PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851145

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851145
Wound Debridement - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
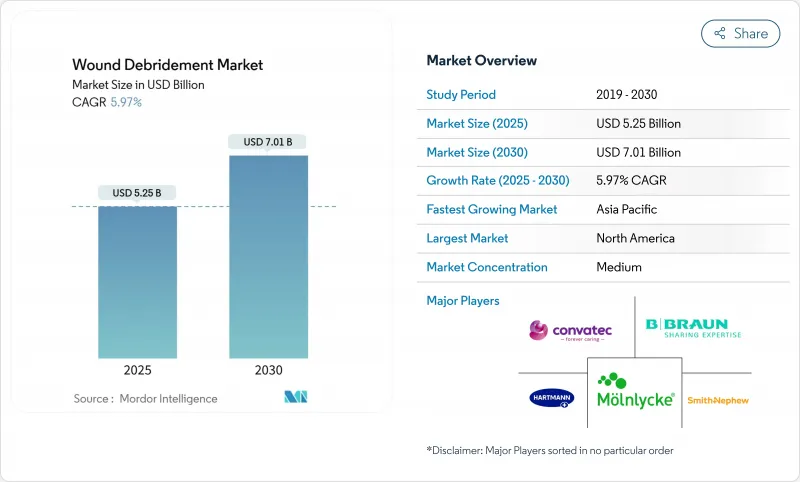
The wound debridement market stood at USD 5.25 billion in 2025 and is on course to reach USD 7.01 billion by 2030, expanding at a 5.97% CAGR.
Demand is propelled by population ageing, the rising burden of diabetes, and the fast uptake of AI-guided diagnostic tools that shorten time to treatment. Health systems also show growing preference for ultrasonic and hydrosurgical technologies that remove necrotic tissue without harming viable structures. Better clinical outcomes, shorter hospital stays, and mounting pressure to curb long-term care costs further support adoption. Meanwhile, sustainability concerns about single-use disposables and tighter regulatory oversight steer innovators toward greener materials and higher-quality evidence.
Global Wound Debridement Market Trends and Insights
Rising incidence of diabetic foot and venous leg ulcers
Diabetic foot ulcers affect 15-25% of people living with diabetes, and 85% of diabetes-related amputations are preceded by such ulcers. Evidence now shows that early, aggressive debridement reaching beyond wound edges removes biofilm and hyperproliferative tissue and markedly lowers amputation risk. This clinical shift increases demand for enzymatic and ultrasonic platforms that deliver tissue-selective removal without collateral damage, while preventive tools such as pressure-altering insoles further elevate upstream intervention needs.
Rapid adoption of advanced hydrosurgical and ultrasonic systems
Saline-jet hydrosurgery, exemplified by the VERSAJET platform, streamlines procedures and preserves healthy tissue. Ultrasonic devices such as SonicOne remove devitalized tissue through low-frequency vibration, are painless, and foster granulation. Hospitals and outpatient centres quickly adopt these modalities as studies report faster closure rates and shorter admissions, accelerating the wound debridement market transition toward non-contact, precision-guided care.
High overall treatment and device costs
Average diabetic foot ulcer episodes cost EUR 4,888 per patient, with most spending tied to lengthier inpatient stays rather than devices. Payers therefore insist on robust evidence showing that premium platforms shorten time to closure or reduce complications before reimbursing higher prices. Providers respond by focusing on total cost-of-care analyses instead of front-end device costs.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Growing volume of complex surgical procedures
- Ageing population with impaired wound healing
- Shortage of certified wound-care specialists
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Hydrosurgical systems secured 28.78% of wound debridement market share in 2024 through their ability to excise devitalised tissue with minimal collateral trauma. Their popularity in operating rooms stems from faster set-up, better visibility, and lower infection risk. Despite this lead, ultrasonic devices are expanding at a 9.76% CAGR, aided by non-contact operation that eases patient discomfort and lowers cross-contamination. Enzymatic gels retain a place in chronic ulcer care, whereas mechanical pads find limited use when only superficial slough must be removed.
Ultrasonic technology builds momentum because adjustable amplitude lets clinicians fine-tune depth of action, which is invaluable for irregular burn beds and fragile diabetic ulcers. These advantages, together with shrinking capital costs, underpin ultrasonic disruption of the wound debridement market. By contrast, biologic methods such as maggot therapy, though clinically effective, confront cultural resistance. Regulatory scrutiny of antimicrobial dressings also pushes innovators toward mechanical options that sidestep resistance issues.
Surgical debridement represented 39.71% of the wound debridement market size in 2024 on account of its role in emergency departments and trauma theatres. Its capacity to remove necrosis and biofilm in one session cements its status among vascular and orthopaedic surgeons. Enzymatic debridement follows, offering a chemical route for patients who cannot tolerate surgery.
Ultrasonic approaches, growing 8.83% yearly, combine precision with patient comfort and can be repeated in outpatient clinics, therefore lowering bed occupancy. Mechanical and autolytic routes continue to serve frail patients, while biologic strategies await clearer regulatory pathways after the FDA transferred oversight of medicinal maggots to CBER in late 2024.
The Wound Debridement Market Report is Segmented by Product (Gels, Ointments & Creams, Surgical Debridement Devices, and More), Method (Surgical, Enzymatic, and More), Wound Type (Chronic Ulcers [Diabetic Foot Ulcer and More], Surgical & Traumatic Wounds and Burns), End User (Hospitals, Ambulatory Surgical Centers and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More. ) the Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
North America generated 37.56% of 2024 sales, anchored by high diabetes prevalence, generous reimbursement, and early uptake of AI-enabled assessment software. Smith+Nephew reported 3.8% underlying growth in its Advanced Wound Management franchise for Q1 2025, underscoring sustained regional demand. Regulations remain supportive, yet recent FDA warning letters emphasise manufacturing quality and favour well-capitalised firms.
