PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851118

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851118
Steam Autoclaves - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The steam autoclaves market stood at USD 2.65 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 3.92 billion by 2030, advancing at an 8.12% CAGR.
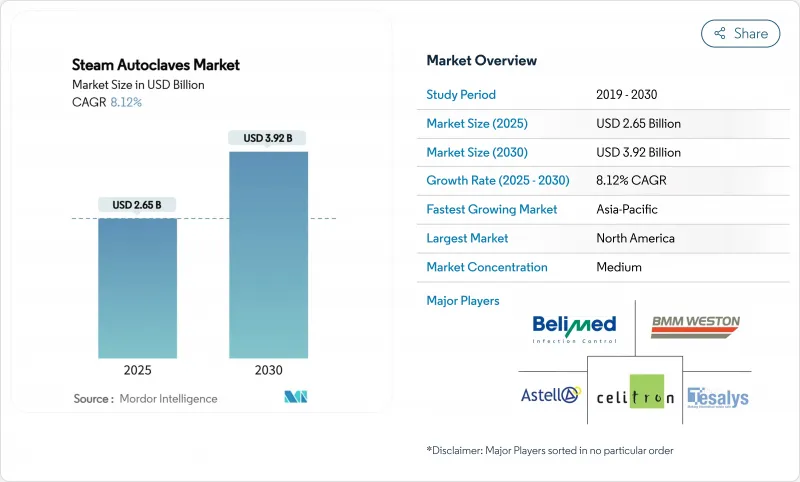
Rising infection-control requirements, tightening emissions rules for ethylene oxide, and the growing urgency to contain healthcare-associated infections are keeping capital expenditure on steam sterilization resilient, even as health systems weigh cost and sustainability trade-offs. North American hospitals continue to refresh their fleets in line with accreditation cycles, while Asia-Pacific providers accelerate first-time installations in response to infrastructure expansion and medical device manufacturing growth. Regulatory shifts-such as the U.S. FDA's alignment of quality system rules with ISO 13485 and the EU's GMP Annex 1 update-favour digitally connected units that automate validation and record-keeping, spurring premium segment demand. Concurrently, vendors are redesigning chambers and cycles to curb water and power usage, appealing to buyers intent on meeting decarbonisation targets without compromising sterilisation efficacy.
Global Steam Autoclaves Market Trends and Insights
Rising Prevalence of Hospital-Acquired Infections
Hospitals worldwide still record roughly 1 in 31 inpatients with at least one healthcare-associated infection, sustaining investment in reliable steam cycles that eradicate resistant organisms. Although the CDC noted double-digit declines in MRSA and CLABSI rates between 2022 and 2023, administrators recognise that prevention remains cheaper than treatment, keeping new-build and replacement demand intact across surgical, critical-care and transplant units. Steam autoclaves deliver rapid, reproducible lethality without chemical residuals, aligning with operating-room turnaround imperatives and environmental, health and safety policies. Suppliers are therefore embedding IoT sensors for automatic cycle tracking, enabling infection-control teams to audit loads in real time and trigger corrective action before breaches escalate. This capability resonates most in tertiary centres where diverse instrument sets require differentiated parameters yet strict chain-of-custody documentation.
Stringent Infection-Control & Accreditation Norms
The FDA's 2025 update to 21 CFR 880.6880 formalised the need for integrated monitoring and electronic records in steam sterilizers, pushing facilities to phase out legacy equipment lacking automated data export. In Europe, Annex 1 places explicit emphasis on contamination-control strategies and quality-risk management that many providers meet by deploying autoclaves with closed-loop sensors and validated leak-rate testing. Dental practices face comparable scrutiny; CDC guidance issued in late 2024 mandates weekly biological monitoring, a requirement easier to satisfy with benchtop units offering built-in printouts or cloud reporting. Comparable regimes in Canada, Japan and Australia mirror these expectations, creating a coordinated global pull for digitally native platforms capable of harmonised audit trails. Resulting procurement cycles favour manufacturers with cross-regional regulatory teams and post-installation service networks that sustain compliance across a device's 15-year life.
