PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851187

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851187
Sulfur Fertilizer - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The sulfur fertilizers market reached USD 5.1 billion in 2025 and is projected to climb to USD 6.5 billion by 2030, advancing at a 4.9% CAGR during the forecast period.
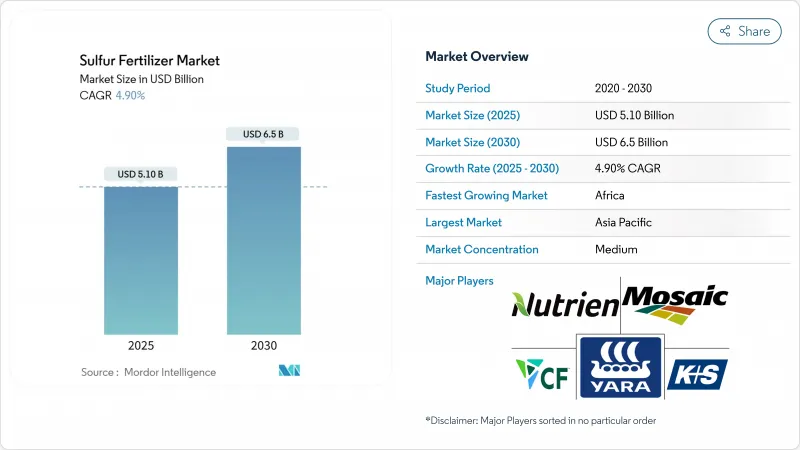
Gains stem from the sharp decline in atmospheric sulfur deposition, which has fallen more than 70% since the 1990s, leaving soils depleted and crops increasingly responsive to applied sulfur. The Asia-Pacific region leads consumption on the back of China's 48.9 million metric tons annual fertilizer use and India's expanding precision fertilization programs. Africa represents the fastest-growing regional opportunity as infrastructure upgrades and food-security initiatives accelerate balanced nutrient adoption. Industry momentum is further supported by refinery desulfurization streams that now provide more than 60% of all elemental sulfur used in fertilizer manufacturing, although supply can tighten whenever refining margins compress.
Global Sulfur Fertilizer Market Trends and Insights
Sulfur Deficiency in Soil
Soil tests indicate sulfur levels have fallen 30-50% during the past three decades as air-quality rules removed sulfate aerosols, making sulfur the fourth most yield-limiting nutrient after nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Crops that receive 30-45 kilograms of sulfur per hectare show wheat yield gains of 15-25% together with higher grain protein. Intensively cropped regions with low organic matter are the most vulnerable, and site-specific test kits now allow farmers to map deficiencies before the season begins. This capability is a primary engine for the sulfur fertilizers market because it converts latent nutrient shortages into measurable demand. Yield monitors on commercial corn farms now record site yield drops of up to 18% when leaf sulfur falls below 0.2%, underscoring the economic stakes for large operations. As climate patterns shift rainfall distribution, leaching losses further lower residual sulfur, making annual supplementation a practical necessity.
Rising Oilseed Acreage and Yields
Oilseed crops such as canola and soybean require two to three times more sulfur per unit of nitrogen than cereals, which intensifies fertilizer demand as the global planted area expands. University field trials in Missouri report 8.1 bushel-per-acre soybean gains from 100 pounds of ammonium sulfate, yielding a USD 80 per-acre profit lift after input costs. The economics encourage continued adoption even in mature markets, reinforcing a stable pull-through on sulfur volumes. Global canola acreage is projected to expand by 1.8 million hectares by 2030, amplifying demand for high-sulfur blends in Canada and Australia. Biotech cultivars with higher protein ceilings also pull more sulfur, linking seed genetics directly to fertilizer strategy.
