PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851351

PUBLISHER: Mordor Intelligence | PRODUCT CODE: 1851351
Variable Frequency Drives - Market Share Analysis, Industry Trends & Statistics, Growth Forecasts (2025 - 2030)
The global variable frequency drives market size was valued at USD 28.09 billion in 2025 and is forecast to reach USD 36.27 billion by 2030, advancing at a 5.24% CAGR.
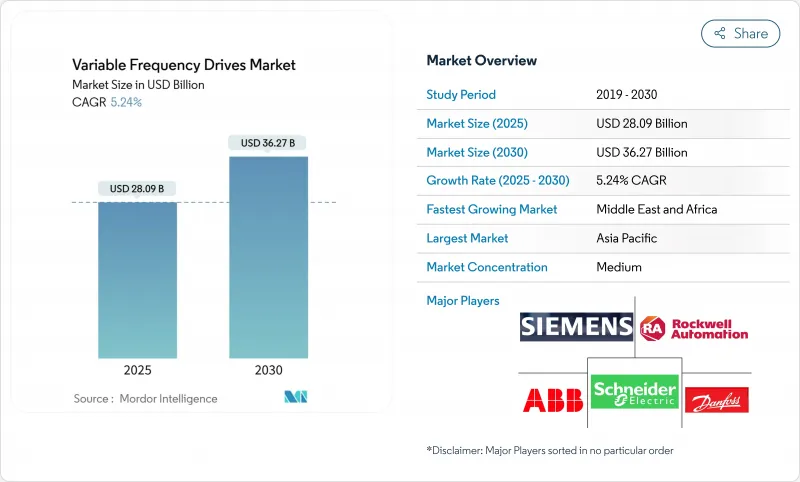
Strong policy pressure for motor-level efficiency, fast paybacks from energy savings, and the migration toward digitalized production lines have steadily widened the adoption base. Demand remained resilient even as capital-spending cycles tightened, because VFD retrofits deliver immediate electricity cost relief in energy-intensive plants. Medium-voltage upgrade projects in mining and metals, desalination build-outs in the Middle East, and HVAC efficiency mandates in commercial buildings collectively broadened the addressable opportunity. Suppliers that embedded Ethernet, cybersecurity features, and silicon-carbide switching devices into their portfolios protected margins and unlocked service revenues. Headwinds tied to SiC/GaN chip shortages and higher electromagnetic-interference compliance costs slightly tempered shipment growth yet did not derail the multiyear efficiency investment trend.
Global Variable Frequency Drives Market Trends and Insights
Digital-native process plants demanding motor-level energy optimisation
Digitally designed plants relied on predictive analytics inside modern VFDs to align motor load with production schedules and real-time electricity prices. Rockwell Automation's PowerFlex 755TS platform, for example, bundled edge analytics and delivered downtime cuts while trimming energy usage across multi-motor lines. Semiconductor fabrication and pharmaceutical facilities led adoption because yield depends on precise speed control and uninterrupted service connectivity.
Mandatory variable-torque efficiency rules in HVAC and water verticals
Efficiency legislation made VFD integration non-negotiable in pumps and air-handling units. The U.S. Department of Energy's 2028 circulator-pump rule in effect required electronically commutated motors paired with sophisticated drives. In anticipation, OEMs such as Trane locked multi-year purchase agreements with Danfoss to guarantee compliant VFD supply.
Rising EMI/harmonics compliance costs above 690 V
Compliance costs linked to electromagnetic interference and harmonic distortion rose sharply after regulators tightened IEEE 519 limits for installations above 690 V. Medium-voltage projects now require oversized reactors, multi-pulse transformers, and shielded cable runs, adding material, commissioning, and engineering expenses that can raise installed drive cost by more than 15%. Smaller manufacturers are disproportionately affected because the design and certification overhead must be spread across lower shipment volumes, which can deter new entrants and accelerate consolidation.
Other drivers and restraints analyzed in the detailed report include:
- Surge in low-latency Ethernet-enabled motors for Industry 4.0 retrofits
- Rapid build-out of desalination and water-reuse infrastructure
- Persistent shortage of power-electronics-grade SiC/GaN chips
For complete list of drivers and restraints, kindly check the Table Of Contents.
Segment Analysis
Low-voltage units below 1 kV remained the workhorse, controlling conveyors, mixers, and HVAC fans across small and mid-sized plants. In 2024 they captured 62.4% revenue, anchoring the variable frequency drives market. Cost-effective installation, plentiful integrator expertise, and abundant supplier catalogs sustained share. Parallelly, brownfield expansions in steel mills and underground mines shifted procurement toward 1-6 kV solutions, propelling the medium-voltage tier at a 6.8% CAGR. Mines upgrading to 995 V grids selected purpose-built drives to limit cable runs and improve voltage stability.
