PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851141

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851141
Automatic Weapons - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
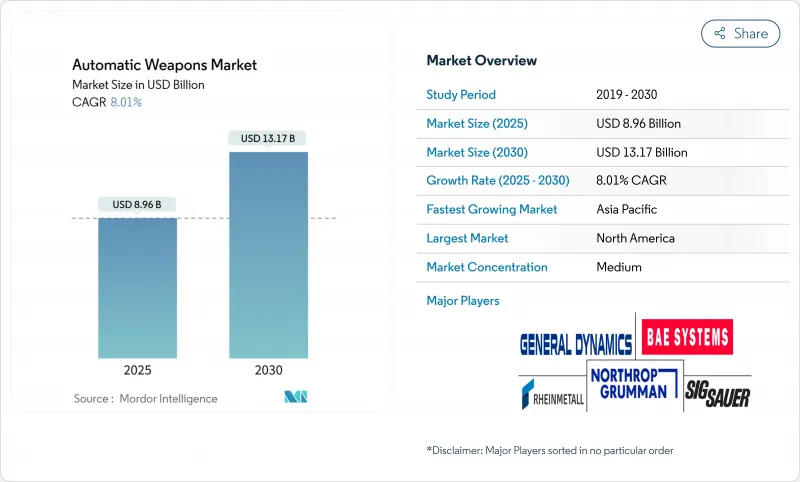
The automatic weapons market reached USD 8.96 billion in 2025, is advancing at an 8.01% CAGR, and is forecasted to attain a market size of USD 13.17 billion by 2030.
Heightened defense spending, persistent geopolitical flashpoints, and the urgency to retire aging Cold War inventories underpin demand for digitally networked, AI-ready small-caliber and medium-caliber systems. Military planners are opting for weapons that plug into broader sensor grids, enabling faster target recognition and data exchange. Procurement is further stimulated by modular designs that allow quick caliber swaps, by the spread of remote weapon stations on land vehicles and patrol craft, and by nationwide initiatives to harden forces against drone swarms. Supply-chain risk around rare-earth magnets, barrel steel, and specialized propellants poses near-term headwinds yet also prompts domestic sourcing initiatives in the United States, Europe, and Asia-Pacific.
Global Automatic Weapons Market Trends and Insights
Escalating Geopolitical Tensions and Multi-Domain Operations Doctrine
Multi-domain doctrine obliges armies to field automatic weapons able to exchange targeting data across land, sea, and air networks in near real time. Ukraine's Sky Sentinel turrets, which employed .50-caliber M2 Browning guns to down six Shahed drones, illustrate the new fusion of legacy firepower with AI sensors. Allied forces, noting similar threats, are integrating smart optics such as the USD 13 million SMASH 2000L scopes that auto-track drones, now fielded by the US Army. Procurement officers now prioritize connectivity protocols and low-latency data links when drafting requirements. In parallel, fleet commanders retrofit remote weapon stations on patrol craft to guard chokepoints against low-cost loitering munitions. Collectively, these measures move the automatic weapons market from stand-alone small arms toward networked effectors embedded in command-and-control webs.
Ongoing Replacement Cycle of Legacy Small-Arms Inventories
NATO members are fast-tracking replacements for aging M16- and AK-family rifles. Sweden rushed a USD 64 million order for 15,000 Colt M4s to bolster reserves amid regional tension. The US Army allotted USD 367.3 million in FY 2025 for Next Generation Squad Weapons that pair 6.8 mm rounds with advanced optics, marking the biggest US small-arms shift in six decades. Singapore chose Colt's IAR6940E-SG to replace the four-decade-old Ultimax 100, showing even tech-savvy nations sometimes import rather than develop locally. Beyond rifles, Israel Weapon Industries (IWI) rolled out the Arbel computerized system, hitting 90% of moving targets during trials, demonstrating how digital fire-control is redefining accuracy benchmarks.