Competition from Multi-Nutrient Specialty Fertilizers
Farmers increasingly favor single-pass blends that address multiple deficiencies, which can dilute standalone demand for sulfur. Suppliers are responding by embedding sulfur into broader nutrient packages, but pricing competition and formulation complexity raise barriers for smaller producers. Large distributors bundle mix and match micronutrient packs that include sulfur at lower incremental cost, eroding standalone sales. To stay relevant, sulfur fertilizer suppliers are exploring co-marketing alliances that offer turnkey crop nutrition programs. Such shifts could compress standalone sulfur margins and push consolidation among smaller players.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Government Incentives for Sustainable Agriculture
- Adoption of Controlled-Release Sulfur-Coated Urea
- Volatility in Elemental Sulfur Prices
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
In 2024, sulfate fertilizers such as ammonium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and single superphosphate delivered 51% of global revenue, reflecting their immediate plant availability and ease of blending. Elemental sulfur, though smaller, is growing faster at a 6.7% CAGR as its higher analysis lowers freight costs and its controlled oxidation fits precision programs. Micronized and pastilled innovations shorten oxidation lag, extending applicability to short-season crops. Split-application strategies combine sulfate for early growth and elemental sulfur for sustained release, underscoring complementary rather than zero-sum demand within the sulfur fertilizers market.
The elemental trend plays into the wider adoption of variable-rate applicators and remote-sensing maps, which rely on higher nutrient density to limit field passes. As sulfur-coated urea and sulfur-bentonite enter mainstream blends, producers that can guarantee uniform particle size and predictable oxidation stand to gain share.
Solid products retained a 70% share in 2024, backed by efficient storage and compatibility with conventional spreaders across broad acres. Granulated and prilled formats dominate cooperative blending plants where throughput and shelf life matter. Yet liquid sulfur is advancing at a 7.2% CAGR on the strength of fertigation and foliar programs in high-value horticulture.
Ammonium thiosulfate (12-0-0-26S) typifies liquid momentum, allowing tank mixing with nitrogen solutions and pesticides for single-pass efficiency. Growers appreciate the uniformity in micro-irrigation as well as quicker plant uptake during critical reproductive stages. Vendors are building regional terminals to shorten hauls, which should reduce delivered cost gaps versus solids and widen addressable acreage across the sulfur fertilizers market.
The Sulfur Fertilizers Market Report is Segmented by Type (Sulfate Fertilizer, Elemental Sulfur, and More), Form (Solid and Liquid), Mode of Application (Soil Application, Fertigation, and More), Crop Type (Cereals and Grains, Oilseeds and Pulses, and More), Distribution Channel (Direct-To-Farm, Retail, and More) and Geography (North America, Europe, and More). The Market Forecasts are Provided in Terms of Value (USD).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific led the sulfur fertilizers market with a 37% share in 2024. China's fertilizer intensity remains above global norms, and efforts to curb excess nitrogen spur the adop-tion of balanced NPK-S regimens that sustain yields while reducing losses. India's shift toward precision spreaders and state subsidies for soil health cards pushes sulfur deeper into standard practice. Southeast Asian nations are raising demand through palm oil estates and double-cropped rice, whereas developed economies such as Japan seek ultra-low chloride options for high-value produce. Regional growth of 5.6% CAGR through 2030 is anchored by policy alignment with climate-smart agriculture goals.
Africa is the fastest-growing region at 6.4% CAGR. Soil surveys indicate sulfur scarcity in many sub-Saharan zones, and governments now couple fertilizer subsidies with extension services that promote balanced nutrition. Ethiopia's domestic complex under construction post-GERD will cut import reliance, while South Africa's commercial farms already leverage elemental sulfur blends to manage alkaline soils. Distribution challenges persist, yet donor-backed corridor projects and private blending hubs aim to improve last-mile reach, brightening prospects for the sulfur fertilizers market.
North America posts a steady 4.1% CAGR as the United States channels 8.2 million metric tons of recovered sulfur each year from refineries into phosphate and ammonium sulfate production. Recent tariffs on Canadian sulfur inject short-term tightness, but abundant domestic gas and refinery networks anchor supply. Precision agronomy, cover-crop adoption, and sustainability certifications fuel incremental demand. Europe, at 3.2% CAGR, balances stringent water-quality directives with the need to uphold crop protein levels, making controlled-release sulfur variants attractive.
- Nutrien Ltd.
- Yara International ASA
- The Mosaic Company
- K+S AG
- Israel Chemicals Ltd.
- Haifa Chemicals Ltd.
- Nufarm Limited
- Koch Industries Inc.
- CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- OCP S.A.
- BASF SE
- Sinochem Holdings Corp. Ltd.
