 5G non-terrestrial networks extend seamless enterprise coverage
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High CAPEX and integration complexity
- 4.3.2 Scarcity of 5G/OT engineering talent
- 4.3.3 Fragmented device-certification ecosystem
- 4.3.4 Local-spectrum rules hinder multi-national roll-outs
- 4.4 Value/Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 MEC and 5G Technical Standards Analysis
- 4.8 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.8.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.8.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.8.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.8.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.8.5 Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Communication Infrastructure Type
- 5.1.1 5G Radio Access Networks (RAN)
- 5.1.2 5G Core Networks
- 5.1.3 Transport/Backhaul Networks
- 5.2 By Deployment Model
- 5.2.1 Private 5G Networks
- 5.2.2 Public 5G Networks
- 5.2.3 Hybrid/Shared Networks
- 5.3 By Spectrum Licensing Type
- 5.3.1 Licensed Spectrum
- 5.3.2 Unlicensed/Shared (e.g., CBRS, LAA)
- 5.3.3 Mixed Licensing
- 5.4 By Enterprise Vertical
- 5.4.1 IT and Telecommunications
- 5.4.2 BFSI
- 5.4.3 Manufacturing - Discrete
- 5.4.4 Manufacturing - Process
- 5.4.5 Retail and E-commerce
- 5.4.6 Healthcare
- 5.4.7 Energy and Utilities
- 5.4.8 Transportation and Logistics
- 5.4.9 Other Verticals
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 South America
- 5.5.2.1 Brazil
- 5.5.2.2 Argentina
- 5.5.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.3 Europe
- 5.5.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.3.2 Germany
- 5.5.3.3 France
- 5.5.3.4 Italy
- 5.5.3.5 Spain
- 5.5.3.6 Russia
- 5.5.3.7 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4.1 China
- 5.5.4.2 India
- 5.5.4.3 Japan
- 5.5.4.4 South Korea
- 5.5.4.5 ASEAN
- 5.5.4.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.3 South Africa
- 5.5.5.4 Nigeria
- 5.5.5.5 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles {(includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share, Products and Services, Recent Developments)}
- 6.4.1 Cisco Systems
- 6.4.2 Ericsson
- 6.4.3 Huawei Technologies
- 6.4.4 Nokia
- 6.4.5 NEC Corporation
- 6.4.6 Samsung Electronics
- 6.4.7 ZTE Corporation
- 6.4.8 Qualcomm
- 6.4.9 Intel Corporation
- 6.4.10 Hewlett Packard Enterprise (Aruba)
- 6.4.11 Dell Technologies
- 6.4.12 Juniper Networks
- 6.4.13 Mavenir
- 6.4.14 Rakuten Symphony
- 6.4.15 CommScope
- 6.4.16 ATandT
- 6.4.17 Verizon Communications
- 6.4.18 Deutsche Telekom AG
- 6.4.19 Siemens AG
- 6.4.20 Fujitsu
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-need Assessment