High Integration Costs of Advanced Sensor Systems
Next-generation optics elevate unit prices far above legacy equivalents. The SMASH 2000L, now standard on some US rifles, demands significant training and lifecycle support, straining the budgets of smaller militaries. Early lots of NGSW weapons cost nearly USD 9,000 each, four times the cost of legacy carbines. Manufacturers seek weight savings to offset price hikes; Sig Sauer's Pitbull remote station dropped from 500 lb to 205 lb, making it feasible for light vehicles. Still, defense ministries with tight budgets defer upgrades, moderating near-term adoption rates.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Rise in Asymmetric Warfare Requirements
- Advanced Fire-Control Electronics and AI Integration
- Supply-Chain Volatility for Critical Materials
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Automatic rifles held the largest share at 36.55% in 2024, underscoring their role as the infantry's backbone. The automatic weapons market size for rifles is projected to grow steadily as armies standardize on modular, suppressor-ready designs. Automatic cannons post the fastest 8.74% CAGR thanks to naval and air-defense applications that demand higher-energy projectiles to defeat drones and light armor.
Growth in cannons is propelled by 30 mm turrets ordered for US Marine ACVs and by European programs adding 35 mm systems with air-burst ammunition. Machine guns enjoy replacement demand but less dramatic growth, while Automatic Launchers gain relevance for counter-UAS tasks in urban environments. Gatling designs, niche yet indispensable for close-in weapon systems, receive electronics upgrades to link with ship radar feeds, ensuring continued production runs through 2030.
Land systems commanded 59.10% of 2024 revenue, reflecting armored vehicle retrofits and dismounted modernization. Yet naval installations will clock a 9.48% CAGR, outpacing the broader automatic weapons market as fleets install remote stations that can lock onto fast, low-flying threats. The automatic weapons market share for land systems is secure, but growth moderates as inventories mature.
Crucially, maritime uptake is widening beyond blue-water navies; Taiwan's patrol frigates will mount 20 mm XTR-102A2 systems to deter incursions in the Taiwan Strait. Airborne mounts concentrate on rotary platforms where door guns remain essential for convoy escort and medical evacuation. Uncrewed surface and ground vehicles open additional hulls and chassis for small, stabilized turrets, expanding the addressable platform base.
The Automatic Weapons Market is Segmented by Type (Automatic Rifles, Machine Guns, Automatic Launchers, Automatic Cannons, and Gatling Gun), Platform (Land, Airborne, and Naval), Caliber (Small Caliber, Medium Caliber, and More), End-User (Defense and Law Enforcement), and Geography (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East and Africa). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America commanded 38.50% of global revenue in 2024, anchored by the United States, which accounts for nearly 40% of worldwide arms exports. Ongoing multi-year contracts for NGSW rifles and remote turrets sustain domestic output, while Canada's NATO commitments and Mexico's internal security procurements add incremental volume. Regional suppliers benefit from short feedback loops with end-users, allowing rapid spiral upgrades and fostering iterative product development that keeps the automatic weapons market competitive.
Asia-Pacific posts the fastest 9.05% CAGR, driven by China's USD 314 billion defense budget and rising outlays by India, Japan, and South Korea. Japan lifted defense spending 21% to USD 55.3 billion, emphasizing long-range fires and hardened base defense. India, the world's top arms importer, promotes local build partnerships that include small arms lines with technology transfer clauses. Taiwan's incremental 1.8% budget hike channels funds into naval remote stations and counter-drone rifles, underscoring the region's seaborne threat focus. Collectively, modernization across diverse operational doctrines creates varied specifications, broadening sales opportunities for global suppliers.