High Capital & Maintenance Costs of Large Units
Floor-standing, double-door autoclaves can command list prices above USD 250,000, excluding site upgrades for electrical, steam and water utilities, a hurdle for resource-strained public hospitals. Annual upkeep-ranging from gasket replacement to chamber re-qualification-adds recurring cost, prompting many facilities in Latin America, the Middle East and parts of Southeast Asia to defer purchases or opt for outsourced reprocessing. Energy and water data further complicate budgeting: a single 400-litre jacketed unit may consume 60 gallons per cycle, challenging sustainability pledges as providers track Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions. Vendors respond with modular chamber designs and heat-recovery systems, yet payback periods remain lengthy, restraining uptake in price-sensitive territories.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing Need to Manage Bio-Hazardous Medical Waste
- Shift Toward Point-of-Use Sterilisation in Ambulatory Settings
- Growing Adoption of Disposable Single-Use Instruments
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Vertical units accounted for 42.35% of steam autoclaves market share in 2024, confirming their popularity in theatres and labs that value narrow footprints and ergonomic top loading. Rising refurbishment of secondary hospitals in Europe and India maintains baseline demand, as these vertical chambers sterilise gowns, handpieces and culture media without extensive plumbing. Table-top models, in contrast, are set to post a 10.25% CAGR through 2030, fuelled by ambulatory centres installing point-of-care sterilisation to shorten instrument turnaround. The CDC's 2024 dental guidance reinforced weekly biological monitoring, encouraging clinics to replace ageing heat-only sterilisers with automated benchtop steam units that document each cycle.
Manufacturers differentiate through cycle versatility and intuitiveness. Touch-screen HMIs, pre-programmed lumened-device cycles and cloud integration have become standard, while optional water-savings kits and HEPA exhaust filters add sustainability. Horizontal floor-standing units still underpin high-throughput central sterile departments, yet their uptake is tempered by space constraints and the -1.3% CAGR drag associated with acquisition and maintenance costs. Nonetheless, orthopaedic centres performing back-to-back joint replacements will continue ordering 600-litre chambers capable of handling large trays, shielding this niche from displacement.
Gravity displacement processes held 46.53% of steam autoclaves market size in 2024 thanks to simplicity, low capital cost and minimal maintenance. In small clinics, gravity cycles remain adequate for solid instruments and liquid media, especially where budgets rule out vacuum pumps. Yet complexity in surgical devices is driving a shift toward pre-vacuum systems that demonstrate a leading 10.85% CAGR. These high-vac units draw air through a series of negative pulses, ensuring steam penetrates lumens and porous wraps, which is essential for robotic instruments and micro-laparoscopes in tertiary hospitals.
Steam-flush pressure pulse (SFPP) chambers serve labs needing rapid turnarounds, cycling loads in under 25 minutes without high-energy vacuum pumps. Meanwhile, pass-through double-door designs address unidirectional workflows between dirty and clean zones, a regulatory requirement in many GMP manufacturing suites. Vendors layer in passive heat recovery and jacket insulation to shrink utility draws by up to 25%, targeting green procurement metrics and life-cycle cost justifications for pre-vacuum installations.
The Steam Autoclave Market Report is Segmented by Product Type (Vertical Steam Autoclaves, Horizontal Steam Autoclaves, and More), Sterilization Technology (Gravity Displacement, Pre-Vacuum, and More), Mobility (Fixed and Portable), End-User (Hospitals and Clinics, Pharmaceutical & Biotech Companies, and More), and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America retained the largest revenue share at 34.82% in 2024 thanks to mature replacement cycles, advanced accreditation requirements and rapid adoption of IoT-enabled sterilisation suites. Hospitals continue swapping legacy gravity units for energy-efficient high-vac autoclaves that integrate with central sterile tracking platforms. Federal incentives for sustainable infrastructure also push providers toward water-saving models, cushioning total-cost-of-ownership concerns.
Europe follows closely, yet faces the dual burden of Medical Device Regulation compliance and Brexit-related supply disruptions. Annex 1 and harmonised standards clamp down on manual documentation, driving upgrades to machines with automated load release and Wi-Fi audit trails. Germany, France and the Nordics lead substitution, whereas Eastern European markets still rely on refurbished imports.