The variable frequency drives market size for medium-voltage equipment is forecast to reach USD 10.4 billion by 2030, benefiting from renewable energy in-feed, which heightens grid-code requirements for harmonic mitigation. Vendors responded with arc-resistant enclosures and modular active-front-end designs that cut total harmonic distortion below 3%. High-voltage products above 6 kV served niche hydro-pumping and rolling-mill projects; their uptake stayed limited by premium price tags and installation complexity.
Micro drives under 20 kW delivered the highest 7.2% CAGR as factories embraced distributed control, embedding small motors in autonomous mobile robots and smart building subsystems. Volume shipments climbed in tandem with sensor-rich HVAC zoning and food-processing feeders. Low-power (20-200 kW) models still underpinned 40.3% of 2024 revenue, proving indispensable to centrifugal pumps and axial fans across chemical and water utilities.
Developers enlarged heat-sink capacity and switched to SiC diodes to lift ambient operating limits beyond 60 °C, a critical differentiator in desert solar fields. The variable frequency drives market share for high-power classes above 600 kW remained below 5%, yet each sale generated sizable aftermarket revenue streams through long-term service agreements covering power-module relays and harmonic filter audits.
The Variable Frequency Drives Market Report is Segmented by Voltage Type (Low Voltage, Medium Voltage, High Voltage), Power Rating (Micro, Low, Medium, High), Drive Type (AC Drives, DC Drives, Servo/Vector Drives, and More), Application (Pumps, Fans and Blowers, and More), End-User Industry (Infrastructure and Buildings, Food and Beverage Processing, and More), and Geography (North America, South America, and More).
Geography Analysis
Asia-Pacific maintained leadership with 46.3% 2024 revenue, underpinned by China's automated appliance plants and India's production-linked incentive schemes that encouraged motor-efficiency retrofits. Local champions such as VEICHI scaled export sales by bundling cloud gateways for continuous monitoring, reinforcing regional cost competitiveness. Government rebate programs and mandatory IE3 motor policies in several ASEAN states sustained baseline demand, while semiconductor fabs in Taiwan and South Korea accelerated servo-drive orders.
The Middle East and Africa posted the highest 7.3% CAGR outlook as sovereign desalination pipelines and copper-belt mining electrification demanded rugged medium-voltage drives with high ingress protection. ACCIONA's Shuqaiq 3 milestone highlighted how water-security imperatives generate multi-megawatt pump-drive contracts. African utilities, though capital-constrained, tapped development-finance institutions to fund VFD-rich water-treatment upgrades, amplifying regional order books.
North America and Europe delivered steady replacement-cycle growth as older installations approached end-of-life and as stricter efficiency codes compelled upgrades. Utility rebate schemes and corporate ESG targets hastened adoption, especially where tariff escalation aligned with aggressive decarbonisation goals. European powder-metallurgy plants opted for active-front-end drives to meet harmonic quotas, while US Midwest chemical plants exploited natural-gas price volatility by modulating motor load with predictive VFD algorithms. Cyber-security hardening requirements extended bid evaluation timelines, yet ultimately enlarged service revenue for vendors offering patch-management and security-certificate renewal packages.
- ABB Ltd.
- Siemens AG
- Schneider Electric SE
- Danfoss A/S
- Rockwell Automation Inc.
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- Fuji Electric Co. Ltd.
- Eaton Corporation plc
- WEG Industries S.A.
- Nidec Corporation
- Toshiba Corporation
- Hitachi Ltd.
- Johnson Controls International plc
- Inovance Technology Co. Ltd.
- Delta Electronics Inc.
- Emerson Electric Co.
- LS Electric Co. Ltd.
- SEW-Eurodrive GmbH & Co KG
- Veichi Electric Co. Ltd.
- Control Techniques (Nidec)
- HARS Drives Co. Ltd.
- Vacon (Part of Danfoss)
- Parker Hannifin - SSD Drives
- Kollmorgen Corporation
- Bonfiglioli Riduttori S.p.A.