Europe is accelerating procurement after Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine, with regional imports rising 47% between 2019 and 2024. EU initiatives to boost joint ammunition production complement bilateral deals such as Lithuania's USD 36 million Minimi machine-gun purchase. Israel's record USD 14.7 billion defense exports in 2024, a large portion to Europe, highlight the region's tilt toward proven off-the-shelf solutions. Simultaneously, European states channel funds into domestic plants to reduce external dependency, stimulating R&D in smart munitions and AI-assisted fire-control tailored for NATO interoperability.
- General Dynamics Corporation
- Northrop Grumman Corporation
- Rheinmetall AG
- Denel Land Systems (Denel SOC Ltd.)
- BAE Systems plc
- Sig Sauer, Inc.
- Israel Weapon Industries (IWI) Ltd.
- Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- Heckler & Koch GmbH
- FN HERSTAL (FN Browning Group)
- Kalashnikov Concern JSC
- Colt CZ Group SE (Ceska Zbrojovka)
- China North Industries Group Corporation Limited (NORINCO Group)
- Advanced Weapons & Equipment India Ltd. (AWEIL)
- PT Pindad
- STV GROUP a.s.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Escalating geopolitical tensions and multi-domain doctrine
- 4.2.2 Replacement of legacy small-arms with modular platforms
- 4.2.3 Asymmetric warfare demand for lightweight, high-mobility weapons
- 4.2.4 Integration of AI-enabled fire-control electronics
- 4.2.5 Proliferation of unmanned and remotely-operated weapon stations
- 4.2.6 Shift to polymer-cased and caseless ammunition
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High integration cost of advanced electro-optical sensors and digital fire-control units
- 4.3.2 Supply-chain volatility for barrel-steel alloys, rare-earth magnets, and energetic chemicals
- 4.3.3 Stringent international arms-transfer rules and complex end-user certificate requirements
- 4.3.4 Duplicate integration-cost pressure on procurement cycles
- 4.4 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Outlook
- 4.6 Technological Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Automatic Rifles
- 5.1.2 Machine Guns
- 5.1.3 Automatic Launchers
- 5.1.4 Automatic Cannons
- 5.1.5 Gatling Gun
- 5.2 By Platform
- 5.2.1 Land
- 5.2.2 Airborne
- 5.2.3 Naval
- 5.3 By Caliber
- 5.3.1 Small Caliber
- 5.3.2 Medium Caliber
- 5.3.3 Large Caliber
- 5.4 By End-User
- 5.4.1 Defense
- 5.4.1.1 Army
- 5.4.1.2 Navy
- 5.4.1.3 Air Force
- 5.4.1.4 Special Operations Forces
- 5.4.2 Law Enforcement
- 5.4.1 Defense
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.2 Germany
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Russia
- 5.5.2.5 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 India
- 5.5.3.3 Japan
- 5.5.3.4 South Korea
- 5.5.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 South America
- 5.5.4.1 Brazil
- 5.5.4.2 Rest of South America
- 5.5.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5.1 Middle East
- 5.5.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.5.5.1.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.5.5.1.3 Israel
- 5.5.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.5.5.2 Africa
- 5.5.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.5.5.2.2 Rest of Africa
- 5.5.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 General Dynamics Corporation
- 6.4.2 Northrop Grumman Corporation
- 6.4.3 Rheinmetall AG
- 6.4.4 Denel Land Systems (Denel SOC Ltd.)
- 6.4.5 BAE Systems plc
- 6.4.6 Sig Sauer, Inc.
- 6.4.7 Israel Weapon Industries (IWI) Ltd.
- 6.4.8 Singapore Technologies Engineering Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Heckler & Koch GmbH
- 6.4.10 FN HERSTAL (FN Browning Group)
- 6.4.11 Kalashnikov Concern JSC
- 6.4.12 Colt CZ Group SE (Ceska Zbrojovka)
- 6.4.13 China North Industries Group Corporation Limited (NORINCO Group)
- 6.4.14 Advanced Weapons & Equipment India Ltd. (AWEIL)
- 6.4.15 PT Pindad
- 6.4.16 STV GROUP a.s.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