Europe remains an innovation hub, with start-ups progressing enzymatic and photonic devices and regulators tightening evidence requirements for antimicrobial agents. Environmental legislation that discourages single-use plastic canisters prompts suppliers to redesign negative-pressure wound therapy consumables.
Asia-Pacific is the growth engine, forecast to deliver a 7.12% CAGR through 2030. Ageing populations, rising surgical volumes, and government investment in tertiary hospitals underpin expansion. ConvaTec has noted regulatory delays in China, yet local trials of biodegradable temporising matrices yielding 94.6% healing rates spotlight domestic appetite for advanced therapy. South-East Asian and South Asian nations invest in tele-mentoring networks to compensate for limited specialist density, a move that stimulates demand for AI-guided tools.
Latin America and the Middle East & Africa show slower uptake because of budget limits and workforce shortages, though incidence of chronic wounds is climbing. Multilateral aid programmes that sponsor diabetic foot clinics are expected to open new pockets of demand beyond 2027.
- Smiths Group
- Convatec
- Molnlycke Health Care
- B. Braun
- Hartmann Group
- Bioventus (Misonix)
- Lohmann & Rauscher
- Solventum
- Coloplast
- DeRoyal Industries
- Arobella Medical
- Histologics LLC
- Medaxis AG
- Soring GmbH
- Zimmer Biomet (Pulsavac)
- RLS Global AB
- PulseCare Medical
- Integra LifeSciences
- Medtronic
- Stryker
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Rising Incidence Of Diabetic Foot & Venous Leg Ulcers
- 4.2.2 Growing Volume Of Complex Surgical Procedures
- 4.2.3 Rapid Adoption Of Advanced Hydrosurgical & Ultrasonic Systems
- 4.2.4 Ageing Population With Impaired Wound Healing
- 4.2.5 AI-Enabled Wound-Assessment Platforms Accelerating Debridement Decisions
- 4.2.6 Biofilm-Targeting Topical Enzymes Improving Debridement Efficiency
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 High Overall Treatment & Device Costs
- 4.3.2 Shortage Of Certified Wound-Care Specialists In Emerging Economies
- 4.3.3 Tightening FDA/EMA Scrutiny On Collagenase & Enzymatic Agents
- 4.3.4 Sustainability Push Against Single-Use NPWT Canisters & Disposables
- 4.4 Value / Supply-Chain Analysis
- 4.5 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.6 Technology Outlook
- 4.7 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.7.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.7.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.7.3 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.7.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.7.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value-USD)
- 5.1 By Product
- 5.1.1 Gels
- 5.1.2 Ointments & Creams
- 5.1.3 Surgical Debridement Devices
- 5.1.4 Hydrosurgical Devices
- 5.1.5 Ultrasound-Assisted Debridement Devices
- 5.1.6 Mechanical Debridement Pads
- 5.1.7 Biologic Debridement (Maggot Therapy)
- 5.1.8 Other Products
- 5.2 By Method
- 5.2.1 Surgical
- 5.2.2 Enzymatic
- 5.2.3 Mechanical
- 5.2.4 Autolytic
- 5.2.5 Biologic
- 5.2.6 Ultrasonic
- 5.3 By Wound Type
- 5.3.1 Chronic Ulcers
- 5.3.1.1 Diabetic Foot Ulcers
- 5.3.1.2 Pressure Ulcers
- 5.3.1.3 Venous Leg Ulcers
- 5.3.2 Surgical & Traumatic Wounds
- 5.3.3 Burns
- 5.3.1 Chronic Ulcers
- 5.4 By End User
- 5.4.1 Hospitals
- 5.4.2 Ambulatory Surgical Centers
- 5.4.3 Home-Care Settings
- 5.5 By Geography
- 5.5.1 North America
- 5.5.1.1 United States
- 5.5.1.2 Canada
- 5.5.1.3 Mexico
- 5.5.2 Europe
- 5.5.2.1 Germany
- 5.5.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.5.2.3 France
- 5.5.2.4 Italy
- 5.5.2.5 Spain
- 5.5.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.5.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.3.1 China
- 5.5.3.2 Japan
- 5.5.3.3 India
- 5.5.3.4 Australia
- 5.5.3.5 South Korea
- 5.5.3.6 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.5.4 Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.4.1 GCC
- 5.5.4.2 South Africa
- 5.5.4.3 Rest of Middle East and Africa
- 5.5.5 South America
- 5.5.5.1 Brazil
- 5.5.5.2 Argentina
- 5.5.5.3 Rest of South America
- 5.5.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Market Share Analysis
- 6.3 Company profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.3.1 Smith+Nephew
- 6.3.2 ConvaTec Group PLC
- 6.3.3 Molnlycke Health Care AB
- 6.3.4 B. Braun SE
- 6.3.5 PAUL HARTMANN AG
- 6.3.6 Bioventus (Misonix)
- 6.3.7 Lohmann & Rauscher
- 6.3.8 Solventum
- 6.3.9 Coloplast A/S
- 6.3.10 DeRoyal Industries Inc.
- 6.3.11 Arobella Medical
- 6.3.12 Histologics LLC
- 6.3.13 Medaxis AG
- 6.3.14 Soring GmbH
- 6.3.15 Zimmer Biomet (Pulsavac)
- 6.3.16 RLS Global AB
- 6.3.17 PulseCare Medical
- 6.3.18 Integra LifeSciences
- 6.3.19 Medtronic plc
- 6.3.20 Stryker Corporation
7 Market Opportunities & Future Outlook
- 7.1 White-space & unmet-need assessment