Additional Benefits:
- The market estimate (ME) sheet in Excel format
- 3 months of analyst support
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1 INTRODUCTION
- 1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
- 1.2 Scope of the Study
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
4 MARKET LANDSCAPE
- 4.1 Market Overview
- 4.2 Market Drivers
- 4.2.1 Digital-native process plants demanding motor-level energy-optimisation
- 4.2.2 Mandatory variable torque efficiency rules in HVAC and water verticals
- 4.2.3 Surge in low-latency, Ethernet-enabled motors for Industry 4.0 retrofits
- 4.2.4 Rapid build-out of desalination and water-reuse infrastructure (Middle-East focus)
- 4.2.5 Electrification of underground mining fleets
- 4.2.6 Inflation-linked electricity tariffs accelerating ROI on VFD retrofits
- 4.3 Market Restraints
- 4.3.1 Rising EMI / harmonics compliance costs above 690 V class
- 4.3.2 Cap-ex squeeze in developing-world utilities
- 4.3.3 Cyber-hardening spend delaying refresh cycles of legacy drives
- 4.3.4 Persistent shortage of power-electronics grade SiC/GaN chips
- 4.4 Impact of Macroeconomic Factors
- 4.5 Investment Analysis
- 4.6 Value Chain Analysis
- 4.7 Regulatory Landscape
- 4.8 Technology Snapshot
- 4.9 Porter's Five Forces Analysis
- 4.9.1 Threat of New Entrants
- 4.9.2 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
- 4.9.3 Bargaining Power of Buyers
- 4.9.4 Threat of Substitutes
- 4.9.5 Degree of Competition
5 MARKET SIZE AND GROWTH FORECASTS (VALUE)
- 5.1 By Voltage Type
- 5.1.1 Low Voltage (<1 kV)
- 5.1.2 Medium Voltage (1-6 kV)
- 5.1.3 High Voltage (>6 kV)
- 5.2 By Power Rating (kW)
- 5.2.1 Micro (<20)
- 5.2.2 Low (20-200)
- 5.2.3 Medium (200-600)
- 5.2.4 High (>600)
- 5.3 By Drive Type
- 5.3.1 AC Drives
- 5.3.2 DC Drives
- 5.3.3 Servo / Vector Drives
- 5.3.4 Multilevel and Matrix Drives
- 5.4 By Application
- 5.4.1 Pumps
- 5.4.2 Fans and Blowers
- 5.4.3 Compressors
- 5.4.4 Conveyors
- 5.4.5 HVAC Systems
- 5.4.6 Extruders and Mixers
- 5.5 By End-user Industry
- 5.5.1 Infrastructure and Buildings
- 5.5.2 Food and Beverage Processing
- 5.5.3 Energy and Power Generation
- 5.5.4 Oil, Gas and Petrochemicals
- 5.5.5 Mining and Metals
- 5.5.6 Pulp and Paper
- 5.5.7 Water and Wastewater
- 5.5.8 Others
- 5.6 By Geography
- 5.6.1 North America
- 5.6.1.1 United States
- 5.6.1.2 Canada
- 5.6.1.3 Mexico
- 5.6.2 South America
- 5.6.2.1 Brazil
- 5.6.2.2 Argentina
- 5.6.2.3 Rest of South America
- 5.6.3 Europe
- 5.6.3.1 United Kingdom
- 5.6.3.2 Germany
- 5.6.3.3 France
- 5.6.3.4 Italy
- 5.6.3.5 Russia
- 5.6.3.6 Rest of Europe
- 5.6.4 Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.4.1 China
- 5.6.4.2 India
- 5.6.4.3 Japan
- 5.6.4.4 South Korea
- 5.6.4.5 Rest of Asia-Pacific
- 5.6.5 Middle East and Africa
- 5.6.5.1 Middle East
- 5.6.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia
- 5.6.5.1.2 UAE
- 5.6.5.1.3 Turkey
- 5.6.5.1.4 Rest of Middle East
- 5.6.5.2 Africa
- 5.6.5.2.1 South Africa
- 5.6.5.2.2 Nigeria
- 5.6.5.2.3 Rest of Africa
- 5.6.1 North America
6 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE
- 6.1 Market Concentration
- 6.2 Strategic Moves
- 6.3 Market Share Analysis
- 6.4 Company Profiles (includes Global level Overview, Market level overview, Core Segments, Financials as available, Strategic Information, Market Rank/Share for key companies, Products and Services, and Recent Developments)
- 6.4.1 ABB Ltd.
- 6.4.2 Siemens AG
- 6.4.3 Schneider Electric SE
- 6.4.4 Danfoss A/S
- 6.4.5 Rockwell Automation Inc.
- 6.4.6 Mitsubishi Electric Corporation
- 6.4.7 Yaskawa Electric Corporation
- 6.4.8 Fuji Electric Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.9 Eaton Corporation plc
- 6.4.10 WEG Industries S.A.
- 6.4.11 Nidec Corporation
- 6.4.12 Toshiba Corporation
- 6.4.13 Hitachi Ltd.
- 6.4.14 Johnson Controls International plc
- 6.4.15 Inovance Technology Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.16 Delta Electronics Inc.
- 6.4.17 Emerson Electric Co.
- 6.4.18 LS Electric Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.19 SEW-Eurodrive GmbH & Co KG
- 6.4.20 Veichi Electric Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.21 Control Techniques (Nidec)
- 6.4.22 HARS Drives Co. Ltd.
- 6.4.23 Vacon (Part of Danfoss)
- 6.4.24 Parker Hannifin - SSD Drives
- 6.4.25 Kollmorgen Corporation
- 6.4.26 Bonfiglioli Riduttori S.p.A.
7 MARKET OPPORTUNITIES AND FUTURE OUTLOOK
- 7.1 White-space and Unmet-Need Assessment