Asia-Pacific is the fastest expanding geography, with an 11.61% CAGR projected through 2030. Extensive hospital construction in China and India, coupled with rising domestic device manufacturing, fuels demand for both large central units and portable field models. Government-subsidised health-insurance schemes in Southeast Asia further incentivise clinics to meet infection-control benchmarks. Meanwhile, Middle East and Africa, along with South America, witness steady adoption as private operators open tertiary centres and specialty clinics, although foreign-exchange volatility and import tariffs temper the pace in select economies.
- Getinge
- STERIS
- Tuttnauer Ltd.
- Steelco S.p.A (Miele Group)
- Shinva Medical Instrument
- Astell Scientific Ltd.
- Belimed
- MELAG Medizintechnik
- Celitron Medical Technologies
- Consolidated Sterilizer Systems
- Midmark
- SciCan Ltd. (Coltene)
- Matachana Group
- BMM Weston
- Rodwell Engineering Group Ltd.
- Priorclave Ltd.
- TESALYS Group
- Hirayama Manufacturing
- Dental X
- Steriflow SAS
- LTE Scientific Ltd.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions & Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Prevalence Of Hospital-Acquired Infections
- 4.2.2 Stringent Infection-Control & Accreditation Norms
- 4.2.3 Growing Need To Manage Bio-Hazardous / Medical Waste
- 4.2.4 Shift Toward Point-Of-Use Sterilization In Ambulatory Settings
- 4.2.5 Emergence Of Energy-Efficient Green Autoclaves
- 4.2.6 Integration of Iot Sensors For Remote Cycle Validation & Compliance
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Capital & Maintenance Costs Of Large Units
- 4.3.2 Growing Adoption Of Disposable Single-Use Instruments
- 4.3.3 Space & Utility Constraints In Resource-Limited Clinics
- 4.3.4 Complex Qualification / Re-Validation Documentation Burden
- 4.4 Porter's Five Forces
- 4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.4.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size & Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Product Type
- 5.1.1 Vertical Steam Autoclaves
- 5.1.2 Horizontal Steam Autoclaves
- 5.1.3 Table-top / Benchtop Autoclaves
- 5.1.4 Large-capacity Floor-standing Autoclaves
- 5.2 By Sterilization Technology
- 5.2.1 Gravity Displacement
- 5.2.2 Pre-vacuum (High-vac)
- 5.2.3 Steam-Flush Pressure Pulse (SFPP)
- 5.2.4 Double-door Pass-through
- 5.3 By Mobility
- 5.3.1 Fixed / Floor-standing
- 5.3.2 Portable
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals & Clinics
- 5.4.2 Pharmaceutical & Biotech Companies
- 5.4.3 Research & Academic Institutes
- 5.4.4 Dental Facilities
- 5.4.5 Veterinary Clinics
- 5.4.6 Contract Sterilization Service Providers
- 5.5 Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Australia
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products & Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Getinge AB
- 6.3.2 STERIS plc
- 6.3.3 Tuttnauer Ltd.
- 6.3.4 Steelco S.p.A (Miele Group)
- 6.3.5 Shinva Medical Instrument Co. Ltd.
- 6.3.6 Astell Scientific Ltd.
- 6.3.7 Belimed AG
- 6.3.8 MELAG Medizintechnik GmbH & Co. KG
- 6.3.9 Celitron Medical Technologies
- 6.3.10 Consolidated Sterilizer Systems
- 6.3.11 Midmark Corporation
- 6.3.12 SciCan Ltd. (Coltene)
- 6.3.13 Matachana Group
- 6.3.14 BMM Weston Ltd.
- 6.3.15 Rodwell Engineering Group Ltd.
- 6.3.16 Priorclave Ltd.
- 6.3.17 TESALYS Group
- 6.3.18 Hirayama Manufacturing Corporation
- 6.3.19 Dental X
- 6.3.20 Steriflow SAS
- 6.3.21 LTE Scientific Ltd.
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & Unmet-need Assessment