- Saudi Arabian Fertilizer Company (SAFCO) (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC))
- Tiger-Sul Products LLC (Tessenderlo Group)
- TogliattiAzot PJSC (Uralchem Group)
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 Introduction
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 Research Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Market Landscape
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Sulfur deficiency in soil
- 4.2.2 Rising oilseed acreage and yields
- 4.2.3 Government incentives for sustainable agriculture
- 4.2.4 Adoption of controlled-release sulfur-coated urea
- 4.2.5 Increasing availability of recovered sulfur from desulfurization units
- 4.2.6 AI-based precision nutrient application platforms
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Competition from multi-nutrient specialty fertilizers
- 4.3.2 Volatility in elemental sulfur feedstock prices
- 4.3.3 Environmental risk of sulfate leaching into groundwater
- 4.3.4 Distribution bottlenecks for prilled elemental sulfur in emerging markets
- 4.4 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.5 Technological Outlook
- 4.6 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.6.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.6.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.6.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.6.4 Threat of Substitute Products
- 4.6.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
5 Market Size and Growth Forecasts (Value, USD)
- 5.1 By Type
- 5.1.1 Sulfate Fertilizers
- 5.1.1.1 Ammonium Sulfate
- 5.1.1.2 Potassium Sulfate
- 5.1.1.3 Calcium Sulfate (Gypsum)
- 5.1.1.4 Single Superphosphate
- 5.1.2 Elemental Sulfur
- 5.1.2.1 Micronized Sulfur
- 5.1.2.2 Prilled/Pastilled Sulfur
- 5.1.3 Sulfate of Micronutrients
- 5.1.3.1 Zinc Sulfate
- 5.1.3.2 Magnesium Sulfate
- 5.1.3.3 Others
- 5.1.4 Others (Sulfur-coated Urea, Sulfur Bentonite)
- 5.1.1 Sulfate Fertilizers
- 5.2 By Form
- 5.2.1 Solid
- 5.2.2 Liquid
- 5.3 By Mode of Application
- 5.3.1 Soil Application
- 5.3.2 Fertigation
- 5.3.3 Foliar Spray
- 5.3.4 Controlled-Release/Coated Granules
- 5.4 By Crop Type
- 5.4.1 Cereals and Grains
- 5.4.2 Oilseeds and Pulses
- 5.4.3 Fruits and Vegetables
- 5.4.4 Turf and Ornamentals
- 5.4.5 Others
- 5.5 By Distribution Channel
- 5.5.1 Direct-to-Farm
- 5.5.2 Retail Dealers
- 5.5.3 Cooperatives
- 5.5.4 Online Platforms
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.1.4 Rest of North America
- 5.6.2 Europe
- 5.6.2.1 Germany
- 5.6.2.2 United Kingdom
- 5.6.2.3 France
- 5.6.2.4 Russia
- 5.6.2.5 Spain
- 5.6.2.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.3 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.3.1 China
- 5.6.3.2 Japan
- 5.6.3.3 India
- 5.6.3.4 South Korea
- 5.6.3.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4 South America
- 5.6.4.1 Brazil
- 5.6.4.2 Argentina
- 5.6.4.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.5 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.2 United Arab Emirates
- 5.6.5.3 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.6 Africa
- 5.6.6.1 South Africa
- 5.6.6.2 Egypt
- 5.6.6.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 Competitive Landscape
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 Nutrien Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Yara International ASA
- 6.4.3 The Mosaic Company
- 6.4.4 K+S AG
- 6.4.5 Israel Chemicals Ltd.
- 6.4.6 Haifa Chemicals Ltd.
- 6.4.7 Nufarm Limited
- 6.4.8 Koch Industries Inc.
- 6.4.9 CF Industries Holdings Inc.
- 6.4.10 OCP S.A.
- 6.4.11 BASF SE
- 6.4.12 Sinochem Holdings Corp. Ltd.
- 6.4.13 Saudi Arabian Fertilizer Company (SAFCO) (Saudi Basic Industries Corporation (SABIC))
- 6.4.14 Tiger-Sul Products LLC (Tessenderlo Group)
- 6.4.15 TogliattiAzot PJSC (Uralchem Group)
7 Market Opportunities and Future Outlook




